Abstract
Background
Day-case laparoscopic Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication (LF) has been demonstrated to be safe in small, prospective cohorts. The purpose of the study was to compare postoperative course, functional results, quality of life, and healthcare costs in patients undergoing LF in a day-case surgical unit with same-day discharge and patients undergoing LF as an inpatient.
Methods
All consecutive patients in our department who underwent a primary LF for symptomatic uncomplicated gastroesophageal reflux disease from 2004 to 2011 were entered into a prospective database (n = 292). From 101 same-day discharge patients (day-case group), control inpatient procedures were randomly matched by age, gender, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, and presence of a hiatal hernia (inpatient group, n = 101).
Results
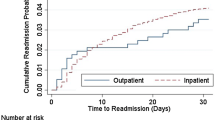
No postoperative deaths occurred and postoperative morbidity occurred in 9.4 % of patients. When comparing day-case and inpatient groups, postoperative morbidity rates were 9.9 vs. 8.9 % (p = 0.81) with median hospital stays and readmission rates of 1 vs. 4 days (p < 0.001) and 7.9 vs. 0 % (p < 0.001), respectively. Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index was significantly enhanced due to surgery (p < 0.001) and comparable in the two groups. Estimated direct healthcare costs per patient were 2,248 euros in the day-case group vs. 6,569 euros in the inpatient group (p < 0.001), equivalent to a cost saving of 3,921 euros.
Conclusions
Day-case and inpatient approaches after LF give similar results in terms of postoperative mortality and morbidity, functional outcomes and quality of life, with a substantial cost saving in favor of a day-case procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, Markiewicz S, Lombard R (1991) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1:138–143
Mariette C, Mabrut JY (2005) Laparoscopic fundoplication: current data. J Chir (Paris) 142:278–283
Salminen P, Hurme S, Ovaska J (2012) Fifteen-year outcome of laparoscopic and open Nissen fundoplication: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Thorac Surg 93:228–233
Trondsen E, Mjâland O, Raeder J, Buanes T (2000) Day-case laparoscopic fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 87:1708–1711
Milford MA, Paluch TA (1997) Ambulatory laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc 11:1150–1152
Bailey ME, Garrett WV, Nisar A, Boyle NH, Slater GH (2003) Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 90:560–562
Mariette C, Piessen G, Balon JM, Guidat A, Lebuffe G, Triboulet JP (2007) The safety of the same-day discharge for selected patients after laparoscopic fundoplication: a prospective cohort study. Am J Surg 194:279–282
Rijnhart-De Jong HG, Draaisma WA, Smout AJ, Broeders IA, Gooszen HG (2008) The Visick score: a good measure for the overall effect of antireflux surgery? Scand J Gastroenterol 43:787–793
Eypasch E, Williams JI, Wood-Dauphinee S, Ure BM, Schmülling C, Neugebauer E, Troidl H (1995) Gastrointestinal quality of life index: development, validation and application of a new instrument. Br J Surg 82:216–222
Caisse Nationale d’Assurance Maladie des Travailleurs Salarie’s (CNMATS): common classification of medical procedures (2013). http://www.ameli.fr/fileadmin/user_upload/documents/CCAM_V31.pdf
Fenton-Lee D, Riach E, Cooke TG (1995) Day surgery and gastroenterology. Gut 36:324–326
McLemore T, Lawrence L (1997) Plan and operation of the national survey of ambulatory surgery. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 37:1–124
Kelly ME, Gallagher TK, Smith MJ, Ridgway PF, Conlon KC (2012) Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: a default pathway or is selection the key? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 22:859–863
Khan SA, Stephens L (2012) Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. JSLS 16:50–54
Mariette C, Pessaux P (2011) Ambulatory laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 25:2859–2864
Coelho JC, Wiederkehr JC, Campos AC, Andrigueto PC (1999) Conversions and complications of laparoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 189:356–361
Apfel CC, Korttila K, Abdalla M, Kerger H, Turan A, Vedder I, Zernak C, Danner K, Jokela R, Pocock SJ, Trenkler S, Kredel M, Biedler A, Sessler DI, Roewer N, IMPACT Investigators (2004) A factorial trial of six interventions for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. N Engl J Med 350:2441–2451
Khatri K, Sajid MS, Brodrick R, Baig MK, Sayegh M, Singh KK (2012) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with or without short gastric vessel division: a meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 26:970–978
Markar SR, Karthikesalingam AP, Wagner OJ, Jackson D, Hewes JC, Vyas S, Hashemi M (2011) Systematic review and meta-analysis of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with or without division of the short gastric vessels. Br J Surg 98:1056–1062
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. William B. Robb for revision of the English language content and the anesthetic team for its involvement in conducting day-case protocols.
Authors contributions
Study conception and design: Mariette.
Acquisition of data: Boutillier, Piessen, Gronnier, Desbeaux.
Analysis and interpretation of data: Gronnier, Boutillier, Mariette.
Drafting of manuscript: Gronnier, Mariette.
Critical revision: Triboulet, Mariette.
Disclosures
Drs. Gronnier, Desbeaux, Piessen, Boutillier, Ruolt, Triboulet, and Mariette have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gronnier, C., Desbeaux, A., Piessen, G. et al. Day-case versus inpatient laparoscopic fundoplication: outcomes, quality of life and cost-analysis. Surg Endosc 28, 2159–2166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3448-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3448-3