Abstract
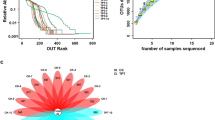
The silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) is an ideal model of Lepidoptera. However, the diversity and function of the intestinal microbiota in the gut of silkworm remain largely unknown. Changes in the intestinal microecology in fluoride-resistant strain T6 and fluoride-susceptible strain 734 of the silkworm in response to fluoride exposure were investigated. T6 and 734 were treated with 200 mg/kg fluoride (designated as T6-T and 734-T groups) and deionized water (designated as T6-C and 734-C groups). Culture-dependent approach revealed that the numbers of intestinal bacteria in the 734-T group significantly decreased compared with that in the 734-C group (4.8 ± 0.6 × 107 CFU/mL vs. 7.5 ± 0.7 × 107 CFU/mL; P < 0.05). Analyses of the intestinal content pH showed that the pH decreased in the 734-T group only. Additionally, SCFA concentrations significantly decreased in both treatment groups compared with the control groups. High-throughput sequencing indicated that the intestinal microbiota in the 734-T group was significantly more diverse than those in the other groups. The bacterial community was composed of two dominant groups (Firmicutes and Proteobacteria). Principal component analyses revealed a significant difference in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in the 734-T group compared with those in the other groups. Thaumarchaeota and Euryarchaeota were more abundant in the 734-T group, but they were less abundant in the other groups. This study enhances our understanding about the diversity and function of silkworm intestinal microbiota in response to fluoride exposure among silkworm strains with diverse resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand AA, Vennison SJ, Sankar SG, Prabhu DI, Vasan PT, Raghuraman T, Geoffrey GJ, Vendan SE (2010) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the gut of Bombyx mori that degrade cellulose, xylan, pectin and starch and their impact on digestion. J Insect Sci 10:1–20
Appel HM, Maynes LW (1995) The influence of host plant on gut conditions of gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar) caterpillars. J Insect Physiol 41:241–246
Bhattarai S, Ross KA, Schmid M, Anselmetti FS, Bürgmann H (2012) Local conditions structure unique archaeal communities in the anoxic sediments of Meromictic Lake Kivu. Microb Ecol 64:291–310
Broderick NA, Raffa KF, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (2004) Census of the bacterial community of the gypsy moth larval midgut by using culturing and culture-independent methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:293–300
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stomabaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widman J, Yatsunenko T, Zanevel J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cheng WX, Chen H, Yan SH, Su JQ (2014) Illumina sequencing-based analyses of bacterial communities during short-chain fatty-acid production from food waste and sewage sludge fermentation at different pH values. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:2387–2395
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garriy GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Buckling A, Charnley AK (2005) Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol Lett 8:1291–1298
Drenovsky RE, Elliott GN, Graham KJ, Scow KM (2004) Comparison of phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) and total soil fatty acid methyl esters (TSFAME) for characterizing soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Bochem 36:179–1800
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Prudom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308:1635–1638
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Felton G, Donato K, Del Vecchio RJ, Duffey SS (1989) Activation of plant foliar oxidases by insect feeding reduces nutritive quality of foliage for noctuid herbivores. J Chem Ecol 15:2667–2694
Felton G, Duffey SS (1991) Reassessment of the role of gut alkalinity and detergency in insect herbivory. J Chem Ecol 17:1821–1836
Feng LY, Wang H, Chen YG (2009) Effect of solids retention time and temperature on waste activated sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation under alkaline conditions in continuous-flow reactors. Bioresour Technol 100:44–49
Ghosh A, Mukherjee K, Ghosh SK, Saha B (2013) Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res Chem Intermed 39:2881–2915
Giordana B, Leonardi MG, Casartelli M, Consonni P, Parenti P (1998) K+-neutral amino acid symport of Bombyx mori larval midgut: a system operative in extreme conditions. Am J Physiol 274:R1361–R1371
Graham C, Mullen A, Whelan K (2015) Obesity and the gastrointestinal microbiota: a review of associations and mechanisms. Nutr Rev 73:376–385
He JZ, Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zheng YM, Xu MG, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-time fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Hirsch PR, Mauchline TH, Clark IM (2010) Culture-independent molecular techniques for soil microbial ecology. Soil Biol Biochem 42:878–887
Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2001) Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 292:1115–1118
Hu HW, Zhang LM, Dai Y, Di HJ, He JZ (2013) pH-dependent distribution of soil ammonia oxidizers across a large geographical scale as revealed by high-throughput pyrosequencing. J Soil Sediment 13:1439–1449
Jami E, Israel A, Kotser A, Mizrahi I (2013) Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. The ISME J 7:1069–1079
Jeong IH, Kim KH, Park JS (2013) Analysis of bacterial diversity in sponges collected off chujado, an island in Korea, using barcoded 454 pyrosequencing: analysis of a distinctive sponge group containing Chloroflexi. J Microbiol 51:570–577
Larentis M, Psenner R, Alfreider A (2015) Prokaryotic community structure in deep bedrock aquifers of the Austrian Central Alps. Anton Leeuw Int J G 107:687–701
Lee OO, Wang Y, Yang J, Lafi FF, Al-Suwailem A, Qian PY (2011) Pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse and specie-specific microbial communities in sponges from the Red Sea. The ISME J 5:650–664
Li G, Tang Q, Chen H, Yao Q, Ning D, Chen K (2011) Display of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus GP64 on the Bacillus subtilis spore coat. Curr Microbiol 62:1368–1373
Liang X, Fu Y, Tong L, Liu H (2014) Microbial shifts of the silkworm larval gut in response to lettuce leaf feeding. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:3769–3776
Lin J (2013) Effect of short chain fatty acids on the intestinal barrier. Curr Nutr Food Sci 9:93–98
Lu XM, Wang F (2002) Inhibition of cultured supernatant of Enterococci strains on germination of Nosema bombycis spores in vitro. Sci Sericulture 28:126–128 (In Chinese)
Maindonald JH (2007) Data analysis and raphics using R: an example-based approach. Cambridge University Press, New York
Martin H, Floch MD (2012) Advances in intestinal microecology: the microbiome, prebiotics, and probiotics. Nutr Clin Pract 27:193–194
McKillip JL, Small CL, Brown JL, Brunner JF, Spence KD (1997) Sporogenous midgut bacteria of the leafroller, Pandemis pyrusana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Environ Entomol 26:1475–1481
Miao YG, Jiang LJ, Bharathi D (2004) Biochemical effects of fluoride on haemolymph of the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Fluoride 37:117–124
Miao YG, Jiang LJ, Bharathi D (2005) Effects of fluoride on the activities of silkworm phosphatase, adenosine triphosphatase, and phosphorylase in the midgut of silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Fluoride 38:32–37
Mrázek J, Štrosová L, Fliegerová K, Kott T, Kopečný J (2008) Diversity of insect intestinal microflora. Folia Microbiol 53:229–233
Nardi JB, Mackie RI, Dawson JO (2002) Could microbial symbionts of arthropod guts contribute significantly to nitrogen fixation in terrestrial ecosystems? J Ins Physiol 48:751–763
Neish AS (2009) Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology 136:65–80
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Resende JA, Godon JJ, Bonnafous A, Arcuri PB, Silva VL, Otenio MH, Diniz CG (2015) Seasonal variation on microbial community and methane production during anaerobic digestion of cattle manure in Brazil. Microb Ecol DOI. doi:10.1007/s00248-015-0647-y
Roos S, Dicksved J, Tarasco V, Locatelli E, Ricceri F, Grandin U, Savino F (2013) 454 pyrosequencing analysis on faecal samples from a randomized DBPC trial of colocky infants treated with Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17936. Plos One 8: 1-5.
Sanderson IR (2004) Short chain fatty acid regulation of signaling genes expressed by the intestinal epithelium. J Nutr 134:S2450–S2454
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing Mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zhang JB, He JZ (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10:1061–1811
Simpson HL, Campbell BJ (2015) Review article: dietary fibre-microbiota interactions. Aliment Pharm Therap 42:158–179
Sun J, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Wei Q (2014) Illumina amplicon sequencing of 16S rRNA tag reveals bacterial community development in the rhizosphere of apple nurseries at a replant disease site and a new planting site. Plos One 9, e111744
Wang HS, Xue T, Cheserek MJ, Shi YH, Le G (2015) Obesity prevention of synthetic polysaccharides in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6 mice. J Funct Foods 17:563–574
Zeng Y, Zhang Y, Zhu Y (2011) Accumulation and metabolism of fluoride in T6 and 734 strains of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Fluoride 44:89–94
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhao L, Li Y, Xie S, Liu Y (2015) Distribution of sediment bacterial and archaeal communities in plateau freshwater lakes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3291–3302
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all who provided the means for us to access free software, which we used cited in this article. We thank all partners and laboratory members for their kind help. We are obliged to the anonymous reviewers of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by The National Agricultural Science and Technology Achievements Transformation Foundation (2012GB2F100376) and The Special Research Foundation of Southwest University (XDJK2014D039).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statements
This paper is our original work. It has not been submitted elsewhere, and it is not under consideration in any other journal. Our study complies with institutional standards on research silkworms. All the authors have seen the manuscript and approved its submission to Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, GN., Xia, XJ., Tang, WC. et al. Intestinal microecology associated with fluoride resistance capability of the silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 6715–6724 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7480-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7480-1