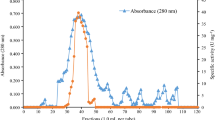
Abstract
A maltotriose-forming amylase (G3Amy) from Kitasatospora sp. MK-1785 was successfully isolated from a soil sample by inhibiting typical extracellular α-amylases using a proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitor. G3Amy was purified from the MK-1785 culture supernatant and characterized. G3Amy produced maltotriose as the principal product from starch and was categorized as an exo-α-amylase. G3Amy could also transfer maltotriose to phenolic and alcoholic compounds. Therefore, G3Amy can be useful for not only maltotriose manufacture but also maltooligosaccharide-glycoside synthesis. Further, the G3Amy gene was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli cells. Analysis of its deduced amino acid sequence revealed that G3Amy consisted of an N-terminal GH13 catalytic domain and two C-terminal repeat starch-binding domains belonging to CBM20. It is suggested that natural G3Amy was subjected to proteolysis at N-terminal region of the anterior CBM20 in the C-terminal region. As with natural G3Amy, recombinant G3Amy could produce and transfer maltotriose from starch.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann E, Ochs B, Abel KJ (1988) Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene 69:301–315. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(88)90440-4
Arai M, Nishimura T, Tsukao K, Kawaguchi T, Hayashi H, Shimizu Y, Murao S (1989) New proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitor (T-76) from Streptomyces nitrosporeus. J Ferment Bioeng 68:56–57. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(89)90215-8
Bae HK, Lee SB, Park CS, Shim JH, Lee HY, Kim MJ, Baek JS, Roh HJ, Choi JH, Choe EO, Ahn DU, Park KH (2002) Modification of ascorbic acid using transglycosylation activity of Bacillus stearothermophilus maltogenic amylase to enhance its oxidative stability. J Agric Food Chem 50:3309–3316. doi:10.1021/jf011550z
Bijttebier A, Delcour JA, Goesaert H (2008) Amylase action pattern on starch polymers. Biologia 63:989–999. doi:10.2478/s11756-008-0169-x
Dauter Z, Dauter M, Christensen S, Brzozowski AM, Borchert TV, Beier L, Davies GJ, Wilson KS (1999) X-ray structure of Novamyl, the five-domain “maltogenic” α-amylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus: maltose and acarbose complexes at 1.7Å resolution. Biochemistry 38:8385–8392. doi:10.1021/bi990256l
Derde LJ, Gomand SV, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2012) Characterisation of three starch degrading enzymes: thermostable β-amylase, maltotetraogenic and maltogenic α-amylases. Food Chem 135:713–721. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.031
Desmet T, Soetaert W, Bojarova P, Kren V, Dijkhuizen L, Eastwick-Field V, Schiller A (2012) Enzymatic glycosylation of small molecules: challenging substrates require tailored catalysts. Chem Eur J 18:10786–10801. doi:10.1002/chem.201103069
Edwards U, Rogall T, Backer H, Emde M, Buttger E (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7843–7853. doi:10.1093/nar/17.19.7843
Jun SY, Kim JS, Choi KH, Cha J, Ha NC (2013) Structure of a novel α-amylase AmyB from Thermotoga neapolitana that produces maltose from the nonreducing end of polysaccharides. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69:442–450. doi:10.1107/S0907444912049219
Kanai R, Haga K, Akiba T, Yamane K, Harata K (2004) Biochemical and crystallographic analyses of maltohexaose-producing amylase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. 707. Biochemistry 43:14047–14056. doi:10.1021/bi048489m
Kashiwagi N, Miyake M, Hirose S, Sota M, Ogino C, Kondo A (2014) Cloning and starch degradation profile of maltotriose-producing amylases from Streptomyces species. Biotechnol Lett 11:2311–2317. doi:10.1007/s10529-014-1611-5
Kelly RM, Leemhuis H, Rozeboom HJ, van Oosterwijk N, Dijkstra BW, Dijkhuizen L (2008) Elimination of competing hydrolysis and coupling side reactions of a cyclodextrin glucanotransferase by directed evolution. Biochem J 413:517–525. doi:10.1042/BJ20080353
Khamna S, Yokota A, Lumyong S (2009) Actinomycetes isolated from medicinal plant rhizosphere soils: diversity and screening of antifungal compounds, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:649–655. doi:10.1007/s11274-008-9933-x
Kobayashi T, Kanai H, Hayashi T, Akiba T, Akaboshi R, Horikoshi K (1992) Haloalkaliphilic maltotriose-forming α-amylase from the archaebacterium Natronococcus sp. strain Ah-36. J Bacteriol 174:3439–3444
Kuriki T, Imanaka T (1999) The concept of the α-amylase family: structural similarity and common catalytic mechanism. J Biosci Bioeng 87:557–565. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(99)80114-5
Lee HY, Kim MJ, Baek JS, Lee HS, Cha HJ, Lee SB, Moon TW, Seo ES, Kim D, Park CS, Park KH (2003) Preparation and characterization of maltosyl-sucrose isomers produced by transglycosylation of maltogenic amylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Mol Catal B Enzym 26:293–305. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2003.08.003
Lee YS, Park DJ, Choi YL (2014) Characterization of maltotriose production by hydrolyzing of soluble starch with α-amylase from Microbulbifer thermotolerans DAU221. J Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-6186-5
Makino T, Kanemaru M, Okuyama S, Shimizu R, Tanaka H, Mizukami H (2013) Anti-allergic effects of enzymatically modified isoquercitrin (α-oligoglucosyl quercetin 3-O-glucoside), quercetin 3-O-glucoside, α-oligoglucosyl rutin, and quercetin, when administered orally to mice. J Nat Med 67:881–886. doi:10.1007/s11418-013-0760-5
Mehta D, Satyanarayana T (2013) Dimerization mediates thermo-adaptation, substrate affinity and transglycosylation in a highly thermostable maltogenic amylase of Geobacillus thermoleovorans. PLoS One 8. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073612
Morishita Y, Hasegawa K, Matsuura Y, Katsube Y, Kubota M, Sakai S (1997) Crystal structure of a maltotetraose-forming exo-amylase from Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Mol Biol 267:661–672. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0887
Nakakuki T, Azuma K, Kainuma K (1984) Action patterns of various exo-amylases and the anomeric configurations of their products. Carbohydr Res 128:297–310. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0887
Nakano H, Kiso T, Okamoto K, Tomita T, Manan MBA, Kitahata S (2003) Synthesis of glycosyl glycerol by cyclodextrin glucanotransferases. J Biosci Bioeng 95:583–588. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(03)80166-4
Nasrollahi S, Golalizadeh L, Sajedi RH, Taghdir M, Asghari SM, Rassa M (2013) Substrate preference of a Geobacillus maltogenic amylase: a kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Int J Biol Macromol 60:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.04.063
Robyt JF, French D (1967) Multiple attack hypothesis of α-amylase action: action of porcine pancreatic, human salivary, and Aspergillus oryzae α-amylases. Arch Biochem Biophys 122:8–16. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(67)90118-X
Roh HJ, Kang SC, Lee HS, Kim DK, Byun SB, Lee SJ, Park KH (2005) Transglycosylation of tagatose with maltotriose by Bacillus stearothermophilus maltogenic amylase (BSMA). Tetrahedron Asymmetry 16:77–82. doi:10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.11.060
Somogyi M (1952) Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem 195:19–23
Sumitani J, Kawaguchi T, Hattori N, Murao S, Arai M (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitor gene from Streptomyces nirosporeus in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1243–1248. doi:10.1271/bbb.57.1243
Sumitani J, Tottori T, Kawaguchi T, Arai M (2000) New type of starch-binding domain: the direct repeat motif in the C-terminal region of Bacillus sp. No. 195 α-amylase contributes to starch binding and raw starch degrading. Biochem J 350:477–484. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3500477
Takasaki Y (1985) An amylase producing maltotriose from Bacillus subtilis. Agric Biol Chem 49:1091–1097. doi:10.1080/00021369.1985.10866865
Takasaki Y, Kitajima M, Tsuruta T, Nonoguchi M, Hayashi S, Imada K (1991) Maltotriose-producing amylase from Microbacterium imperiale. Agric Biol Chem 55:687–692. doi:10.1080/00021369.1991.10870677
Takekawa S, Uozumi N, Tsukagoshi N, Udaka S (1991) Proteases involved in generation of β- and α-amylases from a large amylase precursor in Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol 173:6820–6825
Usui T, Murata T (1988) Enzymatic-synthesis of p-nitrophenyl α-maltopentaoside in an aqueous-methanol solvent system by maltotetraose-forming amylase: a substrate for human amylase in serum. J Biochem 103:969–972
Usui T, Murata T, Yabuuchi Y, Ogawa K (1993) Transglycosylation reaction of maltotriose-forming amylase from Streptomyces griseus. Carbohydr Res 250:57–66. doi:10.1016/0008-6215(93)84154-X
van der Veen BA, Leemhuis H, Kralj S, Uitdehaag JCM, Dijkstra BW, Dijkhuizen L (2001) Hydrophobic amino acid residues in the acceptor binding site are main determinants for reaction mechanism and specificity of cyclodextrin-glycosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 276:44557–44562. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107533200
Wu C, Zhou X, Xu Y, Li H, Tian Y, Xu X, Jin Z (2014) Characterization and mechanism of action of Microbacterium imperiale glucan 1,4-α-maltotriohydrolase. Carbohydr Res 384:46–50. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2013.11.014
Yang CH, Liu WH (2004) Purification and properties of a maltotriose-producing α-amylase from Thermobifida fusca. Enzyme Microb Technol 35:254–260. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2004.05.004
Yang CH, Liu WH (2007) Cloning and characterization of a maltotriose-producing α-amylase gene from Thermobifida fusca. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:325–330. doi:10.1007/s10295-006-0200-6
Yoon JW, Jeon EJ, Jung IH, Min MJ, Lee HY, Kim MJ, Baek JS, Lee HS, Park CS, Oh SS, Park KH, Moon TW (2003) Maltosyl-erythritol, a major transglycosylation product of erythritol by Bacillus stearothermophilus maltogenic amylase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:525–531. doi:10.1271/bbb.67.525
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants-in-aid for scientific research (26450100) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamon, M., Sumitani, Ji., Tani, S. et al. Characterization and gene cloning of a maltotriose-forming exo-amylase from Kitasatospora sp. MK-1785. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4743–4753 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6396-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6396-5