Abstract
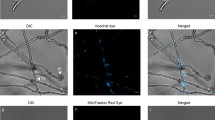
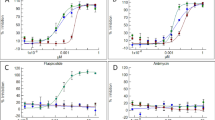
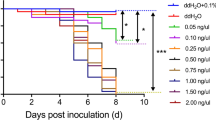
Isolation and expression of effector genes encoding proteins secreted by plant-parasitic nematodes into a host can be helpful in improving the understanding of parasitic interactions. In this study, calreticulin, a highly conserved Ca2+-binding and multifunctional protein, and beta-1,4-endoglucanase, a cell wall-degrading enzyme, both known to be secreted from oesophageal gland cells and injected through the nematode stylet into host tissue, were analysed. Full-length cDNAs from calreticulin (crt) and beta-1,4-endoglucanase (eng) with an estimated size of 1549 and 1342 bp, respectively, were isolated from the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus goodeyi (Pg) by RT-PCR and RACE techniques. Pg-crt and Pg-eng cDNAs were characterized in silico, and their expression assessed by semi-quantitative PCR in nematodes exposed to a chemical stress provided by a Solanum nigrum extract showing nematicidal activity. It was demonstrated that the plant extract down-regulated the levels of Pg-crt mRNA, whereas the transcripts of Pg-eng mRNA held steady. This extract also affected nematode behaviour towards the roots since the number of nematodes that reached and penetrated the roots diminished when the exposure time rose. These observations indicate that the nematicidal compounds present in the plant extract were effective as a signal to influence the infection success of P. goodeyi in vitro and it might be tested against other phytoparasitic nematodes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, P., Favery, B., Rosso, M. N., & Castagnone-Sereno, P. (2003). Root-knot nematode parasitism and host response: molecular basis of a sophisticated interaction. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 217–224.
Abràmoff, M. D., Magalhães, P. J., & Ram, S. J. (2004). Image processing with imageJ. Biophotonics International, 11, 36–42.
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., & Lipman, D. J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Atanu, F. O., Ebiloma, U. G., & Ajayi, E. I. (2011). A review of the pharmacological aspects of Solanum nigrum Linn. Biotechnology and Molecular Biology Review, 6, 1–7.
Danchin, E. G. J., Rosso, M. N., Vieira, P., de Almeida-Engler, J., Coutinho, P. M., Henrissat, B., & Abad, P. (2010). Multiple lateral gene transfers and duplications have promoted plant parasitism ability in nematodes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 107, 17651–17656.
De Luca, F., de Giorgi, C., Di Vito, M., & Lamberti, F. (1996). Sequence analysis of cut-1 gene and of its flanking regions in Meloidogyne artiellia. Nematologia Mediterranea, 24, 125–128.
Fanelli, E., Troccoli, A., Picardi, E., Pousis, C., & De Luca, F. (2014). Molecular characterization and functional analysis of four β-1,4-endoglucanases from the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus vulnus. Plant Pathology. doi:10.1111/ppa.12222.
Guo, L., Groenendyk, J., Papp, S., Dabrowska, M., Knoblach, B., Kay, C., Parker, J. M. R., Opas, M., & Michalak, M. (2003). Identification of an N-domain Histidine essential for chaperone function in calreticulin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 50645–50653.
Haegeman, A., Jacob, J., Vanholme, B., Kyndt, T., & Gheysen, G. (2008). A family of GHF5 endo-1,4-beta-glucanases in migratory plant-parasitic nematode Radopholus similis. Plant Pathology, 57, 581–590.
Haegeman, A., Mantelin, S., Jones, J. T., & Gheysen, G. (2012). Functional roles of effectors of plant-parasitic nematodes. Genes, 492, 19–31.
Hajarnavis, A., & Durbin, R. (2006). A conserved sequence motif in 3′ untranslated regions of ribosomal protein mRNAs in nematodes. RNA, 12, 1786–1789.
Haseeb, A., & Butool, F. (1996). Evaluation of nematicidal properties of some members of the family Solanaceae. Bioresource Technology, 57, 95–97.
Hewezi, T., & Baum, T. J. (2013). Manipulation of plant cells by cyst and root-knot nematode effectors. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 26, 9–16.
Ithal, N., Recknor, J., Nettleton, D., Hearne, L., Maier, T., Baum, T. J., et al. (2007). Parallel genome-wide expression profiling of host and pathogen during soybean cyst nematode infection of soybean. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 20, 293–305.
Jaouannet, M., Perfus-Barbeoch, L., Deleury, E., Magliano, M., Engler, E., Vieira, P., et al. (2012). A root-knot nematode-secreted protein is injected into giant cells and targeted to the nuclei. New Phytologist, 194, 924–931.
Jaouannet, M., Magliano, M., Arguel, M. J., Gourgues, M., Evangelisti, E., Abad, P., et al. (2013). The root-knot nematode calreticulin Mi-crt is a key effector in plant defense suppression. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 26, 97–105.
Jaubert, S., Milac, A. L., Petrescu, A. J., de Almeida-Engler, J., Abad, P., & Rosso, M. N. (2005). In planta secretion of a calreticulin by migratory and sedentary stages of root-knot nematode. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 18, 1277–1284.
Johnson, S., Michalak, M., Opas, M., & Eggleton, P. (2001). The ins and outs of calreticulin: from the ER lumen to the extracellular space. Trends in Cell Biology, 11, 122–129.
Jones, M. G. K., & Fosu-Nyarko, J. (2014). Molecular biology of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) and their interaction with host plants. Annals of Applied Biology, 164, 163–181.
Kyndt, T., Haegeman, A., & Gheysen, G. (2008). Evolution of GHF5 endoglucanase gene structure in plant-parasitic nematodes: no evidence for an early domain shuffling event. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 8, 305–321. doi:10.1186/1471.2148-8-305.
Kyndt, T., Vieira, P., Gheysen, G., & de Almeida-Engler, J. (2013). Nematode feeding sites: unique organs in plant roots. Planta, 238, 807–818. doi:10.1007/s00425-013-1923-z.
Laplaze, L., Ribeiro, A., Franche, C., Duhoux, E., Auguy, F., Bogusz, D., & Pawlowski, K. (2000). Characterization of a Casuarina glauca nodule-specific subtilisin-like protease gene, a homolog of Alnus glutinosa ag12. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 13, 113–117.
Li, X., Zhuo, K., Luo, M., Sun, L., & Liao, J. (2011). Molecular cloning and characterization of a calreticulin cDNA from the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Experimental Parasitology, 128, 121–126.
Martin, V., Groenendyk, J., Steiner, S. S., Guo, L., Dabrowska, M., Parker, J. M. R., et al. (2006). Identification by mutational analysis of amino acid residues essential in the chaperone function of calreticulin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 2338–2346.
Michalak, M., Corbett, E. F., Mesaeli, N., Nakamura, K., & Opas, M. (1999). Calreticulin: one protein, one gene, many functions. Biochemical Journal, 344, 281–292.
Michalak, M., Parker, J. M. R., & Opas, M. (2002). Ca2+ signaling and calcium binding chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Calcium, 32, 269–278.
Mukhtar, T., Kayani, M. Z., & Hussain, M. A. (2013). Nematicidal activities of Cannabis sativa L. and Zanthoxylum alatum Roxb. against Meloidogyne incognita. Industrial Crops and Products, 42, 447–453.
Muto, M., Mulabagal, V., Huang, H.-C., Takahashi, H., Tsay, H.-S., & Huang, J.-W. (2006). Toxicity of black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) extracts on Alternaria brassicicola, causal agent of black leaf spot of Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis). Journal of Phytopathology, 154, 45–50.
Park, B. J., Lee, D. G., Yu, J. R., Jung, S. K., Choi, K., Kim, Y. S., et al. (2001). Calreticulin, a calcium-binding molecular chaperone, is required for stress response and fertility in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 12, 2835–2845.
Peng, H., Gao, B.-I., Kong, L.-A., Yu, Q., Huang, W.-K., He, X.-F., et al. (2013). Exploring the host parasitism of the migratory plant-parasitic nematode Ditylenchus destuctor by expressed sequence tags analysis. PLoS ONE, 8, e69579. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069579.
Pestana, M., Gouveia, M., & Abrantes, I. M. de O. (2009). Efeitos de Solanum sisymbriifolium e S. nigrum sobre o nemátode-das-lesões-radiculares, Pratylenchus goodeyi, parasita da bananeira. Revista de Ciências Agrárias, 32, 174–181.
Pestana, M., Rodrigues, M., Teixeira, L., Abrantes, I. M. de O., Gouveia, M &, Cordeiro, N. (2010). Nematicidal activity of Solanum sisymbriifolium and S. nigrum extracts against the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus goodeyi. In A. Mendez-Vilas (Ed.), Microorganisms in Industry and Environment. From scientific and industrial research to consumer products(pp. 81–85). World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.
Pestana, M., Rodrigues, M., Teixeira, L., Abrantes, I. M. de O., Gouveia, M., & Cordeiro, N. (2014a). In vitro evaluation of nematicidal properties of Solanum sisymbriifolium and S. nigrum extracts on Pratylenchus goodeyi. Nematology, 16, 41–51.
Pestana, M., Abrantes, I. M. de O., & Gouveia, M. (2014b). Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding a Translocon-Associated Protein (TRAP δ) from the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus goodeyi. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 139, 283–292.
Petersen, T. N., Brunak, S., von Heijne, G., & Nielsen, H. (2011). SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nature Methods, 8, 785–786.
Rosso, M. N., Favery, B., Piotte, C., Arthaud, L., De Boer, J. M., Hussey, R. S., et al. (1999). Isolation of cDNA encoding a beta-1,4-endoglucanase in the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita and expression analysis during plant parasitism. Molecular Plant- Microbe Interactions, 12, 585–591.
Sher, S. A., & Allen, M. W. (1953). Revision of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchidae. University of California Publications in Zoology, 57, 441–469.
Smant, G., Stokkermans, J. P. W. G., Yan, Y., de Boer, J. M., Baum, T. J., Wang, X., et al. (1998). Endogenous cellulases in animals: Isolation of β-1,4-endoglucanase genes from two species of plant-parasitic cyst nematodes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 95, 4906–4911.
Uehara, T., Kushida, A., & Momota, Y. (2001). PCR-based cloning of two beta-1,4-endoglucanase from the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus penetrans. Nematology, 3, 335–341.
Wang, C., Lower, S., & Williamson, V. M. (2009). Application of pluronic gel to the study of root-knot nematode behaviour. Nematology, 11, 453–464.
Wubben, M. J., Callahan, F. E., & Scheffler, B. E. (2010). Transcript analysis of sedentary parasitic females of the semi-endoparasitic nematode Rotylenchulus reniformis. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 172, 31–40.
Acknowledgments
M. Pestana thanks to ARDITI for the awarding of a Doctoral grant (Project n.° 001080/2010/132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pestana, M., Abrantes, I. & Gouveia, M. Effect of chemical stress imposed by Solanum nigrum in calreticulin and beta-1,4- endoglucanase genes and in infectivity of Pratylenchus goodeyi . Eur J Plant Pathol 141, 747–759 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0575-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0575-6