Abstract
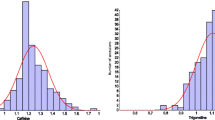
The exploration of accessions originating from Ethiopia is one option available to increase the genetic basis of new coffee cultivars. The aim of this study was to describe the chemical composition variability of Ethiopian coffee accessions maintained in Londrina and to evaluate the year effect on that. We observed no significant interaction between the years of cultivation and the amounts of caffeine, protein, lipids, chlorogenic acids, sucrose, cafestol and kahweol, thereby suggesting that evaluations of one year were reliable to describe this collection. All compounds showed variability, but the highest variability was found in cafestol and kahweol (32.81 and 34.45 %, respectively). Significant correlations among caffeine, chlorogenic acids and protein as well as between sucrose and lipids were observed. A significant negative correlation was found between kahweol and cafestol, and kahweol had positive and negative correlation with caffeine and chlorogenic acids, respectively. Hierarchical clustering analyses identified groups in the population, and the diversity found in one crop year was similar to that for 3 years. Greater diversity of composition was observed among the Western accessions compared to the ones from the East, but no clear separation was found between the accessions of these regions. These accessions are potential sources to increase the genetic diversity to obtain new coffee cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addinsoft (2010) XLStat: software for statistical analysis. Versão 2008.4.02 (2008). Paris. 1 CD-ROM
Anthony F, Bertrand B, Quiros O, Lashermes P, Berthaud J, Charrier A (2001) Genetic diversity of wild coffee (Coffea arabica L) using molecular marker. Euphytica 118:53–65. doi:10.1023/A:1004013815166
Anthony F, Combes MC, Astorga C, Bertrand B, Grazosi G, Leshermes P (2002) The origin of cultivated Coffea arabica L. varieties revealed by AFLP and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:894–900. doi:10.1007/s00122-001-0798-8
Barre P, Akaffou S, Louarn J, Charrier A, Hamon S, Noirot M (1998) Inheritance of caffeine and heteroside contents in an interspecific cross between a cultivated coffee species Coffea liberica var dewevrei and a wild species caffeine-free C pseudozanguebariae. Theor Appl Genet 96:306–311
Bertrand B, Guyot B, Anthony F, Lashermes P (2003) Impact of the Coffea canephora gene introgression on beverage quality of C. arabica. Theor Appl Genet 107:387–394. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1203-6
Bertrand B, Etienne H, Lashermes P, Guyot B, Davrieux F (2005) Can near-infrared reflectance of green coffee be used to detect introgression in Coffea arabica cultivars? J Sci Food Agric 85:955–962. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2049
Bertrand B, Boulanger R, Dussert S, Ribeyre F, Berthiot L, Descroix F, Joët T (2012) Climatic factors directly impact the volatile organic compound fingerprint in green Arabica coffee bean as well as coffee beverage quality. Food Chem 135:2575–2583. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.060
Butt MS, Sultan MT (2011) Coffee and its consumption: benefits and risks. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 51:363–373
Casal S, Mendes E, Oliveira MBPP, Ferreira MA (2005) Roast effects on coffee amino acid enantiomers. Food Chem 89:333–340. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.02.039
Chu Y-F, Chen Y, Black RM, Brown PH, Lyle BJ, Hand Liu R, Ouc B (2011) Type 2 diabetes-related bioactivities of coffee: assessment of antioxidant activity, NF-kB inhibition, and stimulation of glucose uptake. Food Chem 124:914–920. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.019
Ciampa A, Renzi G, Taglienti A, Sequi P, Valentini M (2010) Studies on coffee roasting process by means of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Food Qual 33:199. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4557.2010.00306.x
Clifford MN, Wight JC (1976) The measurement of feruloylquinic acids and caffeoylquinic acid in coffee beans. Development of the technique and its preliminary application to green coffee beans. J Sci Food Agric 27:73–84. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740270112
Cuniff P (ed) (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC-International, 16th edn. AOAC International Method, Gaithersburg
D’Amelio N, Fontanive L, Uggeri F, Suggi-Liverani F, Navarini L (2009) NMR reinvestigation of the caffeine–chlorogenate complex in aqueous solution and in coffee brews. Food Biophys 4:321–330. doi:10.1007/s11483-014-9368-x
Dias RCE, Campanha FG, Vieira LGE, Pereira LP, Pot D, Marraccini P, Benassi MT (2010) Evaluation of kahweol and cafestol in coffee tissues and roasted coffee by a new high-performance liquid chromatography methodology. J Agric Food Chem 58:88–93. doi:10.1021/jf9027427
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (1968) Coffee mission to Ethiopia 1964–65. FAO, Rome
Farah A, Donangelo CM (2006) Phenolic compounds in coffee. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:23–26. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202006000100003
Farah A, Depaulis T, Trugo LC, Martin PR (2005) Effect of roasting on the formation of chlorogenic acid lactones in coffee. J Agric Food Chem 53:1505–1513. doi:10.1021/jf048701t
Farah A, Monteiro MC, Calado V, Franca AS, Trugo LC (2006) Correlation between cup quality and chemical attributes of Brazilian coffee. Food Chem 98:373–380. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.032
Franca AS, Mendonça JCF, Oliveira SD (2005) Composition of green and roasted coffees of different cup qualities. LWT Food Sci Technol 38:709–715. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2004.08.014
International Coffee Organization (ICO) (2011–2012) World coffee trade. http://www.ico.org/trade_trade/Coffee. Accessed 3 January 2016
Joët T, Laffargue A, Salmona J, Doulbeau S, Descroix F, Bertrand B, De Kochko A, Dussert S (2009) Metabolic pathways in tropical dicotyledonous albuminous seeds: Coffea arabica as a case study. New Phytol 182:146–162. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02742.x
Joët T, Laffargue A, Descroix F, Doulbeau S, Bertrand B, Kochko A, Dussert S (2010) Influence of environmental factors, wet processing and their interactions on the biochemical composition of green coffee beans. Food Chem 118:693–701. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.048
Kitzberger CSG, Scholz MBS, Pereira LFP, Vieira LGE, Sera T, Silva JBGD, Benassi MT (2010) Analysis of diterpenes in green and roasted coffee of Coffea arabica cultivars growing in the same edapho-climatic conditions. In: 23 International conference on coffee science, vol 1, Bali, pp 110–117
Kitzberger CSG, Scholz MBS, Pereira LFP, Benassi MT (2013a) Composição química de cafés arábica de cultivares tradicionais e modernas. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira 48:1498–1506. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2013001100011
Kitzberger CSG, Scholz MBS, Pereira LFP, Vieira LGE, Sera T, Silva JBGD, Benassi MT (2013b) Diterpenes in green and roasted coffee of Coffea arabica cultivars growing in the same edapho-climatic conditions. J Food Compos Anal 30:50–57. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2013.01.007
Muriel P, Arauz J (2010) Coffee and liver diseases. Fitoterapia 8:297–305. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2009.10.003
Pagiatto NF, Ivamoto S, Sera T, Kitzberger CSG, Scholz MBS, Charmetant P, Lerroy T, Domingues D, Pereira LFP (2012) Evaluation of kahweol and cafestol levels in Ethiopian Coffea arabica L. accessions grown in Brazil. In: 24 International conference on coffee science, San José, p 217
Charmetant P, Andrade AC, Gisely A, Ferreira RV, Marraccini P, Guerra A, Bartholo GF, Pot D, Leroy T, Sera T, Pereira, LFP (2012) Phenotyping and genotyping genetic resources of Coffea arabica at IAPAR. FAO collection. Preliminary results. In: 24 International conference on coffee science, San José, p 221
Roos B, Van Der Weg G, Urgert R, Van De Bovenkamp P, Charrier A, Katan MB (1997) Levels of cafestol, kahweol, and related diterpenoids in wild species of the coffee plant Coffea. J Agric Food Chem 45:3065–3069. doi:10.1021/jf9700900
Scholz MBS, Figueiredo VRG, Silva JVN, Kitzberger CSG (2011) Características físico-químicas de grãos verdes e torrados de cultivares de café do Iapar. Coffee Sci 6:245–255
Scholz MBS, Pagiatto NF, Kitzberger CSG, Pereira LFP, Davrieux F, Charmetant P, Leroy T (2014a) Validation of near-infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of cafestol and kahweol in green coffee. Food Res Int 61:176–182. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2013.12.008
Scholz MBS, Kitzberger CSG, Pereira LFP, Davrieux F, Pot D, Charmetant P, Leroy T (2014b) Application of near infrared spectroscopy for green coffee biochemical phenotyping. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 22:411–421. doi:10.1255/jnirs.1134
Scholz MBS, Kitzberger CSG, Durand N, Charmetant P (2015) Ácidos orgânicos e açúcares em acessos da coleção de café da Etiópia do Iapar e cultivares de café arábica. IX Simpósio de Pesquisa dos Cafés do Brasil, 24 a 25 de julho de 2015, Curitiba-PR
Selmar D, Bytof G, Knopp S (2008) The storage of green coffee (Coffea arabica): decrease of viability and changes of potential aroma precursors. Ann Bot 101:31–38. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm277
Silvarolla MB, Mazzafera P, Lima MMA (2000) Caffeine content of Ethiopian coffee arabica beans. Genet Mol Biol 23:213–215. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572000000100036
Silvarolla MB, Mazzafera P, Fazuoli LC (2004) Plant biochemistry: a naturally decaffeinated Arabica coffee. Nature 429:826
Speer K, Kölling-Speer I (2006) The lipid fraction of the coffee bean—mini-review. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:201–216. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202006000100014
Sridevi V, Giridhar P, Ravishankar GA (2010) Free diterpenes cafestol and kahweol in beans and in vitro cultures of Coffea species. Curr Sci 99:1101–1104
Steiger DL, Nagai C, Moore PH, Morden CW, Osgood RV, Ming R (2002) AFLP analysis of genetic diversity within and among Coffea arabica cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 105:209–215. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0939-8
Tessema A, Alamerew S, Kufa T, Garedew W (2011) Variability and association of quality biochemical attributes in some promising Coffea arabica germplasm collections in Southwestern Ethiopia. Int J Plant Breed Genet 5:302–316. doi:10.3923/ijpbg.2011.302.316
Vaast P, Betrand B, Perriot JJ, Guyot B, Génard M (2006) Fruit thinning and shade improve bean characteristics and beverage quality of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) under optimal conditions. J Sci Food Agric 86:197–204. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2338
Ivamoto ST, Pot D, Charmetant P, Marraccini P, Ferreira LP, Domingues DS, Vieira, LGE, Pereira, LFP (2012) Diterpenes in Coffea arabica: biochemical aspects and transcriptional analysis of candidate CYPS involved in cafestol and kahweol biosynthesis. In: 24 International conference on coffee science, San José, p 216
Yuyama PM, Pot D, Dereeper A, Pointet S, Silva JBGD, Sera GH, Sera T, Charmetant P, Domingues DS, Leroy T, Pereira LFP (2012) Identificação de polimorfismos em genótipos de Coffea arabica de uma coleção da Etiópia VIII Simpósio de Pesquisa dos Cafés do Brasil 25 a 28 de novembro de 2013, Salvador
Acknowledgments
To Capes (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), to Agropolis Foundation for their support to the joint Cirad—UEL—IAPAR Project No. 1002-02, INCT_ Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia do Café and CNPq fellowship received by LFP Pereira.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, M.B.S., Kitzberger, C.S.G., Pagiatto, N.F. et al. Chemical composition in wild ethiopian Arabica coffee accessions. Euphytica 209, 429–438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1653-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1653-y