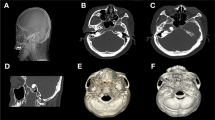
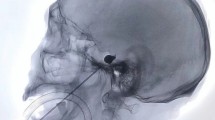
Abstract
Background
Percutaneous balloon compression (PBC) of the Gasserian ganglion is steadily gaining traction within the trigeminal neuralgia (TN) community. Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia (BTN) is a rare condition, and its treatment remains challenging. As far as we know, there are currently no research reports on the treatment outcomes of PBC for BTN.The purpose of this study is to meticulously evaluate the efficacy and safety of PBC for BTN in our medical institution.
Methods
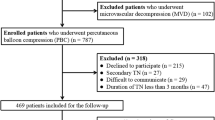
In this retrospective study, we collected and analyzed the medical records of all patients with BTN who underwent the PBC procedure at the Department of Neurosurgery at Hebei General Hospital from July 2017 to July 2023. After undergoing PBC therapy, all patients were promptly assessed for treatment efficacy based on the modified Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) pain intensity grading scale.
Results
All 37 patients with BTN experienced significant pain relief (BNI I-IIIb) immediately following unilateral PBC treatment. Among these patients, 25 reported relief from pain on the non-operative side, which was effectively managed with medication. Out of the 12 patients who did not experience improvement in contralateral symptoms, 11 received contralateral PBC. Out of the 48 treated sides, 47 sides (97.9%) achieved excellent pain control following a single PBC procedure. The follow-up times ranged from 2 to 62 months. At the 1-year follow-up, 94.6% of the patients maintained excellent therapeutic outcomes.Three recurrent patients underwent repeated unilateral PBC, and all of them maintained excellent pain control postoperatively. At the last follow-up, satisfaction was at 91.7% (measured using the Likert scale), with no severe complications occurring.
Conclusions
The results indicate that PBC is an effective and relatively safe method for treating BTN, offering a valuable option for pain control in these rare cases of TN.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors are requested to make sure that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
Code availability
The article does not contain custom code.
References
Asplund P, Blomstedt P, Bergenheim AT (2016) Percutaneous Balloon Compression vs Percutaneous Retrogasserian Glycerol Rhizotomy for the Primary Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia. Neurosurgery 78(3):421–428
Bozkurt M, Al-Beyati ES, Ozdemir M, Kahilogullari G, Elhan AH, Savas A, Kanpolat Y (2012) Management of bilateral trigeminal neuralgia with trigeminal radiofrequency rhizotomy: a treatment strategy for the life-long disease. Acta Neurochir 154(5):785–792
Brisman R (1987) Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 67(1):44–48
Cheng JS, Lim DA, Chang EF, Barbaro NM (2014) A review of percutaneous treatments for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 10(1):25–33
Ferraro D, Annovazzi P, Moccia M, Lanzillo R, De Luca G, Nociti V, Fantozzi R, Paolicelli D, Ragonese P, Gajofatto A, Boffa L, Cavalla P, Lo Fermo S, Buscarinu MC, Lorefice L, Cordioli C, Calabrese M, Gallo A, Pinardi F, Tortorella C, Di Filippo M, Camera V, Maniscalco GT, Radaelli M, Buttari F, Tomassini V, Cocco E, Gasperini C, Solaro C (2019) Characteristics and treatment of Multiple Sclerosis-related trigeminal neuralgia: An Italian multi-centre study. Mult Scler Relat Dis 37:101461
Frazier CH (1934) Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. Ann Surg 100(4):770–778
Gündüz HB, Kurşun AS, Ekşi F, Öztürk F, Karataş Okumuş SY, Tütüncü M, Soysal A, Emel E (2023) The Comparison of General Characteristics and Early and Late Post-intervention Results in Patients With Trigeminal Neuralgia Secondary to Multiple Sclerosis and Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated With Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation. Cureus 15 (9)
Harris W (1926) Neuritis and neuralgia. Oxford Medical Publications, New York p, p 394
Harris W (1940) An analysis of 1,433 cases of paroxysmal trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminaltic) and the end-results of gasserian alcohol injection. Brain 63(3):209–224
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) (2013) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 33 (9): 629–808
Henderson WR (1967) Trigeminal neuralgia: the pain and its treatment. Br Med J 1(5531):7–15
Hooge JP, Redekop WK (1995) Trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 45(7):1294–1296
Huang E, Teh BS, Zeck O, Woo SY, Lu HH, Chiu JK, Butler EB, Gormley WB, Carpenter LS (2002) Gamma knife radiosurgery for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis patients. Stereot Funct Neuros 79(1):44–50
Inoue T, Hirai H, Shima A, Suzuki F, Fukushima T, Matsuda M (2017) Diagnosis and management for trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression. Acta Neurochir 159(4):681–688
Jensen TS, Rasmussen P, Reske-Nielsen E (1982) Association of trigeminal neuralgia with multiple sclerosis: clinical and pathological features. Acta Neurol Scand 65(3):182–189
Koopman JS, Dieleman JP, Huygen FJ, de Mos M, Martin CG, Sturkenboom MC (2009) Incidence of facial pain in the general population. Pain 147(1–3):122–127
Li MW, Jiang XF, Niu CS (2021) Efficacy of and risk factors for percutaneous balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia in elderly patients. Brit J Neurosurg 35(3):280–284
Lv W, Hu W, Chi L, Zhang L (2022) Factors that may affect recurrence of trigeminal neuralgia after percutaneous balloon compression. J Clin Neurosci 99:248–252
McMillan R (2011) Trigeminal Neuralgia - a debilitating facial pain. Rev Pain 5(1):26–34
Montano N, Papacci F, Cioni B, Di Bonaventura R, Meglio M (2012) What is the best treatment of drug-resistant trigeminal neuralgia in patients affected by multiple sclerosis? A literature analysis of surgical procedures. Clin Neurol Neurosur 115(5):567–572
Mullan S, Lichtor T (1983) Percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 59(6):1007–1012
Obermann M (2010) Treatment options in trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Adv Neurol Diso 3(2):107–115
Pollack IF, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ (1988) Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia: a 14-year experience with microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 68(4):559–565
Raval AB, Salluzzo J, Dvorak T, Price LL, Mignano JE, Wu JK (2014) Salvage Gamma Knife Radiosurgery after failed management of bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol Int 5:160
Rushton JG, Olafson RA (1965) Trigeminal neuralgia associated with multiple sclerosis A case report. Arch Neurol-chicago 13(4):383–386
Tacconi L, Miles JB (2000) Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia: a therapeutic dilemma. Brit J Neurosurg 14(1):33–39
Texakalidis P, Xenos D, Tora MS, Wetzel JS, Boulis NM (2019) Comparative safety and efficacy of percutaneous approaches for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosur 182:112–122
Velasco-Siles JM, Ouaknine GE, Mohr G, Molina-Negro P, Hardy J (1981) Bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol 16(2):106–108
Worm J, Noory N, Smilkov EA, Heinskou TB, Andersen ASS, Springborg JB, Rochat P, Frederiksen JL, Bendtsen L, Maarbjerg S (2023) Efficacy of surgical treatment in patients with trigeminal neuralgia secondary to multiple sclerosis: A prospective study of 18 cases with evaluation of outcome and complications by independent evaluators. Cephalalgia 43(5):3331024231167130
Xu R, So RJ, Lee KK, Kalluri AL, Materi J, Nair SK, Huang J, Lim M, Bettegowda C (2023) Sequential onset of bilateral trigeminal neuralgia: clinical presentation and outcomes. Clin Neurol Neurosur 229:107745
Zhao H, Wang XH, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Tang YD, Zhou P, Zhu J, Li ST (2018) Management of Primary Bilateral Trigeminal Neuralgia with Microvascular Decompression: 13-Case Series. World Neurosurg 109:e724–e730
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Yinzhan Wang, Wenchang Guo, Yihui Du, Yang Li, Haowei Shi and Tao Qian. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yinzhan Wang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Due to the retrospective nature of this study, informed consent was not required.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit and that they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out, before the work is submitted.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Comments
Interesting study from Hebei, China on unilateral percutaneous balloon compresion of the Gasserian ganglion in bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. It is noteworthy that 25/37 treated only unilateral got sufficient bilateral relief, thus underscoring a staged approach in this condition.
Carsten Reidies Bjarkam.
Aalborg, Denmark.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Guo, W., Du, Y. et al. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous balloon compression for bilateral trigeminal neuralgia: a retrospective study. Acta Neurochir 166, 51 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-05947-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-05947-w