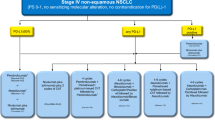
Summary
After the massive approval of checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of numerous malignancies and settings, checkpoint inhibitors-based combination therapies are emerging as a new therapeutic modality. Nivolumab and pembrolizumab (anti-PD1 agents) were recently approved as second-line treatment in NSCLC after progression on platinum-doublets. In parallel, targeting EGFR/ALK in NSCLC using tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) demonstrated remarkable outcomes and was approved as standard treatment, in patients with EGFR mutation or ALK rearrangement. Combining TKI targeting EGFR/ALK with checkpoint inhibitors seems a promising therapeutic option and is being evaluated in different trials. We aimed in this paper to elucidate the rationale behind this combination, to report the premilinary results of ongoing trials evaluating this association and finally, to discuss briefly the possible future indication of this treatment modality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kourie HR, Klastersky J (2016) Immune checkpoint inhibitors side effects and management. Immunotherapy 8(7):799–807. doi:10.2217/imt-2016-0029
Kourie HR, Klastersky JA (2016) Side-effects of checkpoint inhibitor-based combination therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 28(4):306–313
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, et al. (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced Nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373(17):1627–1639. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, et al. (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373(2):123–135
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, et al. (2015) Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372(21):2018–2028
Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, et al. (2015) Cancer immunology: mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 348:124–128
Akbay EA, Koyama S, Carretero J, et al. (2013) Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov 3:1355–1363
Chen N, Fang W, Zhan J, et al. (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR activation mediates the immune escape in EGFR-driven NSCLC: implication for optional immune targeted therapy for NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation. J Thorac Oncol 10(6):910–923
Gainor JF, Shaw AT, Sequist LV et al. (2016). EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements Are Associated with Low Response Rates to PD-1 Pathway Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Retrospective Analysis. Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-3101
Hong S, Chen N, Fang W, et al. (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 by EML4-ALK fusion protein mediates the immune escape in ALK positive NSCLC: implication for optional anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune therapy for ALK-TKIs sensitive and resistant NSCLC patients. Oncoimmunology 5(3):e1094598
Ota K, Azuma K, Kawahara A, et al. (2015) Induction of PD-L1 expression by the EML4-ALK Oncoprotein and downstream signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21(17):4014–4021
Koh J, Jang JY, Keam B, et al. (2015) EML4-ALK enhances programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma via hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and STAT3. Oncoimmunology 5(3):e1108514
D'Incecco A, Andreozzi M, Ludovini V, et al. (2015) PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in molecularly selected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer 112(1):95–102
Gettinger SH 2013 Efficacy of nivolumab in patients with previously traeted advanced non-small cell lung cancer: subpopulation response analysis in a phase I trial. Presented at: IASLC 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer, Sydney, Australia P2.11–038
Zhang Y, Wang L, Li Y, Pan Y, Wang R, Hu H, et al. (2014) Protein expression of programmed death 1 ligand 1 and ligand 2 independently predict poor prognosis in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 7:567–573
Ji M, Liu Y, Li Q (2015) PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer and its relation with EGFR mutation. J Transl Med 13:5. doi:10.1186/s12967-014-0373-0
Rizvi NA, Chow LQ, Borghaei H, et al. (2014) suppl; abstr 8022 Safety and response with nivolumab (anti-PD-1; BMS-936558, ONO-4538) plus erlotinib in patients (pts) with epidermal growth factor receptor mutant (EGFR MT) advanced NSCLC. J Clin Oncol 32(5 s)
Gibbons DL, Chow LQ, Kim D et al. (2016) Efficacy, safety and tolerability of MEDI4736 (durvalumab [D]), a human IgG1 anti-programmed cell death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) antibody, combined with gefitinib (G): A phase I expansion in TKI-naïve patients (pts) with EGFR mutant NSCLC. ELCC, Abstract 570
Ahn M, Yang J, Yu H et al. (2016) Osimertinib combined with durvalumab in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Results from the TATTON phase Ib trial. ELCC, abstract 1360
Tabchi S, Messier C, Blais N (2016) Immune-mediated respiratory adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Opin Oncol 28(4):269–277
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, et al. (2015) Nivolumab versus Everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373(19):1803–1813
Kourie HR, Awada G, Awada AH (2016) Learning from the “tsunami” of immune checkpoint inhibitors in 2015. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 101:213–220
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362(25):2380–2388
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. (2011) Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 12(8):735–742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabchi, S., Kourie, H.R. & Kattan, J. Adding checkpoint inhibitors to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting EGFR/ALK in non-small cell lung cancer: a new therapeutic strategy. Invest New Drugs 34, 794–796 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0383-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0383-2