Abstract
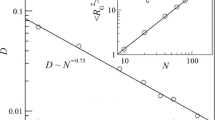
The effects of crowded environment with nano particles are studied for polymer translocation through a small pore. The translocation time τ is simulated by Fokker-Planck equation at different free energy landscapes F and diffusion coefficients of polymer D. The free energy is calculated using the Rosenbluth-Rosenbluth method, and the diffusion coefficient is followed the relation \(D \sim \frac {1}{N} e^{-\triangle F}\). We find that the free energy is dependent on polymer-nanoparticle interaction, size of the nanoparticle, and position of the nanoparticle. The attractive nanoparticles at the trans side can provide a driving force to polymer by lowering the free energy, but the exclusive effect of nanoparticle can raise the free energy of polymer. There exists an optimum interaction that τ is roughly independent on the size and position of nanoparticles. It is found that these effects are related to the conformational change of polymer chain in crowded environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simon SM, Blobel G (1991) A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 65:371
Kasianowicz JJ, Brandin E, Branton D, Deamer DW (1996) Characterization of individual polynucleotide molecules using a membrane channel. Proc Natl Scad Sci USA 93:13770
Hanss B, Leal-Pinto EB, Copland TD, Klotman PE (1998) Identification and characterization of a cell membrane nucleic acid channel. Proc Natl Scad Sci USA 95:1921
Kasimova AO, Pavan GM, Danani A, Mondon K, Cristiani A, Scapozza L, Gurny R, Möller M (2012) Validation of a novel molecular dynamics simulation approach for lipophilic drug incorporation into polymer micelles. J Phys Chem B 116:4338
Zimm BH, Levene SD (1992) Problems and prospects in the theory of gel electrophoresis of DNA. Q Rev Biophys 25:171
Akeson M, Branton D, Kasianowicz JJ, Brandin E, Deamer DW (1999) Microsecond time-scale discrimination among polycytidylic acid, polyadenylic acid, and polyuridylic acid as homopolymers or as segments within single RNA molecules. Biophys J 77:3227
Meller A, Branton D (2002) Single molecule measurements of DNA transport through a nanopore. Electrophoresis 23:2583
Meller A, Nivon L, Branton D (2001) Voltage-Driven DNA Translocations through a nanopore. Phys Rev Lett 86:3435
Tian P, Smith GD (2003) Translocation of a polymer chain across a nanopore: a Brownian dynamics simulation study. J Chem Phys 119:11475
Henrickson SE, Misakian M, Robertson B, Kasianowicz JJ (2000) Driven DNA transport into an asymmetric Nanometer-Scale pore. Phys Rev Lett 85:3057
Muthukumar M (2003) Polymer escape through a nanopore. J Chem Phys 118:5174
Luo KF, Ala-Nissila T, Ying SC, Bhattacharya A (2007) Influence of Polymer-Pore interactions on translocation. Phys Rev Lett 99:148102
Luo MB (2007) Translocation of polymer chains through interacting nanopores. Polymer 48:7679
Wei DS, Yang W, Jin XG, Liao Q (2007) Unforced translocation of a polymer chain through a nanopore: the solvent effect. J Chem Phys 126:204901
Sung W, Park PJ (1996) Polymer translocation through a pore in a membrane. Phys Rev Lett 77:783
Chuang J, Kantor Y, Kantar M (2001) Anomalous dynamics of translocation. Phys Rev E 65:011802
Muthukumar M (2001) Translocation of a confined polymer through a hole. Phys Rev Lett 86:3188
Sebastian KL, Paul AKR (2000) Kramers problem for a polymer in a double well. Phys Rev E 62:927
Muthukumar M, Baumgaertner A (1989) Effects of entropic barriers on polymer dynamics. Macromoleules 22:1937
Wei C, Srivastava D (2003) Theory of transport of long polymer molecules through carbon nanotube channels. Phys Rev Lett 91:235901
Cao WP, Sun LZ, Wang C, Luo MB (2011) Monte Carlo simulation on polymer translocation in crowded environment. J Chem Phys 135:174901
Matlack KES, Mothes W, Rapoport TA (1998) Protein translation: tunnel vision. Cell 92:381
Neupert W, Brunner M (2002) The protein import motor of mitochondria. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:555
Yu WC, Luo KF (2011) Chaperone-assisted translocation of a polymer through a nanopore. J Am Chem Soc 133:13565
Saxton MJ (1994) Anomalous diffusion due to obstacles: a Monte Carlo study. Biophys J 66:394
Gopinathan A, Kim YW (2007) Polymer translocation in crowded environments. Phys Rev Lett 99:228106
Yu WC, Ma YD, Luo KF (2012) Translocation of stiff polymers through a nanopore driven by binding particles. J Chem Phys 137:244905
Chen YH, Luo KF (2013) Dynamics of polymer translocation through a nanopore induced by different sizes of crowding agents. J Chem Phys 138:204903
Li CY, Qian CJ, Yang QH, Luo MB (2014) Study on the polymer diffusion in a media with periodically distributed nano-sized fillers. J Chem Phys 140:104902
Fulton AB (1982) How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell 30:345
Chen JX, Zhu JX, Ma YQ, Cao JS (2014) Translocation of a forced polymer chain through a crowded channel. EPL 106:18003
Machta J, Guyer RA (1989) Polymers in a disordered environment. J Phys A: Math Gen 22:2539
Xue XG, Zhao L, Lv ZY, Li ZS (2012) Free energy and scalings for polymer translocation through a nanopore: a molecular dynamics simulation study combined with milestoning. Phys Lett A 376:290
Sun LZ, Cao WP, Luo MB (2009) Free energy landscape for the translocation of polymer through an interacting pore. J Chem Phys 131:194904
Sun LZ, Cao WP, Luo MB (2011) Translocation properties of copolymer (AnBm)l through an interacting pore. Phys Rev E 84:041912
Rosenbluth MN, Rosenbluth AW (1954) Monte carlo calculation of the average extension of molecular chains. J Chem Phys 23:356
Grassberger P (1997) Pruned-enriched Rosenbluth method: simulations of 𝜃 polymers of chain length up to 1000000. Phys Rev E 56:3682
Risken H (1984) The Fokker-Planck equation. Springer, Berlin
Cao WP, Wang C, Sun LZ, Luo MB (2012) Effects of an attractive wall on the translocation of polymer under driving. J Phys: Condens Matter 24:325104
Milchev A (2011) Single-polymer dynamics under constraints: scaling theory and computer experiment. J Phys: Condens Matter 23:103101
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11447184, and this work was also supported from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. LQ14A040001 and No. LQ14A040004. W.P.C and Y.J.C thank the financial support by the physics from the most important among all the top priority disciplines of Zhejiang Province under Grant Nos. xkzwl14 and xkzw113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ᅟ
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, QB., Ma, SH., Chen, YJ. et al. Numerical simulation on polymer translocation into crowded environment with nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 294, 1351–1357 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3891-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3891-x