Abstract
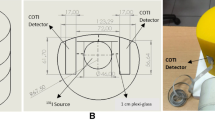
Radionuclide therapy using I-131 is commonly used for the treatment of benign thyroid diseases. The therapeutic dose to be administered is calculated based on the type of disease, the volume of the thyroid, and the measured uptake percentage. This methodology assumes a similar biological half-life of iodine, whereas in reality a large variation in biological half-life is observed. More knowledge about the actual biological half-life of iodine for individual patients will improve the quantification of the delivered radiation dose during radioiodine therapy and could aid the evaluation of the success of the therapy. In this feasibility study we used a novel measurement device [Collar Therapy Indicator (CoTI)] to measure the uptake curve of patients undergoing I-131 radioiodine therapy. The CoTI device is a light-weight wearable device that contains two independent gamma radiation detectors that are placed in a collar. By comparing results of thyroid uptake measurements with results obtained with a gamma camera, the precision of the system is demonstrated. Additionally, for three patients the uptake curve is measured during 48 h of admission in the hospital. The presented results demonstrate the feasibility of the new measurement device to measure the uptake curve during radioiodine therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Czepczynski R. Nuclear medicine in the diagnosis of benign thyroid diseases. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2012;15:113–9.
Becker DV, Sawin CT. Radioiodine and thyroid disease: the beginning. Semin Nucl Med. 1996;26:155–64.
Kobe C, Eschner W, Wild M, Rahlff I, Sudbrock F, Schmidt M, et al. Radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid disorders: what are the effective thyroidal half-life and uptake of 131I? Nucl Med Commun. 2010;31:201–5.
Willegaignon J, Sapienza MT, Coura Filho GB, Traino AC, Buchpiguel CA. Determining thyroid (131)I effective half-life for the treatment planning of Graves’ disease. Med Phys. 2013;40:022502.
Berg GE, Michanek AM, Holmberg EC, Fink M. Iodine-131 treatment of hyperthyroidism: significance of effective half-life measurements. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:228–32.
Flower MA, Schlesinger T, Hinton PJ, Adam I, Masoomi AM, Elbelli MA, et al. Radiation dose assessment in radioiodine therapy. 2. Practical implementation using quantitative scanning and PET, with initial results on thyroid carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 1989;15:345–57.
Stokkel MP, Handkiewicz Junak D, Lassmann M, Dietlein M, Luster M. EANM procedure guidelines for therapy of benign thyroid disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:2218–28.
Hanscheid H, Canzi C, Eschner W, Flux G, Luster M, Strigari L, et al. EANM Dosimetry Committee series on standard operational procedures for pre-therapeutic dosimetry II. Dosimetry prior to radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid diseases. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1126–34.
Benjamin RS, Amro A, El-Desouki MI. Measurement of iodine-123 thyroid uptake using a gamma camera with LEAP collimator. J Nucl Med Technol. 1999;27:215–9.
Balon HR, Silberstein EB, Meier DA, Charkes ND, Royal HD, Sarkar SD, Donohoe KJ. Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Thyroid Uptake Measurement. Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guidelines 2006.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge AG Medical for supplying the CoTI device for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants in this study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinks, P., Van Gils, K., Kranenborg, E. et al. Measuring the actual I-131 thyroid uptake curve with a collar detector system: a feasibility study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44, 935–940 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3595-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3595-y