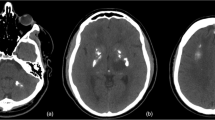
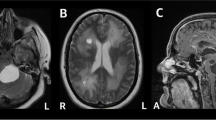
Abstract
We present a clinical, neuro-radiological and genetic study on a family with members suffering from an autosomal dominantly inherited syndrome characterised by epilepsy, cerebral calcifications and cysts, bone abnormalities; progressive neuro-cognitive deterioration and paranasal sinusitis. This syndrome shares several features with leukoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts also called Labrune syndrome and the condition of cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts (CRMCC; Coats plus syndrome). Genetic studies in this family did not reveal mutations in the CTC1 gene defected in CRMCC. We interpret our results as those supporting recent findings that despite clinical similarities, late-onset Labrune and Coats plus syndrome might be distinct entities. This family may have Labrune syndrome or a yet unclassified entity; exploration of similar cases could help classifying this one, and related conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggs TA, Abdel-Salam GM, Balicki M et al (2008) Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts (CRMCC). Am J Med Genet A 146A(2):182–190
Savage SA, Giri N, Baerlocher GM, Orr N, Lansdorp PM, Blanche P (2008) TINF2, a component of the shelterin telomere protection complex, is mutated in dyskeratosis congenita. Am J Hum Genet 82(2):501–509. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.10.004
Van der Knaap M, Valk J (2005) Leucoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts. In: Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders, pp 505–509
Toiviainen-Salo S, Linnankivi T, Saarinen A, Mäyränpää MK, Karikoski R, Mäkitie O (2011) Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts: characterization of the skeletal phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 155A(6):1322–1328
Labrune P, Lacroix C, Goutiéres F et al (1996) Extensive brain calcifications, leukodystrophy, and formation of parenchymal cysts: a new progressive disorder due to diffuse cerebral microangiopathy. Neurology 46:1297–1301
Nagae-Poetscher LM, Bibat G, Philippart M et al (2004) Leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications and cysts: new observations. Neurology 62:1206–1209
Sener U, Zorlu Y, Men S, Bayol U, Zanapalioglu U (2006) Leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(1):200–203
Wang Y, Cheng G, Dong C, Zhang J, Meng Y (2013) Adult-onset leukoencephalothy, brain calcifications and cysts: a case report. J Med Case Rep 7(1):151
Polvi A, Linnankivi T, Kivelä T, Herva R, Keating JP, Mäkitie O, Pareyson D, Vainionpää L, Lahtinen J, Hovatta I, Pihko H, Lehesjoki AE (2012) Mutations in CTC1, encoding the CTS telomere maintenance complex component 1, cause cerbroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts. Am J Hum Genet 7:540–549
Ooba H, Abe T, Hisamitsu Y, Fujiki M (2013) Repeated cyst formation in a patient with leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts: effectiveness of stereotactic aspiration with Ommaya reservoir placement. J Neurosurg Pediatr 12(2):155–159
Kleinschmidt-Demasters BK, Cummings TJ, Hulette CM, Morgenlander JC, Corboy JR (2009) Adult cases of leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts: expanding the spectrum of the disorder. J Neuropath Exp Neur 7:432–439
Gulati A, Singh P, Ramanathan S, Khandelwal N (2011) A case of leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications and cysts. Ann Indian Acad Neur 14(4):310–312
Lohle PNM, van Mameren H, Zwindermann KH et al (2000) On the pathogenesis of brain tumour cysts: a volumetric study of tumour, oedema and cyst. Neuroradiology 42:639–642
Bertotti MM, Linhares MN, Ferreira R et al (2011) Leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts: entity that can mimic a neoplasm. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69(4):717–722
Labauge P, Berger E, Magnin E, Rumbach L, Mine M, Renard D (2012) A new form of leukoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts with nonrecessive inheritance and absence of gadolinium enhancement. Eur Neurol 67(3):151–153
Marelli C, Savoiardo M, Fini N et al (2008) Late presentation of leucoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts: report of two cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 79(11):1303–1304
Revesz T, Fletcher S, Al-Gazali LI, DeBuse P (1992) Bilateral retinopathy, aplastic anaemia, and central nervous system abnormalities: a new syndrome? J Med Genet 29(9):673–675
Linnankivi T, Polvi A, Mäkitie O, Lehesjoki A-E, Kivelä T (2013) Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts, Revesz syndrome and aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(1):153
Tolmie L, Browne H, McGettrick M, Stephenson B (1988) A familial syndrome with Coats reaction retinal angiomas, hair and nail defects and intracranial calcification. Eye (Lond) 2((Pt 3)):297–303
Vivarelli R, Grosso S, Cioni M, Galluzzi P, Monti L, Morgese G, Balestri P (2001) Pseudo-TORCH syndrome or Baraitser–Reardon syndrome: diagnostic criteria. Brain Dev 23(1):18–23
Orcesi S, La Piana R, Fazzi E (2009) Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. Br Med Bull 89:183–201. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldn049
Linnankivi T, Valanne L, Paetau A, Alafuzoff I, Hakumäki JM, Kivelä T, Lönnqvist T, Mäkitie O, Pääkkönen L, Vainionpää L, Vanninen R, Herva R, Pihko H (2006) Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts. Neurology 67:1437–1443
Anderson BH, Kasher PR, Mayer J et al (2012) Mutations in CTC1, encoding conserved telomere maintenance component 1, cause Coats plus. Nat Genet 44(3):338–342
Savage SA (2012) Connecting complex disorders through biology. Nat Genet 44:238–240
Berry-Candelario J, Kasper E, Eskandar E, Chen CC (2011) Neurosurgical management of leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts: a case report and review of literature. Surg Neurol Int 2:160
Kajtár P, Méhes K (1994) Bilateral Coats retinopathy associated with aplastic anaemia and mild dyskeratotic signs. Am J Med Genet 49(4):374–377
Mafee MF, Valvassori GE, Becker M (2012) Imaging of the head and neck, 2nd edn. Thieme, Germany, pp 66–67
Sasa GS, Ribes-Zamora A, Nelson ND, Bertuch AA (2012) Three novel truncating TINF2 mutations causing severe dyskeratosis congenita in early childhood. Clin Genet 81(5):470–478
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Hungarian Brain Research Program.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All studies have been approved by the institutional ethics committee of the National Institute of Clinical Neurosciences, and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlinger, K., Tárnoki, Á.D., Tárnoki, D.L. et al. Leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications and cysts: a family study. J Neurol 261, 1911–1916 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7393-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7393-9