Abstract
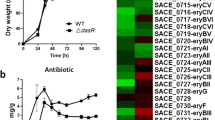
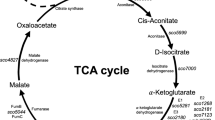
A novel two-component system (TCS) of DraR-K was previously identified as playing differential roles in the biosynthesis of antibiotics (blue-pigmented type II polyketide actinorhodin (ACT), red-pigmented tripyrrole undecylprodigiosin (RED), and yellow-pigmented type I polyketide (yCPK)) in Streptomyces coelicolor M145 under the conditions of minimal medium (MM) supplemented with a high concentration of different nitrogen sources (e.g., 75 mM glutamine). To assess whether DraR-K has more globalized roles, a genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of the parental strain M145 and a ΔdraR-K mutant under the condition of MM supplemented with 75 mM glutamine was performed using DNA microarray analysis combined with real-time reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-qPCR). The analyses showed that deletion of the draR-K genes led to the differential expression not only of the biosynthetic gene clusters of ACT, RED, and yCPK but also of other five secondary metabolite biosynthetic clusters. In addition, a number of primary metabolism-related genes in the ΔdraR-K mutant, such as ureA/B/C/D/G/F, the pstSCAB operon, and the chb gene, exhibited altered expression, which might enable the organism to balance the C/N/P ratio under the condition of a high concentration of glutamine. We also found that the expression of many developmental genes, including ramR, chpA/D/E, and the whiE gene cluster, was affected by the draR-K deletion. Furthermore, the direct role of DraR-K on the transcription of several genes, including chb and pepA/pepA2, was validated using electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs). In summary, our transcriptomic analyses revealed that DraR-K plays global regulatory roles in the physiological and morphological differentiation of S. coelicolor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allenby NE, Laing E, Bucca G, Kierzek AM, Smith CP (2012) Diverse control of metabolism and other cellular processes in Streptomyces coelicolor by the PhoP transcription factor: genome-wide identification of in vivo targets. Nucleic Acids Res 40(19):9543–9556
Anderson TB, Brian P, Champness WC (2001) Genetic and transcriptional analysis of absA, an antibiotic gene cluster-linked two-component system that regulates multiple antibiotics in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 39(3):553–566
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417(6885):141–147
Capstick DS, Willey JM, Buttner MJ, Elliot MA (2007) SapB and the chaplins: connections between morphogenetic proteins in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 64(3):602–613
Claessen D, Stokroos I, Deelstra HJ, Penninga NA, Bormann C, Salas JA, Dijkhuizen L, Wösten HA (2004) The formation of the rodlet layer of streptomycetes is the result of the interplay between rodlins and chaplins. Mol Microbiol 53(2):433–443
den Hengst CD, Tran NT, Bibb MJ, Chandra G, Leskiw BK, Buttner MJ (2010) Genes essential for morphological development and antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor are targets of BldD during vegetative growth. Mol Microbiol 78(2):361–379
Fischer M, Alderson J, van Keulen G, White J, Sawers RG (2010) The obligate aerobe Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) synthesizes three active respiratory nitrate reductases. Microbiology 156:3166–3179
Flärdh K, Buttner MJ (2009) Streptomyces morphogenetics: dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(1):36–49
Gao C, Hindra, Mulder D, Yin C, Elliot MA (2012) Crp is a global regulator of antibiotic production in Streptomyces. mBio 3(6):e00407–e00412
Gottelt M, Kol S, Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb M, Takano E (2010) Deletion of a regulatory gene within the cpk gene cluster reveals novel antibacterial activity in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 156:2343–2353
Hesketh A, Kock H, Mootien S, Bibb M (2009) The role of absC, a novel regulatory gene for secondary metabolism, in zinc-dependent antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 74(6):1427–1444
Higo A, Hara H, Horinouchi S, Ohnishi Y (2012) Genome-wide distribution of AdpA, a global regulator for secondary metabolism and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces, revealed the extent and complexity of the AdpA regulatory network. DNA Res 19(3):259–273
Hutchings MI, Hoskisson PA, Chandra G, Buttner MJ (2004) Sensing and responding to diverse extracellular signals? Analysis of the sensor kinases and response regulators of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 150:2795–2806
Imbert M, Béchet M, Blondeau R (1995) Comparison of the main siderophores produced by some species of Streptomyces. Curr Microbiol 31(2):129–133
Izumikawa M, Shipley PR, Hopke JN, O’Hare T, Xiang LK, Noel JP, Moore BS (2003) Expression and characterization of the type III polyketide synthase 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene synthase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30(8):510–515
Jiang J, He X, Cane DE (2006) Geosmin biosynthesis. Streptomyces coelicolor germacradienol/germacrene D synthase converts farnesyl diphosphate to geosmin. J Am Chem Soc 128(25):8128–8129
Jiang J, He X, Cane DE (2007) Biosynthesis of the earthy odorant geosmin by a bifunctional Streptomyces coelicolor enzyme. Nat Chem Biol 3(11):711–715
Kallifidas D, Pascoe B, Owen GA, Strain-Damerell CM, Hong HJ, Paget MS (2010) The zinc-responsive regulator Zur controls expression of the coelibactin gene cluster in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 192(2):608–611
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Butter MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim MS, Dufour YS, Yoo JS, Cho YB, Park JH, Nam GB, Kim HM, Lee KL, Donohue TJ, Roe JH (2012) Conservation of thiol-oxidative stress responses regulated by SigR orthologues in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 85(2):326–344
Kodani S, Hudson ME, Durrant MC, Buttner MJ, Nodwell JR, Willey JM (2004) The SapB morphogen is a lantibiotic-like peptide derived from the product of the developmental gene ramS in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(31):11448–11453
Lewis RA, Shahi SK, Laing E, Bucca G, Efthimiou G, Bushell M, Smith CP (2011) Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of the response to nitrogen limitation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). BMC Res Notes 4:78
Li W, Bottrill AR, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Paget MSB, Kleanthous C (2003) The role of zinc in the disulphide stress-regulated anti-sigma factor RsrA from Streptomyces coelicolor. J Mol Biol 333(2):461–472
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu GQ, Tan HR (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77(1):112–143
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lu YH, He JM, Zhu H, Yu ZY, Wang R, Chen YL, Dang FJ, Zhang WW, Yang S, Jiang WH (2011) An orphan histidine kinase, OhkA, regulates both secondary metabolism and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 193(12):3020–3032
Martin JF (2004) Phosphate control of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites is mediated by the PhoR-PhoP system: an unfinished story. J Bacteriol 186(16):5197–5201
Martin JF, Liras P (2010) Engineering of regulatory cascades and networks controlling antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(3):263–273
O’Connor TJ, Kanellis P, Nodwell JR (2002) The ramC gene is required for morphogenesis in Streptomyces coelicolor and expressed in a cell type-specific manner under the direct control of RamR. Mol Microbiol 45(1):45–57
Pullan ST, Chandra G, Bibb MJ, Merrick M (2011) Genome-wide analysis of the role of GlnR in Streptomyces venezuelae provides new insights into global nitrogen regulation in actinomycetes. BMC Genomics 12:175
Rico S, Santamaria RI, Yepes A, Rodriguez H, Laing E, Bucca G, Smith CP, Diaz M (2014) Deciphering the regulon of Streptomyces coelicolor AbrC3, a positive response regulator of antibiotic production. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(8):2417–2428
Rodríguez H, Rico S, Díaz M, Santamaría RI (2013) Two-component systems in Streptomyces: key regulators of antibiotic complex pathways. Microb Cell Fact 12:127
Rodriguez-Garcia A, Barreiro C, Santos-Beneit F, Sola-Landa A, Martin JF (2007) Genome-wide transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the primary response to phosphate limitation in Streptomyces coelicolor M145 and in a ∆phoP mutant. Proteomics 7(14):2410–2429
Rozas D, Gullon S, Mellado RP (2012) A novel two-component system involved in the transition to secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31760
Sambrook J, Fritsch T, Maniatis E (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Santos-Beneit F, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Franco-Dominguez E, Martin JF (2008) Phosphate-dependent regulation of the low- and high-affinity transport systems in the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 154:2356–2370
Schneider D, Bruton CJ, Chater KF (2000) Duplicated gene clusters suggest an interplay of glycogen and trehalose metabolism during sequential stages of aerial mycelium development in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Gen Genet 263(3):543–553
Schrempf H (2001) Recognition and degradation of chitin by streptomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 79(3–4):285–289
Sheeler NL, MacMillan SV, Nodwell JR (2005) Biochemical activities of the absA two-component system of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 187(2):687–696
Shin JH, Oh SY, Kim SJ, Roe JH (2007) The zinc-responsive regulator Zur controls a zinc uptake system and some ribosomal proteins in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 189(11):4070–4077
Shu D, Chen L, Wang WH, Yu ZY, Ren C, Zhang WW, Yang S, Lu YH, Jiang WH (2009) afsQ1-Q2-sigQ is a pleiotropic but conditionally required signal transduction system for both secondary metabolism and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(6):1149–1160
Sola-Landa A, Moura RS, Martin JF (2003) The two-component PhoR-PhoP system controls both primary metabolism and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Streptomyces lividans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(10):6133–6138
Sola-Landa A, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Franco-Dominguez E, Martin JF (2005) Binding of PhoP to promoters of phosphate-regulated genes in Streptomyces coelicolor: identification of PHO boxes. Mol Microbiol 56(5):1373–1385
Takano H, Obitsu S, Beppu T, Ueda K (2005) Light-induced carotenogenesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): identification of an extracytoplasmic function sigma factor that directs photodependent transcription of the carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster. J Bacteriol 187(5):1825–1832
Thomas-Chollier M, Defrance M, Medina-Rivera A, Sand O, Herrmann C, Thieffry D, van Helden J (2011) RSAT 2011: regulatory sequence analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W86–W91
Tiffert Y, Supra P, Wurm R, Wohlleben W, Wagner R, Reuther J (2008) The Streptomyces coelicolor GlnR regulon: identification of new GlnR targets and evidence for a central role of GlnR in nitrogen metabolism in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 67(4):861–880
Tiffert Y, Franz-Wachtel M, Fladerer C, Nordheim A, Reuther J, Wohlleben W, Mast Y (2010) Proteomic analysis of the GlnR-mediated response to nitrogen limitation in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(4):1149–1159
Turatsinze JV, Thomas-Chollier M, Defrance M, van Helden J (2008) Using RSAT to scan genome sequences for transcription factor binding sites and cis-regulatory modules. Nat Protoc 3(10):1578–1588
van Keulen G, Jonkers HM, Claessen D, Dijkhuizen L, Wösten HA (2003) Differentiation and anaerobiosis in standing liquid cultures of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 185(4):1455–1458
van Keulen G, Alderson J, White J, Sawers RG (2005) Nitrate respiration in the actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor. Biochem Soc Trans 33:210–212
Wang Y, Cen XF, Zhao GP, Wang J (2012) Characterization of a new GlnR binding box in the promoter of amtB in Streptomyces coelicolor inferred a PhoP/GlnR competitive binding mechanism for transcriptional regulation of amtB. J Bacteriol 194(19):5237–5244
Wang R, Mast Y, Wang J, Zhang WW, Zhao GP, Wohlleben W, Lu YH, Jiang WH (2013) Identification of two-component system AfsQ1/Q2 regulon and its cross-regulation with GlnR in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 87(1):30–48
Willenborg J, de Greeff A, Jarek M, Valentin-Weigand P, Goethe R (2014) The CcpA regulon of Streptococcus suis reveals novel insights into the regulation of the streptococcal central carbon metabolism by binding of CcpA to two distinct binding motifs. Mol Microbiol 92(1):61–83
Yeo M, Chater K (2005) The interplay of glycogen metabolism and differentiation provides an insight into the developmental biology of Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 151:855–861
Yu ZY, Zhu H, Dang FJ, Zhang WW, Qin ZJ, Yang S, Tan HR, Lu YH, Jiang WH (2012) Differential regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis by DraR-K, a novel two-component system in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 85(3):535–556
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA022107), National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB721103), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31121001, 31370081, and 31430004). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of SA-SIBS scholarship program and TOLO Biotechnology (Shanghai, China) for their excellent assistance in DNase I footprinting assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 320 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Zhu, H., Zheng, G. et al. A genome-wide transcriptomic analysis reveals diverse roles of the two-component system DraR-K in the physiological and morphological differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 9351–9363 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6102-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6102-z