Abstract
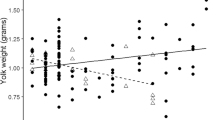
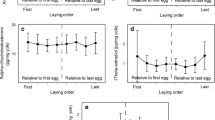
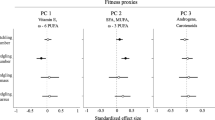
Maternally derived hormones in cleidoic eggs have been implicated in mediating growth, behavior, and social interactions among offspring. Given these widespread and significant effects, hormonal investments have the potential to greatly influence fitness of offspring. Intraspecific variation can exist at three levels (within individual eggs, among eggs within clutches, and among eggs from different females), each of which has different implications for offspring. We characterized all three levels of variation in maternally derived androgens (testosterone and androstenedione) present in yolks of American coot eggs. We found no variation in testosterone levels within eggs which suggests that embryos are exposed to constant androgen levels during development, and that field-based yolk biopsies are an appropriate way to sample eggs for this species. Within clutches, early-laid eggs had higher androgen levels than late-laid eggs, and this pattern may exacerbate negative effects of hatching asynchrony on chicks from late-hatching eggs if androgens provide chicks with a behavioral or growth advantage over chicks from eggs with lower androgen levels. American coots lay large clutches, and unequal resource allocation among offspring may be the optimal strategy for females with access to limited resources. Most of the variation in androgen levels occurred among eggs from different females. Females nesting on ponds with two other pairs laid eggs with significantly higher androgen levels than females living on ponds with fewer pairs. This suggests that increased territory defense behaviors influence the levels of androgens allocated to eggs and may be one mechanism underlying density-dependent effects on reproduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, W.L., Vleck, C.M. Functional significance of variation in egg-yolk androgens in the American coot. Oecologia 128, 164–171 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100642
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100642