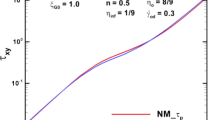
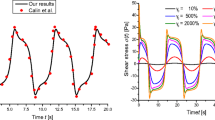
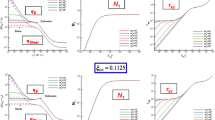
Abstract
The steady and transient nonlinear rheological behaviors of dilute rod-like micellar solutions are predicted here with a particular case of the generalized Bautista–Manero–Puig (BMP) model that consists of the upper-convected Maxwell constitutive equation and a dissipative power-dependent kinetic equation, which takes into account the formation and disruption of shear-induced structures (SISs). This model has been derived using the extended irreversible thermodynamic (EIT) formalism. In steady shear, the model predicts a Newtonian region at low shear rates and a characteristic shear rate (\( {\dot{\upgamma}}_{\mathrm{c}} \)) at which shear thickening develops. In the shear thickening region, the model predicts either a reentrant zone, which is caused by multi-valued shear stresses when the data are collected with a shear stress-controlled mode or a continuous increase in the shear stress-shear rate flow curve, when the data are collected with a shear rate-controlled mode; in this region, two coexisting phases are predicted. The coexisting phases at the same shear rate in the two-phase envelope and the spinodal-like region were evaluated from the extended Maxwell equal-area criterion, which was calculated from the equal values of the two minima of the plot of the extended Gibbs free energy versus shear rate. At higher shear rates, the model predicts a transition to shear thinning, and under transient flows, an induction time and a saturation time are obtained from the predicted and the experimental data as detailed in the text. The magnitudes of both, the induction and the saturation times, diminish as the shear rate departs from \( {\dot{\upgamma}}_{\mathrm{c}} \), but only the induction time decreases according to a power law with shear rate. The conditions under which these rheological responses arise are derived and justified in detail with the BMP model. The model predictions are compared with experimental data of two dilute micellar solutions. The model parameters were determined from a set of independent experiments without fitting.

<!-- [INSERT GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT TEXT HERE] -->










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjari A (1998) Rheological behavior of a solution of particles aggregating in the containing walls. Phys Rev E 58:6294
Aradian A, Cates ME (2006) Minimal model for chaotic shear banding in shear thickening fluids. Phys Rev E 73:041508
Barentin C, Liu AJ (2001) Shear thickening in dilute solutions of wormlike micelles. Europhys Lett 55:432–438
Bautista F, de Santos JM, Puig JE, Manero O (1999) Understanding thixtropic and antithixotropic behavior of viscoelastic micellar solutions and liquid crystalline dispersions. 1. The model. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 80:93–113
Baustista F, Pérz-López JH, García JP, Puig JE,Manero O (2007) Stability analysis of shear banding flow with the BMP model. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechs 144:160–16
Berret J-F, Gámez-Corrales R, Oberdisse J, Walker LM, Lidner P (1998) Flow-structure relationship of shear-thickening surfactant solutions. Europhys Lett 41:677–682
Berret J-F, Gámez-Corrales R, Lerouge S, Decruppe J-P (2000) Shear-thickening transition in surfactant solutions: New experimental features from rheology and flow birefringence. Eur Phys J E 2:343–350
Berret J-F, Gámez-Corrales R, Séréro Y, Molino F, Lindner P (2001) Shear-induced micellar growth in dilute surfactant solutions. Europhys Lett 54:605–611
Berret J-F, Lerouge S, Decruppe J-P (2002) Kinetics of the shear-thickening transition observed in dilute surfactant solutions and investigated by flow birefringence. Langmuir 18:7279–7286
Boltenhagen P, Hu YT, Matthys EF, Pine DJ (1997a) Inhomogeneous structure formation in shear-thickening in worm-like micellar solutions. Europhys Lett 38:389–394
Boltenhagen P, Hu YT, Matthys EF, Pine D (1997b) Observation of bulk phase separation and coexistence in a sheared micellar solutions. J Phys Rev Lett 79(12):2359–2362
Castillo-Tejas J, Alvarado JFJ, Carro S, Pérez-Villaseñor F, Bautista F, Manero O (2011) Rheology of wormlike micelles from non-equilibrium molecular dynamics. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 166:194–207
Cates ME, Candau SJ (2001) Ring-driven shear thickening in wormlike micelles. Europhys Lett 55:887–893
Cates ME, Turner MS (1990) Flow-induced gelation of rodlike micelles. Europhys Lett 11:681–686
Dehmoune, J., Manneville, S., Decruppe, JP (2011) Local velocity measurements in the shear-thickening transition of dilute micellar solutions of surfactants. Langmuir 27(3): 1108–1115
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2008) Gradient and vorticity banding. Rheol Acta 47(3):257–281
Dormand JR, Prince PJ (1980) J comp Appl Math 6:19–26
Gámez-Corrales R, Berret J-F, Walker LM, Oberdisse J (1999) Shear-thickening dilute surfactant solutions: equilibrium structure as studied by small-angle neutron scattering. Langmuir 15:6755–6676
Goveas JL, Olmsted PD (2001) A minimal model for vorticity and gradient banding in complex fluids. Eur Phys J E 6:79–89
Goveas JL, Pine DJ (1999) A phenomenological model for shear-thickening in wormlike micelle solutions. Europhys Lett 48:706–712
Ha B-Y, Liu AJ (1997) Counterion-mediated attraction between two like-charged rods. Phys Rev Lett 79:887902
Hartmann V, Cresseley R (1997) Shear thickening of an aqueous micellar solution of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium tosylate. J Phys II France 7(8):1087–1098
Hartmann V, Cresseley R (1998) Occurrence of shear thickening in aqueous micellar solutions of CTAB with some added organic counterions. Colloid Polym Sci 276(2):169–175
Hassan PA, Yakhmi JV (2000) Growth of cationic micelles in the presence of organic additives. Langmuir 16(18):7187–7191
Herle V, Manneville S, Fischer P (2008) Ultrasound velocimetry in a shear-thickening wormlike micellar solution: evidence for the coexistence of radial and vorticity shear bands. Eur Phys JE 26(1–2):3–12
Hu YT, Matthys E (1997) Rheological and rheo-optical characterization of shear-induced structure formation in a nonionic drag-reducing surfactant solution. J Rheol 41(1):151–166
Hu Y, Wang S, Jamieson A (1993) Kinetic studies of a shear thickening micellar solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 156(1):31–37
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Pine DJ (1998a) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. I Direct visualization of transient behavior and phase transitions. J Rheol 42:1185–1210
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Mathys E, Pine DJ (1998b) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. II. Slip, fracture, and stability of the shear induced phase. J Rheol 42(5):1209–1229
Jahromi HRT, Webster MF, Aguayo JP, Manero O (2011) Numerical investigation of transient contraction flows for worm-like micellar systems using Bautista-Manero models. JNNFM 166:102–117
Kline SR (1999) Polymerization of rod-like micelles. Langmuir 15:2726–2732
Lerouge S, Berret JF (2010) Shear-Induced transitions and instabilities in surfactant worm-like. Adv Polym Sci 230:1–71
López-Aguilar JE, Webster MF, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Manero O (2014) A new constitutive model for worm-like micellar systems—numerical simulation of confined contraction-expansion flows. JNNFM 204:7–21
Lopez-Diaz D, Sarmiento-Gomez E, Garza C, Castillo R (2010) A rheological study in the dilute regime of the worm-micelle fluid made of zwitterionic surfactant (TDPS), anionic surfactant (SDS), and brine. J Coll Interface Sci 348:152–158
Macías ER, González A, Manero O, González-Nuñez R, Soltero JFA, Attané P (2001) Flow regimes of dilute surfactant solutions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 101:149–171
Macías ER, Bautista F, Soltero JFA, Puig JE, Attané P, Manero O (2003) On shear thickening flow of dilute CTAT worm-like micellar solutions. J Rheol 47:643–658
Manero O, Bautista F, Soltero JFA, Puig JE (2002) Dynamics of worm-like micelles: the Cox-Mertz rule. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 106:1–15
Manero O, Bautista F, Pérez-López JH, Puig JE (2007) A thermodynamic approach to rheology of complex fluids: the generalized BMP model. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 146(1–3):22–29
Marín-Santibáñez BM, Pérez-González J, Rodríguez-González F (2014) Origin of shear thickening in semidilute wormlike micellar solutions and evidence of elastic turbulence. J Rheol 58:1917–1933
Oda R, Weber V, Lindner P, Pine DJ, Mendes E, Schosseler F (2000) Time-resolved small-angle neutron scattering study of shear-thickening surfactant solutions after the cessation of flow. Langmuir 16:4859–4863
Olmsted PD, Lu C-YD (1999) Phase separation of rigid-rod suspensions in shear flow. Phys Rev E 60:4397–4415
Onsager L (1944) Crystal statistics. I. A two-dimensional model with an order-disorder transition. Phys Rev 65:117–149
Picard G, Adjari A, Bocquet L, Lequeux F (2002) Simple model for heterogeneous flows of yield stress fluids. Phys Rev E 66:051501
Porte G, Berret J-F, Harden JL (1997) Inhomogeneous flows of complex fluids: mechanical instability versus non-equilibrium phase transition. J Phys II Fr 7:459–472
Pröztl B, Springer J (1997) Light scattering experiments on shear induced structures of micellar solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 190:327–333
Puig JE, Bautista F, Soltero JFA, Manero O (2007) Nonlinear rheology of giant micelles. In: Zana R, Kaler EW (eds) Giant Micelles: Properties and Applications. Francis and Taylor, New York pp, pp. 289–322
Rehage H, Hoffmann H (1982) Shear induced phase transitions in highly dilute aqueous detergent solutions. Rheol Acta 21(4–5):561–563
Sandler SI (2006) Chemical, biochemical and engineering thermodynamics, 4th edn. Wiley, New York
Séréro Y, Jacobsen V, Berret J-F, May R (2000) Evidence of nonlinear chain stretching in the rheology of a transient network. Macromolecules 33(5):1841–1847
Soltero JFA, Puig JE, Manero O (1996) Rheology of cetyltrimethylammonium tosylate system. 2. Linear viscoelastic regime. Langmuir 12:2654–2662
Soltero JFA, Álvarez-Ramírez JG, Fernández VVA, Tepale N, Bautista F, Macías ER, Pérez-López JH, Schulz PC, Manero O, Soláns C, Puig JE (2007) Phase and rheological behavior of the polymerizable surfactant CTAVB and water. J Colloid Interf Sci 312:130–138
Stukan, MR; Boek, ES; Padding, JT; Crawshaw, JP, (2007) Influence of system size and solvent flow on the distribution of wormlike micelles in a contraction-expansion geometry. Eur Phys J E 26, 63–71.
Truong MT, Walker LM (2002) Quantifying the importance of micellar microstructure and electrostatic interactions on the shear-induced structural transition of cylindrical micelles. Langmuir 18:2024–2031
Wang S-Q (1991) Growth of dynamic polymers (micelles) in shear flow. Macromolecules 24:3004–3009
Wang S.-Q., W. M. Gelbart, and A. Ben-Shad (1990) Flow Effects on Micellar Size Distribution 94(6): 2019–2022
Weber V, Schosseler F (2002) Shear-thickening in salt-free aqueous solutions of a gemini cationic surfactant: a study by small angle light scattering. Langmuir 18:9705–9712
Wunderlich I, Hoffmann H, Rehage H (1987) Flow birefringence and rheological measurements on shear induced micellar structures Rheol. Acta 26:532–542
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) grant no. 235880.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landázuri, G., Macías, E.R., García-Sandoval, J.P. et al. On the modelling of the shear thickening behavior in micellar solutions. Rheol Acta 55, 547–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-016-0933-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-016-0933-8