Abstract
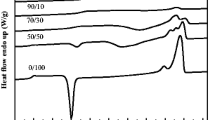
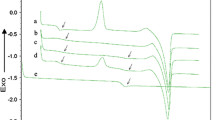
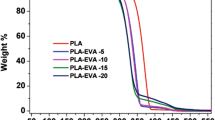
The present work is focused on the development of binary blends from poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and poly(caprolactone) (PCL). Miscibility, mechanical and thermal properties as well as blends morphology are evaluated in terms of the blend composition. Binary PHB–PCL blends were manufactured by melt compounding in a twin screw co-rotating extruder and injection molded. The composition of PHB–PCL covered the full range between individual polymers at 25 wt% increments. The obtained results show that PCL acts as an impact modifier, thus leading to an increase in flexibility and ductility as the PCL content in the PHB–PCL blends increases with a noticeable increase in elongation at break and on the energy absorption in impact conditions. The tensile strength and the elastic modulus decrease with increasing PCL content in the PHB–PCL blends; nevertheless, the flexural strength and the flexural modulus reach the highest values for the PHB–PCL blends containing 25 wt% PCL, with a remarkable decrease over this composition. The analysis of fractured surfaces by field emission scanning electron microscopy and thermal properties obtained by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and TGA give clear evidences of the immiscibility of these two biodegradable polymers. Additionally, DSC results showed an increase in crystallinity of both PHB and PCL with regard to individual polymers for PHB–PCL blends containing 25 wt% PCL. Furthermore, an increase in the degradation onset (T 0) of about 30 °C higher was detected for the same blends. Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis showed slightly shifted glass transition temperatures of each individual polymer, thus indicating that although both PHB and PCL are not fully miscible, some interactions between them occur.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrieta MP, Samper MD, López J, Jiménez A (2014) Combined effect of poly(hydroxybutyrate) and plasticizers on polylactic acid properties for film intended for food packaging. J Polym Environ 22:460–470. doi:10.1007/s10924-014-0654-y
Zhang M, Thomas NL (2011) Blending polylactic acid with polyhydroxybutyrate: the effect on thermal, mechanical, and biodegradation properties. Adv Polym Technol 30:67–79. doi:10.1002/adv.20235
Simoes CL, Viana JC, Cunha AM (2009) Mechanical properties of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and poly(lactic acid) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 112:345–352. doi:10.1002/app.29425
Wei L, Liang S, McDonald AG (2015) Thermophysical properties and biodegradation behavior of green composites made from polyhydroxybutyrate and potato peel waste fermentation residue. Ind Crops Prod 69:91–103. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.02.011
Dias M, Moraes Antunes MC, Santos AR Jr, Felisberti MI (2008) Blends of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(p-dioxanone): miscibility, thermal stability and biocompatibility. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:3535–3544. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3531-1
Catiker E, Sancaktar E (2014) Blends of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) with poly(b-alanine) and its derivatives. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40484. doi:10.1002/app.40484
Janigova I, Lacik I, Chodak I (2002) Thermal degradation of plasticized poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) investigated by DSC. Polym Degrad Stab 77:35–41. doi:10.1016/s0141-3910(02)00077-0
Abdelwahab MA, Flynn A, Chiou B-S, Imam S, Orts W, Chiellini E (2012) Thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of plasticized PLA-PHB blends. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1822–1828. doi:10.1016/j.Polymdegradstab.05.036
Ma P, Cai X, Wang W, Duan F, Shi D, Lemstra PJ (2014) Crystallization behavior of partially crosslinked poly(beta-hydroxyalkonates)/poly(butylene succinate) Blends. J Appl Polym Sci 131:41020. doi:10.1002/app.41020
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Zhang Y, Lemstra PJ (2014) Enhancement in crystallization kinetics of the bacterially synthesized poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) by poly(butylene succinate). Polym Bull 71:907–923. doi:10.1007/s00289-014-1101-x
Al-Salah HA (1998) Crystallization and morphology of poly(ethylene succinate) and poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) blends. Polym Bull 41:593–600. doi:10.1007/s002890050406
Gassner F, Owen AJ (1994) Physical-properties of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) poly(epsilon-caprolactone) blends. Polymer 35:2233–2236. doi:10.1016/0032-3861(94)90258-5
Lovera D, Marquez L, Balsamo V, Taddei A, Castelli C, Muller AJ (2007) Crystallization, morphology, and enzymatic degradation of polyhydroxybutyrate/polycaprolactone (PHB/PCL) blends. Macromol Chem Phys 208:924–937. doi:10.1002/macp.200700011
Kim BO, Woo SI (1998) Compatibilizing capability of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate-co-epsilon-caprolactone) in the blend of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(epsilon-caprolactone). Polym Bull 41:707–712. doi:10.1007/s002890050422
Valdes Garcia A, Ramos Santonja M, Beltran Sanahuja A, del Carmen Garrigos Selva M (2014) Characterization and degradation characteristics of poly (epsilon-caprolactone)-based composites reinforced with almond skin residues. Polym Degrad Stab 108:269–279. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.03.011
Patricio T, Bartolo P (2013) Thermal stability of PCL/PLA blends produced by physical blending process. Procedia Eng 59:292–297. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2013.05.124
Harrison KL, Jenkins MJ (2004) The effect of crystallinity and water absorption on the dynamic mechanical relaxation behaviour of polycaprolactone. Polym Int 53:1298–1304. doi:10.1002/pi.1517
Fukushima K, Luis Feijoo J, Yang M-C (2013) Comparison of abiotic and biotic degradation of PDLLA, PCL and partially miscible PDLLA/PCL blend. Eur Polym J 49:706–717. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2012.12.011
Li Y, Dong Q, Han C, Bian Y, Zhang X, Dong L (2014) Toward environment-friendly composites of poly(e-caprolactone) reinforced with stereocomplex-type poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide). J Appl Polym Sci 131:40208. doi:10.1002/app.40208
Imre B, Pukanszky B (2013) Compatibilization in bio-based and biodegradable polymer blends. Eur Polym J 49:1215–1233. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.01.019
Hinueber C, Haeussler L, Vogel R, Bruenig H, Heinrich G, Werner C (2011) Hollow fibers made from a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly-epsilon-caprolactone blend. eXPRESS Polym Lett 5:643–652. doi:10.3144/expresspolymlett.2011.62
Kumagai Y, Doi Y (1992) Enzymatic degradation and morphologies of binary blends of microbial poly(3-hydroxy butyrate) with poly(epsilon-caprolactone), poly(1,4-butylene adipate and poly(vinyl acetate). Polym Degrad Stab 36:241–248. doi:10.1016/0141-3910(92)90062-a
Avella M, Martuscelli E, Raimo M (2000) Review—properties of blends and composites based on poly(3-hydroxy)butyrate (PHB) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) copolymers. J Mater Sci 35:523–545. doi:10.1023/a:1004740522751
Katsumata K, Saito T, Yu F, Nakamura N, Inoue Y (2011) The toughening effect of a small amount of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) on the mechanical properties of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/PCL blend. Polym J (Tokyo, Jpn) 43:484–492. doi:10.1038/pj.2011.12
Monticelli O, Calabrese M, Gardella L, Fina A, Gioffredi E (2014) Silsesquioxanes: novel compatibilizing agents for tuning the microstructure and properties of PLA/PCL immiscible blends. Eur Polym J 58:69–78. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.06.021
Prakalathan K, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2014) Reinforcing effect and isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) nanocomposites blended with organically modified montmorillonite. Polym Compos 35:999–1012. doi:10.1002/pc.22746
Wang L, Zhu W, Wang X, Chen X, Chen G-Q, Xu K (2008) Processability modifications of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by plasticizing, blending, and stabilizing. J Appl Polym Sci 107:166–173. doi:10.1002/app.27004
Mofokeng JP, Luyt AS (2015) Morphology and thermal degradation studies of melt-mixed poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-valerate) (PHBV)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) biodegradable polymer blend nanocomposites with TiO2 as filler. J Mater Sci 50:3812–3824. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-8950-z
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness—MINECO, Ref: MAT2014-59242-C2-1-R. The authors also thank the “Conselleria d’Educació, Cultura i Esport”–Generalitat Valenciana, Ref: GV/2014/008 for financial support. D. Garcia-Garcia thanks the Spanish Ministry of Education, Culture and Sports for their financial support through an FPU Grant (FPU13/06011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Garcia, D., Ferri, J.M., Boronat, T. et al. Processing and characterization of binary poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and poly(caprolactone) (PCL) blends with improved impact properties. Polym. Bull. 73, 3333–3350 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1659-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1659-6