Abstract
Objective
Zuojin Pill has been shown to inhibit the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 isoenzyme in vitro. In Chinese individuals, CYP 2D6*10 is the most common allele with reduced enzyme activity. In this study, we investigated the pharmacokinetic interaction between Zuojin Pill and the sensitive CYP2D6 probe dextromethorphan in healthy Chinese volunteers with CYP2D6*10 genotype.
Methods
A pharmacokinetics interaction study was carried out in three groups with CYP2D6*1/*1 (n = 6), CYP2D6*1/*10 (n = 6), and CYP2D6*10/*10 (n = 6) genotypes. Each participant received a single oral dose of dextromethorphan (15 mg) followed by Zuojin Pill (3 g twice daily) for 7 days, and received 3 g Zuojin Pill with 15 mg dextromethorphan in the last day. Blood samples (0–24 h) and urine samples (0–12 h) were collected at baseline and after the administration of Zuojin Pill, and the samples’ concentration of dextromethorphan and its main metabolite dextrorphan was determined.
Results
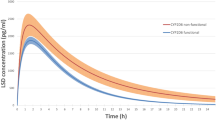
Compared to baseline values, co-administration of Zuojin Pill (3 g twice daily) for 7 days increased the AUC0-24 of dextromethorphan [mean (90 % CI)] by 3.00-fold (2.49∼3.61) and 1.71-fold (1.42∼2.06), and decreased oral clearance(CL/F) by 0.27-fold (0.2-0.40) and 0.57-fold (0.48-0.67) in the participants with CYP2D6*1/*1 and CYP2D6*1/*10 genotypes, respectively. In contrast, no significant change was observed in these pharmacokinetic parameters of the participants with CYP2D6*10/*10 genotype.
Conclusion
These data demonstrated that administration of Zuojin Pill inhibited moderately CYP2D6-mediated metabolism of dextromethorphan in healthy volunteers. The inhibitory influence of CYP2D6 was greater in CYP2D6*1/*1 and CYP2D6*1/*10 groups than CYP2D6 *10/*10 group.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
The State Pharmacopoeia Commission of PR China (2010) The Pharmacopoeia of PR China. China Medical Science and Technology Press, PR China, in Chinese
Gao X, Yang XW, Marriott PJ (2010) Simultaneous analysis of seven alkaloids in Coptis-Evodia herb couple and Zuojin pill by UPLC with accelerated solvent extraction. J Sep Sci 33:2714–2722
Zhang X, Qiu F, Jiang J, Gao C, He M (2010) Simultaneous determination of 6 alkaloids in Zuojin Pill and Xianglian Pill by LC-MS/MS. Chin Traditional Patent Med 32(4):597–600
Han YL, Yu HL, Li D, Meng XL, Zhou ZY, Yu Q, Zhang XY, Wang FJ, Guo C (2011) In vitro inhibition of huanglian [Rhizoma coptidis (L.)] and its six active alkaloids on six cytochrome P450 isoforms in human liver microsomes. Phytother Res 25:1660–1665
Wojtczak A, Rychlik-Sych M, Krochmalska-Ulacha E, Skrêtkowicz J (2007) CYP2D6 phenotyping with dextromethorphan. Pharmacol Rep 59:734–738
Teh LK, Bertilsson L (2012) Pharmacogenomics of CYP2D6: molecular genetics, interethnic differences and clinical importance. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 27:55–67
Qu Q, Qu J, Lu H, Zhan M, Wu LX, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhou H (2014) Inhibitory effects of phytochemicals on metabolic capabilities of CYP2D6*1 and CYP2D6*10 using cell-based models in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35:685–696
Zhou SF (2009) Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6, its clinical significance: part I. Clin Pharmacokinet 48(11):689–723
Zhou SF (2009) Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: part II. Clin Pharmacokinet 48(12):761–804
Wang GX, Zhang H, He FF, Fang XM (2006) Effect of the CYP2D6*10 C188T polymorphism on postoperative tramadol analgesia in a Chinese population. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:927–931
Bondolfi G, Eap CB, Bertschy G, Zullino D, Vermeulen A, Baumann P (2002) The effect of fluoxetine on the pharmacokinetics and safety of risperidone in psychotic patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 35:50–56
Llerena A, Berecz R, de la Rubia A, Fernandez-Salguero P, Dorado P (2001) Effect of thioridazine dosage on the debrisoquine hydroxylation phenotype in psychiatric patients with different CYP2D6 genotypes. Ther Drug Monit 23:616–20
Abdel-Rahman SM, Gotschall RR, Kauffman RE, Leeder JS, Kearns GL (1999) Investigation of terbinafine as a CYP2D6 inhibitor in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther 65:465–472
Fukuda T, Nishida Y, Imaoka S, Hiroi T, Naohara M, Funae Y, Azuma J (2000) The decreased in vivo clearance of CYP2D6 substrates by CYP2D6*10 might be caused not only by the low-expression but also by low affinity of CYP2D6. Arch Biochem Biophys 380(2):303–308
Lee LS, Nafziger AN, Bertino JS (2005) Evaluation of inhibitory drug interactions during drug development: genetic polymorphisms must be considered. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(1):1–6
US Food and Drug Administration (2012) Draft guidance for industry: drug interaction studies—study design, data analysis, and implications for dosing and labeling. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/default.htm
Qiao H, Jia L, Zhang L, Guo Y, Zhang Q, Liu F (2003) Bioequivalence of dextromethorphan hydrobromide tablets in healthy volunteers. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 12(1):11–13
Chow SC, Wang H (2001) On sample size calculation in bioequivalence trials. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 28(2):155–169
Cabaleiro T, Ochoa D, Román M, Moreno I, López-Rodrίguez R, Novalbos J, Abad-Santos F (2015) Polymorphisms in CYP2D6 have a greater effect on variability of risperidone pharmacokinetics than gender. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 116:124–128
Frank D, Jaehde U, Fuhr U (2007) Evaluation of probe drugs and pharmacokinetic metrics for CYP2D6 phenotyping. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:321–333
Yu A, Haining RL (2001) Comparative contribution to dextromethorphan metabolism by cytochrome P450 isoforms in vitro: can dextromethorphan be used as a dual probe for both CYP2D6 and CYP3A activities? Drug Metab Dispos 29(11):1514–1520
Liu S, Qiu F, Miao P, Zhu, Zeng J, Li Q, He M, Jiang J (2015) Activity of CYP3A4 influenced by Zuojin Pills taken in healthy Chinese volunteers. Chin Traditional Patent Med 37(7):1427–1430
Zuo LJ, Guo T, Xia DY, Jia LH (2012) Allele and genotype frequencies of CYP3A4, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 in Han, Uighur, Hui, and Mongolian Chinese populations. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 16:102–108
Qian JC, Xu XM, Hu GX, Dai DP, Xu RA, Hu LM, Li FH, Zhang XH, Yang JF, Cai JP (2013) Genetic variations of human CYP2D6 in the Chinese Han population. Pharmacogenomics 14:1731–1743
Bello CL, LaBadie RR, Ni G, Boutros T, McCormick C, Ndongo MN (2012) The effect of dacomitinib (PF-00299804) on CYP2D6 activity in healthy volunteers who are extensive or intermediate metabolizers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:991–997
Dudhatra GB, Mody SK, Awale MM, Patel HB, Modi CM, Kumar A, Kamani DR, Chauhan BN (2012) Comprehensive review on pharmacotherapeutics of herbal bioenhancer. Sci World J 637953:1–33
Oishi M, Chiba K, Malhotra B, Tio S (2010) Effect of the CYP2D6*10 genotype on tolterodine pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Dispos 38(9):1456–1463
Ma BL, Yao MK, Zhong J, Ma YM, Gao CL, Wu JS, Qiu FR, Wang CH, Wang XH (2012) Increased systemic exposure to rhizoma coptidis alkaloids in lipopolysaccharide-pretreated rats attributable to enhanced intestinal absorption. Drug Metab Dispos 40(2):381–388
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (Grant 81173118), the National Key New Drug Creation Special Programme (Grant 2012ZX09303009-001), and the Shanghai Key Lab of Traditional Clinical Medicine (Grant C10dZ2220200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Furong Qiu and Songcan Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, F., Liu, S., Miao, P. et al. Effects of the Chinese herbal formula “Zuojin Pill” on the pharmacokinetics of dextromethorphan in healthy Chinese volunteers with CYP2D6*10 genotype. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72, 689–695 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2048-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2048-7