Abstract
Key message
The first report on the recombinant production of a candidate vaccine in the moss system.
Abstract
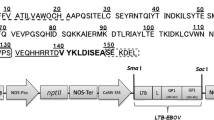
The need for economical and efficient platforms for vaccine production demands the exploration of emerging host organisms. In this study, the production of an antigenic protein is reported employing the moss Physcomitrella patens as an expression host. A multi-epitope protein from the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) based on epitopes from gp120 and gp41 was designed as a candidate subunit vaccine and named poly-HIV. Transgenic moss plants were generated carrying the corresponding poly-HIV transgene under a novel moss promoter and subsequently seven positive lines were confirmed by PCR. The poly-HIV protein accumulated up to 3.7 µg g−1 fresh weight in protonema cultures. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of the moss-produced recombinant poly-HIV are evidenced by Western blots and by mice immunization assays. The elicitation of specific antibodies in mice was observed, reflecting the immunogenic potential of this moss-derived HIV antigen. This is the first report on the production of a potential vaccine in the moss system and opens the avenue for glycoengineering approaches for the production of HIV human-like glycosylated antigens as well as other vaccine prototypes under GMP conditions in moss bioreactors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AVMA (2013) Guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2013 edition. American Veterinary Medical Association 1931 N. Meacham road, Schaumburg, IL 60173. ISBN 978-1-882691-21-0
Baur A, Reski R, Gorr G (2005) Enhanced recovery of a secreted recombinant human growth factor using stabilizing additives and by co-expression of human serum albumin in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Biotechnol J 3:331–340
Buettner-Mainik A, Parsons J, Jerome H, Hartmann A, Lamer S, Schaaf A, Schlosser A, Zipfel PF, Reski R, Decker EL (2011) Production of biologically active recombinant human factor H in Physcomitrella. Plant Biotechnol J 9:373–383
Cueno ME, Hibi Y, Karamatsu K, Yasutomi Y, Imai K, Laurena AC, Okamoto T (2010) Preferential expression and immunogenicity of HIV-1 Tat fusion protein expressed in tomato plant. Transgenic Res 19:889–895
De Virgilio M, De Marchis F, Bellucci M, Mainieri D, Rossi M, Benvenuto E, Arcioni S, Vitale A (2008) The human immunodeficiency virus antigen Nef forms protein bodies in leaves of transgenic tobacco when fused to zeolin. J Exp Bot 59:2815–2829
Decker EL, Reski R (2007) Moss bioreactors producing improved biopharmaceuticals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:393–398
Decker EL, Reski R (2008) Current achievements in the production of complex biopharmaceuticals with moss bioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:3–9
Decker EL, Reski R (2012) Glycoprotein production in moss bioreactors. Plant Cell Rep 31:453–460
Decker EL, Parsons J, Reski R (2014) Glyco-engineering for biopharmaceutical production in moss bioreactors. Front Plant Sci 5:346
Dong XN, Wu Y, Chen Y (2005) The neutralizing epitope ELDKWA on HIV-1 gp41: genetic variability and antigenicity. Immunol Lett 101:81–86
Excler JL, Robb ML, Kim JH (2014) HIV-1 vaccines: challenges and new perspectives. Hum Vaccine Immunother 10:1734–1746
Forsell MN, Schief WR, Wyatt RT (2009) Immunogenicity of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein oligomers. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 4:380–387
Frank W, Decker EL, Reski R (2005) Molecular tools to study Physcomitrella patens. Plant Biol 7:220–227
Franklin S, Ngo B, Efuet E, Mayfield SP (2002) Development of a GFP reporter gene for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. Plant J 30:733–744
Girard MP, Osmanov SK, Kieny MP (2006) A review of vaccine research and development: the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Vaccine 24:4062–4081
Gitzinger M, Parsons J, Reski R, Fussenegger M (2009) Functional cross-kingdom conservation of mammalian and moss (Physcomitrella patens) transcription, translation and secretion machineries. Plant Biotechnol J 7:73–86
Gonzalez-Rabade N, McGowan EG, Zhou F, McCabe M, Bock R, Dix PJ, Gray JC, Ma JKC (2011) Immunogenicity of chloroplast-derived HIV-1 p24 and a p24-Nef fusion protein following subcutaneous and oral administration in mice. Plant Biotechnol J 9:629–638
Govea-Alonso DO, Gomez-Cardona EE, Rubio-Infante N, Garcia-Hernandez AL, Varona-Santos JT, Salgado-Bustamante M, Korban SS, Moreno-Fierros L, Rosales-Mendoza S (2013) Production of an antigenic C4(V3)6 multiepitopic HIV protein in bacterial and plant systems. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 113:73–79
Graham BS, McElrath MJ, Keefer MC, Rybczyk K, Berger D, Weinhold KJ, Ottinger J, Ferrari G, Montefiori DC, Stablein D, Smith C, Ginsberg R, Eldridge J, Duerr A, Fast P, Haynes BF (2010) Immunization with cocktail of HIV-derived peptides in Montanide ISA-51 is immunogenic, but causes sterile abscesses and unacceptable reactogenicity. PLoS One 5:e11995
Haynes BF, Ma B, Montefiori DC, Wrin T, Petropoulos CJ, Sutherland LL, Scearce RM, Denton C, Xia SM, Korber BT, Liao HX (2006) Analysis of HIV-1 subtype B third variable region peptide motifs for induction of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 primary isolates. Virology 345:44–55
Hohe A, Decker EL, Gorr G, Schween G, Reski R (2002) Tight control of growth and cell differentiation in photoautotrophically growing moss (Physcomitrella patens) bioreactor cultures. Plant Cell Rep 20:1135–1140
Hohe A, Egener T, Lucht JM, Holtorf H, Reinhard C, Schween G, Reski R (2004) An improved and highly standardised transformation procedure allows efficient production of single and multiple targeted gene knockouts in a moss, Physcomitrella patens. Curr Genet 44:339–347
Huether CM, Lienhart O, Baur A, Stemmer C, Gorr G, Reski R, Decker EL (2005) Glyco-engineering of moss lacking plant-specific sugar residues. Plant Biol 7:292–299
Kajikawa A, Zhang L, Long J, Nordone S, Stoeker L, LaVoy A, Bumgardner S, Klaenhammer T, Dean G (2012) Construction and immunological evaluation of dual cell surface display of HIV-1 Gag and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium FliC in Lactobacillus acidophilus for vaccine delivery. Clin Vaccine Immunol 19:1374–1381
Koprivova A, Altmann F, Gorr G, Kopriva S, Reski R, Decker EL (2003) N-glycosylation in the moss Physcomitrella patens is organized similarly to higher plants. Plant Biol 5:582–591
Koprivova A, Stemmer C, Altmann F, Hoffmann A, Kopriva S, Gorr G, Reski R, Decker EL (2004) Targeted knockouts of Physcomitrella lacking plant-specific immunogenic N-glycans. Plant Biotechnol J 2:517–523
Krachmarov CP, Kayman SC, Honnen WJ, Trochev O, Pinter A (2001) V3-specific polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from sera of infected humans effectively neutralize primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 17:1737–1748
Kubo M, Imai A, Nishiyama T, Ishikawa M, Sato Y, Kurata T, Hiwatashi Y, Reski R, Hasebe M (2013) System for stable β-estradiol-inducible gene expression in the moss Physcomitrella patens. PLoS One 8:e77356
Letvin NL, Robinson S, Rohne D, Axthelm MK, Fanton JW, Bilska M, Palker TJ, Liao HX, Haynes BF, Montefiori DC (2001) Vaccine-elicited V3 loop-specific antibodies in rhesus monkeys and control of a simian-human immunodeficiency virus expressing a primary patient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate envelope. J Virol 75:4165–4175
Liao HX, Etemad-Moghadam B, Montefiori DC, Sun Y, Sodroski J, Scearce RM, Doms RW, Thomasch JR, Robinson S, Letvin NL, Haynes BF (2000) Induction of antibodies in guinea pigs and rhesus monkeys against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope: neutralization of nonpathogenic and pathogenic primary isolate simian/human immunodeficiency virus strains. J Virol 74:254–263
Mascola JR, Snyder SW, Weislow OS, Belay SM, Belshe RB, Schwartz DH, Clements ML, Dolin R, Graham BS, Gorse GJ, Keefer MC, McElrath MJ, Walker MC, Wagner KF, McNeil JG, McCutchan FE, Burke DS (1996) Immunization with envelope subunit vaccine products elicits neutralizing antibodies against laboratory-adapted but not primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis 173:340–348
Mueller SJ, Lang D, Hoernstein SNW, Lang EGE, Schuessele C, Schmidt A, Fluck M, Leisibach D, Niegl C, Zimmer AD, Schlosser A, Reski R (2014) Quantitative analysis of the mitochondrial and plastid proteomes of the moss Physcomitrella patens reveals protein macrocompartmentation and microcompartmentation. Plant Physiol 164:2081–2095
Müller K, Siegel D, Rodriguez-Jahnke F, Gerrer K, Wend S, Decker EL, Reski R, Weber W, Zurbriggen MD (2014) A red light-controlled synthetic gene expression switch for plant systems. Mol BioSyst 10:1679–1688
Parsons J, Altmann F, Arrenberg CK, Koprivova A, Beike AK, Stemmer C, Gorr G, Reski R, Decker EL (2012) Moss-based production of asialo-erythropoietin devoid of Lewis A and other plant-typical carbohydrate determinants. Plant Biotechnol J 10:851–861
Parsons J, Altmann F, Graf M, Stadlmann J, Reski R, Decker EL (2013) A gene responsible for prolyl-hydroxylation of moss-produced recombinant human erythropoietin. Sci Rep 3:3019
Patterson LJ, Robey F, Muck A, van Remoortere K, Aldrich K, Richardson E, Alvord WG, Markham PD, Cranage M, Robert-Guroff M (2001) A conformational C4 peptide polymer vaccine coupled with live recombinant vector priming is immunogenic but does not protect against rectal SIV challenge. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 17:837–849
Potter M (1985) History of the BALB/c family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 122:1–5
Reski R, Abel WO (1985) Induction of budding on chloronemata and caulonemata of the moss, Physcomitrella patens, using isopentenyladenine. Planta 165:354–358
Rosales-Mendoza S, Rubio-Infante N, Govea-Alonso DO, Moreno-Fierros L (2012) Current status and perspectives of plant-based candidate vaccines against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Plant Cell Rep 31:495–511
Rosales-Mendoza S, Orellana-Escobedo L, Romero-Maldonado A, Decker EL, Reski R (2014a) The potential of Physcomitrella patens as a platform for the production of plant-based vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines 13:203–212
Rosales-Mendoza S, Rubio-Infante N, Monreal-Escalante E, Govea-Alonso DO, García-Hernández AL, Salazar-González JA, González-Ortega O, Paz-Maldonado LMT, Moreno-Fierros L (2014b) Chloroplast expression of an HIV envelop-derived multiepitope protein: towards a multivalent plant-based vaccine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 116:111–123
Rubio-Infante N, Govea-Alonso DO, Alpuche-Solis AG, Garcia-Hernandez AL, Soria-Guerra RE, Paz-Maldonado LMT, Ilhuicatzi-Alvarado D, Varona-Santos JT, Verdin-Teran L, Korban SS, Moreno-Fierros L, Rosales-Mendoza S (2012) A chloroplast-derived C4V3 polypeptide from the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is orally immunogenic in mice. Plant Mol Biol 78:337–349
Schuster M, Jost W, Mudde G, Wiederkum S, Schwager C, Janzek E, Altmann F, Stadlmann J, Stemmer C, Gorr G (2007) In vivo glyco-engineered antibody with lytic potential produced by an innovative non-mammalian expression system. Biotechnol J 2:700–708
Schween G, Fleig S, Reski R (2002) High-throughput-PCR screen of 15,000 transgenic Physcomitrella plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:43–47
Stott EJ, Almond N, Kent K, Walker B, Hull R, Rose J, Silvera P, Sangster R, Corcoran T, Lines J, Silvera K, Luciw P, Murphy-Corb M, Momin P, Bruck C (1998) Evaluation of a candidate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vaccine in macaques: effect of vaccination with HIV-1 gp120 on subsequent challenge with heterologous simian immunodeficiency virus-HIV-1 chimeric virus. J Gen Virol 79:423–432
Weise A, Altmann F, Rodriguez-Franco M, Sjoberg ER, Baumer W, Launhardt H, Kietzmann M, Gorr G (2007) High-level expression of secreted complex glycosylated recombinant human erythropoietin in the Physcomitrella Δ-fuc-t Δ-xyl-t mutant. Plant Biotechnol J 5:389–401
White HN, Meng Q (2012) Diversification of specificity after maturation of the antibody response to the HIV gp41 epitope ELDKWA. PLoS One 7:e31555
WHO (2014) World Health Organization on HIV/AIDS. Fact Sheet No. 360, Geneva, Sep 2014. http://www.who.int/hiv/data/en/
Zimmer AD, Lang D, Buchta K, Rombauts S, Nishiyama T, Hasebe M, van de Peer Y, Rensing SA, Reski R (2013) Reannotation and extended community resources for the genome of the non-seed plant Physcomitrella patens provide insights into the evolution of plant gene structures and functions. BMC Genom 14:498
Zolla-Pazner S, Cohen SS, Krachmarov C, Wang S, Pinter A, Lu S (2008) Focusing the immune response on the V3 loop, a neutralizing epitope of the HIV-1 gp120 envelope. Virology 372:233–246
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Excellence Initiative of the German Federal and State Governments (EXC294 to R.R.). L.O.-E and S.R.-M received DAAD fellowships to conduct part of this project. We are grateful to Anne Katrin Prowse for proofreading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Schillberg.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orellana-Escobedo, L., Rosales-Mendoza, S., Romero-Maldonado, A. et al. An Env-derived multi-epitope HIV chimeric protein produced in the moss Physcomitrella patens is immunogenic in mice. Plant Cell Rep 34, 425–433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1720-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1720-6