Summary
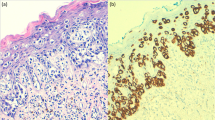
Extramammary Paget’s disease is a malignant intraepithelial carcinoma, which constitutes less than 1 % of all vulvar malignancies. Surgical resection is the first treatment of choice and standard chemotherapy has not been established for advanced or recurrent disease. Experimental and clinical studies have identified human epidermal growth receptor 2 as a potential therapeutic target. A 63-year-old male was referred for recurrent extramammary Paget’s disease after surgery. Human epidermal growth receptor 2 was shown to be overexpressed and amplified by immunohistochemical analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis, respectively. After two cycles of trastuzumab monotherapy, all lymph node metastases decreased in size. However, he experienced recurrence in the lymph nodes during the seven courses of trastuzumab. As a subsequent treatment, trastuzumab was administered in combination with docetaxel and pertuzumab; clinical response was sustained for 12 months without significant adverse events.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parker LP, Parker JR, Bodurka-Bevers D et al (2000) Paget’s disease of the vulva: pathology, pattern of involvement, and prognosis. Gynecol Oncol 77:183–189
Fanning J, Lambert HC, Hale TM et al (1999) Paget’s disease of the vulva: prevalence of associated vulvar adenocarcinoma, invasive Paget’s disease, and recurrence after surgical excision. Am J Obstet Gynecol 180:24–27
Tebes S, Cardosi R, Hoffman M (2002) Paget’s disease of the vulva. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:281–283, discussion 283–284
Tokuda Y, Arakura F, Uhara H (2015) Combination chemotherapy of low-dose 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced extramammary Paget’s disease. Int J Clin Oncol 20:194–197
Oashi K, Tsutsumida A, Namikawa K et al (2014) Combination chemotherapy for metastatic extramammary Paget disease. Br J Dermatol 170:1354–1357
Brummer O, Stegner HE, Bohmer G et al (2004) HER-2/neu expression in Paget disease of the vulva and the female breast. Gynecol Oncol 95:336–340
Richter CE, Hui P, Buza N et al (2010) HER-2/NEU overexpression in vulvar Paget disease: the Yale experience. J Clin Pathol 63:544–547
Barth P, Dulaimi Al-Saleem E, Edwards KW et al (2015) Metastatic extramammary Paget’s disease of scrotum responds completely to single agent Trastuzumab in a hemodialysis patient: case report molecular profiling and brief review of the literature. Case Rep Oncol Med 2015:895151
Wakabayashi S, Togawa Y, Yoneyama K et al (2012) Dramatic clinical response of relapsed metastatic extramammary Paget’s disease to Trastuzumab Monotherapy. Case Rep Dermatol Med 2012:401362
von Minckwitz G, du Bois A, Schmidt M et al (2009) Trastuzumab beyond progression in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive advanced breast cancer: a German breast group 26/breast international group 03–05 study. J Clin Oncol 27:1999–2006
Swain SM, Kim SB, Cortes J et al (2013) Pertuzumab, Trastuzumab, and docetaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (CLEOPATRA study): overall survival results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 14:461–471
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 15 K21525, Uehara Memorial Foundation, and Takeda Science Foundation.
Authors’ contributions
SW and MT were responsible for clinical management of the patient, acquisition of data, and drafting the manuscript; TI, TT, JT, YW, NI, JT, TS, KS, KN and KN were responsible for interpretation of data and critical revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Patient consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images before the patient received chemotherapy.
Conflict Interest
Kazuhiko Nakagawa received honoraria from Chugai pharmaceuticals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, S., Takeda, M., Takahama, T. et al. Successful human epidermal growth receptor 2-targeted therapy beyond disease progression for extramammary Paget’s disease. Invest New Drugs 34, 394–396 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0329-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0329-8