Abstract
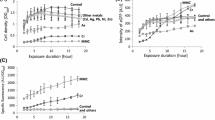
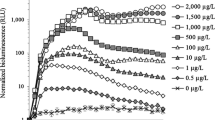
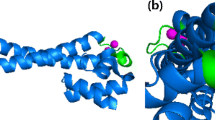
Whole-cell bioreporters (WCBs) have attracted increasing attention during the last few decades because they allow fast determination of bioavailable heavy metals in contaminated sites. Various WCBs to monitor specific heavy metals such as arsenic and cadmium in diverse environmental systems are available. However, currently, no study on simultaneous analysis of arsenic and cadmium has been reported, even though soils are contaminated by diverse heavy metals and metalloids. We demonstrated herein the development of dual-sensing WCBs to simultaneously quantify bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in contaminated sites by employing the promoter regions of the ars and znt operons as separate metal-sensing domains, and egfp and mcherry as reporter genes. The dual-sensing WCBs were generated by inserting two sets of genes into E. coli DH5α. The capability of WCBs was successfully proved to simultaneously quantify bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in amended Landwirtschaftliche Untersuchungs und Forschungsanstalt (LUFA) soils, and then, it was applied to contaminated field soils collected from a smelter area in Korea. As a result, it was noticed that the bioavailable portion of cadmium was higher than that of arsenic while the absolute amount of bioavailable arsenic and cadmium level was opposite. Since both cadmium and arsenic were assessed from the same E. coli cells, the data obtained by using dual-sensing WCBs would be more efficient and convenient than that from comparative WCB assay. In spite of advantageous aspects, to our knowledge, this is the first report on a dual-sensing WCB for rapid and concurrent quantification of bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Cresser MS, Meharg AA, Feldmann J, Cotter-Howells J (2002) Arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 36(5):962–968
Abernathy CO, Thomas DJ, Calderon RL (2003) Health effects and risk assessment of arsenic. J Nutr 133(5 Suppl 1):1536S–1538S
Baumann B, van der Meer JR (2007) Analysis of bioavailable arsenic in rice with whole cell living bioreporter bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 55(6):2115–2120. doi:10.1021/jf0631676
Belkin S (2003) Microbial whole-cell sensing systems of environmental pollutants. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(3):206–212
Branco R, Cristovao A, Morais PV (2013) Highly sensitive, highly specific whole-cell bioreporters for the detection of chromate in environmental samples. PLoS One 8(1):e54005. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054005
Brocklehurst KR, Hobman JL, Lawley B, Blank L, Marshall SJ, Brown NL, Morby AP (1999) ZntR is a Zn(II)-responsive MerR-like transcriptional regulator of zntA in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 31(3):893–902
Corbisier P, van der Lelie D, Borremans B, Provoost A, de Lorenzo V, Brown NL, Lloyd JR, Hobman JL, Csöregi E, Johansson G (1999) Whole cell-and protein-based biosensors for the detection of bioavailable heavy metals in environmental samples. Anal Chim Acta 387(3):235–244
Diesel E, Schreiber M, van der Meer JR (2009) Development of bacteria-based bioassays for arsenic detection in natural waters. Anal Bioanal Chem 394(3):687–693. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-2785-x
Garcia-Morales P, Saceda M, Kenney N, Kim N, Salomon DS, Gottardis MM, Solomon HB, Sholler PF, Jordan VC, Martin MB (1994) Effect of cadmium on estrogen receptor levels and estrogen-induced responses in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 269(24):16896–16901
Gireesh-Babu P, Chaudhari A (2012) Development of a broad-spectrum fluorescent heavy metal bacterial biosensor. Mol Biol Rep 39(12):11225–11229. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2033-x
Ivask A, Francois M, Kahru A, Dubourguier HC, Virta M, Douay F (2004) Recombinant luminescent bacterial sensors for the measurement of bioavailability of cadmium and lead in soils polluted by metal smelters. Chemosphere 55(2):147–156. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.064
Ivask A, Rolova T, Kahru A (2009) A suite of recombinant luminescent bacterial strains for the quantification of bioavailable heavy metals and toxicity testing. BMC Biotechnol 9:41. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-9-41
Jain CK, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34(17):4304–4312. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00182-2
Jusoh WNAW, Wong LS (2014) Exploring the potential of whole cell biosensor: a review in environmental applications. Int J Chem Environ Biol Sci 2:52–56
Kaur H, Kumar R, Babu JN, Mittal S (2015) Advances in arsenic biosensor development–a comprehensive review. Biosens Bioelectron 63:533–545
Liang Y, Wong J, Wei L (2005) Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58(4):475–483
Maderova L, Paton GI (2013) Deployment of microbial sensors to assess zinc bioavailability and toxicity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 66:222–228. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.07.017
Magrisso S, Erel Y, Belkin S (2008) Microbial reporters of metal bioavailability. Microb Biotechnol 1(4):320–330
Mirasoli M, Feliciano J, Michelini E, Daunert S, Roda A (2002) Internal response correction for fluorescent whole-cell biosensors. Anal Chem 74(23):5948–5953
Morrison JL (1969) Distribution of arsenic from poultry litter in broiler chickens, soil, and crops. J Agric Food Chem 17(6):1288–1290
Nachman KE, Graham JP, Price LB, Silbergeld EK (2005) Arsenic: a roadblock to potential animal waste management solutions. Environ Health Perspect 113(9):1123–1124
Petanen T, Romantschuk M (2003) Toxicity and bioavailability to bacteria of particle-associated arsenite and mercury. Chemosphere 50(3):409–413
Priyadarshi H, Alam A, Gireesh-Babu P, Das R, Kishore P, Kumar S, Chaudhari A (2012) A GFP-based bacterial biosensor with chromosomally integrated sensing cassette for quantitative detection of Hg(II) in environment. J Environ Sci (China) 24(5):963–968
Riether KB, Dollard MA, Billard P (2001) Assessment of heavy metal bioavailability using Escherichia coli zntAp::lux and copAp::lux-based biosensors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57(5–6):712–716
Robbens J, Dardenne F, Devriese L, De Coen W, Blust R (2010) Escherichia coli as a bioreporter in ecotoxicology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(5):1007–1025. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2826-6
Roda A, Roda B, Cevenini L, Michelini E, Mezzanotte L, Reschiglian P, Hakkila K, Virta M (2011) Analytical strategies for improving the robustness and reproducibility of bioluminescent microbial bioreporters. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(1):201–211. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5091-3
Rowe JL, Starnes GL, Chivers PT (2005) Complex transcriptional control links NikABCDE-dependent nickel transport with hydrogenase expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187(18):6317–6323. doi:10.1128/JB.187.18.6317-6323.2005
Selifonova O, Burlage R, Barkay T (1993) Bioluminescent sensors for detection of bioavailable Hg(II) in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(9):3083–3090
Song Y, Jiang B, Tian S, Tang H, Liu Z, Li C, Jia J, Huang WE, Zhang X, Li G (2014) A whole-cell bioreporter approach for the genotoxicity assessment of bioavailability of toxic compounds in contaminated soil in China. Environ Pollut 195:178–184. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.08.024
Sorensen SJ, Burmolle M, Hansen LH (2006) Making bio-sense of toxicity: new developments in whole-cell biosensors. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(1):11–16. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2005.12.007
Su L, Jia W, Hou C, Lei Y (2011) Microbial biosensors: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):1788–1799. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.005
Tao HC, Peng ZW, Li PS, Yu TA, Su J (2013) Optimizing cadmium and mercury specificity of CadR-based E. coli biosensors by redesign of CadR. Biotechnol Lett 35(8):1253–1258. doi:10.1007/s10529-013-1216-4
Tchounwou PB, Centeno JA, Patlolla AK (2004) Arsenic toxicity, mutagenesis, and carcinogenesis–a health risk assessment and management approach. Mol Cell Biochem 255(1–2):47–55
Turpeinen R, Virta M, Haggblom MM (2003) Analysis of arsenic bioavailability in contaminated soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(1):1–6
van der Meer JR, Belkin S (2010) Where microbiology meets microengineering: design and applications of reporter bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(7):511–522. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2392
Williams C, David D (1976) The accumulation in soil of cadmium residues from phosphate fertilizers and their effect on the cadmium content of plants. Soil Sci 121(2):86–93
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182
Wood KV, Gruber MG (1996) Transduction in microbial biosensors using multiplexed bioluminescence. Biosens Bioelectron 11(3):207–214
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecology 2011
Yoon Y, Kang Y, Chae Y, Kim S, Lee Y, Jeong SW, An YJ (2015) Arsenic bioavailability in soils before and after soil washing: the use of Escherichia coli whole-cell bioreporters. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5457-8
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korean Ministry of the Environment as a GAIA Project (2014000560001); the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, & Future Planning (2015 A0020074); and the Ministry of Education (2013R1A1A2061386).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
Youngdae Yoon declares that he has no conflict of interest. Sunghoon Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yooeun Chae declares that she has no conflict of interest. Shin Woong Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yerin Kang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Seung-Woo Jeong declares that he has no conflict of interest. Youn-Joo An declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 107 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, Y., Kim, S., Chae, Y. et al. Simultaneous detection of bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils using dual-sensing bioreporters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3713–3722 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7338-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7338-6