Abstract
Rationale
Cocaine produces significant aversive/anxiogenic actions whose underlying neurobiology remains unclear. A possible substrate contributing to these actions is the serotonergic (5-HT) pathway projecting from the dorsal raphé (DRN) to regions of the extended amygdala, including the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) which have been implicated in the production of anxiogenic states.
Objectives
The present study examined the contribution of 5-HT signaling within the BNST to the anxiogenic effects of cocaine as measured in a runway model of drug self-administration.
Methods
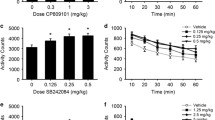
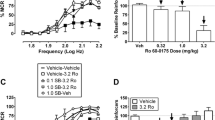
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were fitted with bilateral infusion cannula aimed at the BNST and then trained to traverse a straight alley once a day for a single 1 mg/kg i.v. cocaine infusion delivered upon goal-box entry on each of 16 consecutive days/trials. Intracranial infusions of CP 94,253 (0, 0.25, 0.5, or 1.0 μg/side) were administered to inhibit local 5-HT release via activation of 5-HT1B autoreceptors. To confirm receptor specificity, the effects of this treatment were then challenged by co-administration of the selective 5-HT1B antagonist NAS-181.
Results
Intra-BNST infusions of the 5-HT1B autoreceptor agonist attenuated the anxiogenic effects of cocaine as reflected by a decrease in runway approach-avoidance conflict behavior. This effect was reversed by the 5-HT1B antagonist. Neither start latencies (a measure of the subject’s motivation to seek cocaine) nor spontaneous locomotor activity (an index of motoric capacity) were altered by either treatment.
Conclusions
Inhibition of 5-HT1B signaling within the BNST selectively attenuated the anxiogenic effects of cocaine, while leaving unaffected the positive incentive properties of the drug.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams JK, Johnson PL, Hay-Schmidt a et al (2005) Serotonergic systems associated with arousal and vigilance behaviors following administration of anxiogenic drugs. Neuroscience 133:983–997. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.03.025
Adell A, Celada P, Artigas F (2001) The role of 5-HT 1B receptors in the regulation of serotonin cell firing and release in the rat brain. J Neurochem 79:172–182. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00550.x
Adhikari A (2014) Distributed circuits underlying anxiety. Front Behav Neurosci 8:112. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00112
Aston-Jones G, Georges F, Aston-Jones G (2001) Potent regulation of midbrain dopamine neurons by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurosci 21:RC160
Ben-Shahar O, Ahmed SH, Koob GF, Ettenberg A (2004) The transition from controlled to compulsive drug use is associated with a loss of sensitization. Brain Res 995:46–54. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2003.09.053
Blanchard DC, Blanchard RJ (1999) Cocaine potentiates defensive behaviors related to fear and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:981–991
Castanon N, Scearce-Levie K, Lucas JJ, Rocha B, Hen R (2000) Modulation of the effects of cocaine by 5-HT1B receptors: a comparison of knockouts and antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:559–566. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(00)00389-0
Cunningham KA, Paris JM, Goeders NE (1992a) Serotonin neurotransmission in cocaine sensitization. Ann N Y Acad Sci 654:117–127
Cunningham KA, Paris JM, Goeders NE (1992b) Chronic cocaine enhances serotonin autoregulation and serotonin uptake binding. Synapse 11:112–123. doi:10.1002/syn.890110204
Davis M, Walker DL, Miles L, Grillon C (2010) Phasic vs sustained fear in rats and humans: role of the extended amygdala in fear vs anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:105–135. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.109
De Almeida RMM, Rosa MM, Santos DM, Saft DM, Benini Q, Miczek KA (2006) 5-HT(1B) receptors, ventral orbitofrontal cortex, and aggressive behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 185:441–450. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0333-3
De Groote L, Klompmakers AA, Olivier B, Westenberg HGM (2003) An evaluation of the effect of NAS-181, a new selective 5-HT1B receptor antagonist, on extracellular 5-HT levels in rat frontal cortex. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 367:89–94. doi:10.1007/s00210-002-0685-0
De Groote L, Olivier B, Westenberg HG (2002) Extracellular serotonin in the prefrontal cortex is limited through terminal 5-HT1B autoreceptors: a microdialysis study in knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 162:419–424. doi:10.1007/s00213-002-1117-z
Dumont EC, Williams JT (2004) Noradrenaline triggers GABAA inhibition of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis neurons projecting to the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 24:8198–8204. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0425-04.2004
Ettenberg A (2009) The runway model of drug self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:271–277. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.11.003
Ettenberg A (2004) Opponent process properties of self-administered cocaine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:721–728. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.11.009
Ettenberg A, Bernardi R (2007) Effects of buspirone on the immediate positive and delayed negative properties of intravenous cocaine as measured in the conditioned place preference test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 87:171–178. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2007.04.014
Ettenberg A, Bernardi R (2006) Anxiolytic-like actions of buspirone in a runway model of intravenous cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:393–399. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.09.007
Ettenberg A, Geist TD (1993) Qualitative and quantitative differences in the operant runway behavior of rats working for cocaine and heroin reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:191–198
Ettenberg A, Geist TD (1991) Animal model for investigating the anxiogenic effects of cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:455–461
Ettenberg A, Raven MA, Danluck DA, Necessary BD (1999) Evidence for opponent-process actions of intravenous cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:507–512
Ettenberg A, Ofer O, Mueller C (2011) Inactivation of the dorsal raphe nucleus reduces the anxiogenic response of rats running an alley for intravenous cocaine. Pharmacol 97:632–639. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.11.008
Filip M, Alenina N, Bader M, Przegaliński E (2010) Behavioral evidence for the significance of serotoninergic (5-HT) receptors in cocaine addiction. Addict Biol 15:227–249. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00214.x
Filip M, Bubar M, Cunningham KA (2004) Contribution of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) 5-HT2 receptor subtypes to the hyperlocomotor effects of cocaine: acute and chronic pharmacological analyses. J Pharmacol 310:1246–1254. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.068841.effects
Filip M, Papla I, Nowak E, Czepiel K, Przegaliński E (2003) Effects of 5-HT1B receptor ligands microinjected into the ventral tegmental area on cocaine discrimination in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 459:239–245. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(02)02873-X
Gawin FH (1991) Cocaine psychology and addiction: neurophysiology. Science 251:1580–1586
Geist TD, Ettenberg A (1990) A simple method for studying drug reinforcement in a runway. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:703–706
George O, Le Moal M, Koob GF (2012) Allostasis and addiction: role of the dopamine and corticotropin-releasing factor systems. Physiol Behav 106:58–64. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.11.004
Georges F, Aston-Jones G (2002) Activation of ventral tegmental area cells by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: a novel excitatory amino acid input to midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 22:5173–5187
Guo J-D, Hammack SE, Hazra R, Levita L, Rainnie DG (2009) Bi-directional modulation of bed nucleus of stria terminalis neurons by 5-HT: molecular expression and functional properties of excitatory 5-HT receptor subtypes. Neuroscience 164:1776–1793. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.09.028
Guo J-D, Rainnie DG (2010) Presynaptic 5-HT1B receptor-mediated serotonergic inhibition of glutamate transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Neuroscience 165:1390–1401
Hammack SE, Guo J-D, Hazra R, Dabrowska J, Myers KM, Rainnie DG (2009) The response of neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis to serotonin: implications for anxiety. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1309–1320. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.05.013
Hayase T, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto K (2005) Persistent anxiogenic effects of a single or repeated doses of cocaine and methamphetamine: interactions with endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands. Behav Pharmacol 16:395–404
Hazra R, Guo JD, Dabrowska J, Rainnie DG (2012) Differential distribution of serotonin receptor subtypes in BNST (ALG) neurons: modulation by unpredictable shock stress. Neuroscience 225:9–21. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.014
Jalabert M, Aston-Jones G, Herzog E et al (2009) Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the control of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol Psychiatry 33:1336–1346. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.07.010
Jennings JH, Sparta DR, Stamatakis AM, Ung RL, Pleil KE, Kash TL, Stuber GD (2013) Distinct extended amygdala circuits for divergent motivational states. Nature 496:224–228. doi:10.1038/nature12041
Jhou TC, Good CH, Rowley CS, Xu S-P, Wang H, Burnham NW, Hoffman AF, Lupica CR, Ikemoto S (2013) Cocaine drives aversive conditioning via delayed activation of dopamine-responsive habenular and midbrain pathways. J Neurosci 33:7501–7512. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3634-12.2013
Knackstedt L, Samimi MM, Ettenberg A (2002) Evidence for opponent-process actions of intravenous cocaine and cocaethylene. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:931–936. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(02)00764-5
Koe BK, Nielsen JA, Macor JE, Heym J (1992) Biochemical and behavioral studies of the 5-HT{-1B} receptor agonist, CP-94, 253. Drug Dev Res 26:241–250
Koob G (1999) The role of the striatopallidal and extended amygdala systems in drug addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:445–460
Koob G (2003) Neuroadaptive mechanisms of addiction: studies on the extended amygdala. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13:442–452. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2003.08.005
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2008) Review. Neurobiological mechanisms for opponent motivational processes in addiction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 363:3113–3123. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0094
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2016) Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry 3:760–773. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(16)00104-8
Kreek MJ, Koob GF (1998) Drug dependence: stress and dysregulation of brain reward pathways. Drug Alcohol Depend 51:23–47
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Ikemoto S (1999) Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies. Behav Brain Res 101:129–152
Miszkiel J, Filip M, Przegaliński E (2011) Role of serotonin (5-HT) 1B receptors in psychostimulant addiction. Pharmacol Reports 63:1310–1315
Parsons L, Weiss F, Koob G (1998) Serotonin1B receptor stimulation enhances cocaine reinforcement. J Neurosci 18:10078–10089
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Raven MA, Necessary BD, Danluck DA, Ettenberg A (2000) Comparison of the reinforcing and anxiogenic effects of intravenous cocaine and cocaethylene. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:117–124. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.8.1.117
Resnick RB, Kestenbaum RS, Schwartz LK (1977) Acute systemic effects of cocaine in man: a controlled study by intranasal and intravenous routes. Science 195:696–698. doi:10.1126/science.841307
Riad M, Garcia S, Watkins KC et al (2000) Somatodendritic localization of 5-HT1A and preterminal axonal localization of 5-HT1B serotonin receptors in adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 417:181–194. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(20000207)417:2<181::AID-CNE4>3.0.CO;2-A
Rogerio R, Takahashi RN (1992) Anxiogenic properties of cocaine in the rat evaluated with the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:631–633
Sari Y, Lefèvre K, Bancila M, Quignon M, Miquel M-C, Langois X, Hamon M, Vergé D (1997) Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical visualization of 5-HT1B receptors in the rat brain. Brain Res 760:281–286. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(97)00400-9
Sarhan H, Fillion G (1999) Differential sensitivity of 5-HT 1B auto and heteroreceptors. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 360:382–390. doi:10.1007/s002109900067
Sartor GC, Aston-Jones G (2012) Regulation of ventral tegmental area by bed nucleus of the stria terminalis is required for expression of cocaine preference. Eur J Neurosci 100:130–134. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08277.x
Sena LM, Bueno C, Pobbe RLH et al (2003) The dorsal raphe nucleus exerts opposed control on generalized anxiety and panic-related defensive responses in rats. Behav Brain Res 142:125–133. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00399-6
Solomon RL, Corbit JD (1974) An opponent-process theory of motivation. I. Temporal dynamics of affect. Psychol Rev 81:119–145. doi:10.1037/h0036128
Sparta DR, Jennings JH, Ung RL, Stuber GD (2013) Optogenetic strategies to investigate neural circuitry engaged by stress. Behav Brain Res 255:19–25. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2013.05.007
Stamatakis AM, Sparta DR, Jennings JH, McElligott ZA, Decot H, Stuber GD (2014) Amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis circuitry: implications for addiction-related behaviors. Neuropharmacology 76:320–328. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.046
Stuber GD, Britt J, Bonci A (2012) Optogenetic modulation of neural circuits that underlie reward seeking. Biol Psychiatry 71:1061–1067. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.11.010.Optogenetic
Su Z-I, Wenzel J, Baird R, Ettenberg A (2011) Comparison of self-administration behavior and responsiveness to drug-paired cues in rats running an alley for intravenous heroin and cocaine. Psychopharmacology 214:769–778. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-2088-0
Su Z-I, Wenzel J, Ettenberg A, Ben-Shahar O (2013) Prior extended daily access to cocaine elevates the reward threshold in a conditioned place preference test. Addict Biol. doi:10.1111/adb.12053
Sullivan GM, Apergis J, Bush DEA, Johnson LR, Hou M, LeDoux JE (2004) Lesions in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis disrupt corticosterone and freezing responses elicited by a contextual but not by a specific cue-conditioned fear stimulus. Neuroscience 128:7–14. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.015
Stenfors C, Yu H, Ross SB (2000) Enhanced 5-HT metabolism and synthesis rate by the new selective r5-HT1B receptor antagonist, NAS-181 in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 39:553–560. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(99)00173-2
Tatarczyńska E, Kńodzińska A, Stachowicz K, Chojnacka-Wojcik E (2004) Effects of a selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist and antagonists in animal models of anxiety and depression. Behav Pharmacol 15(8):523–534
Tatarczyńska E, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Kłodzińska A et al (2005) Antidepressant-like effect of the selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist CP 94253: a possible mechanism of action. Eur J Pharmacol 516:46–50. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.04.025
Threlfell S, Greenfield SA, Cragg SJ (2010) 5-HT(1B) receptor regulation of serotonin (5-HT) release by endogenous 5-HT in the substantia nigra. Neuroscience 165:212–220. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.005
Veiga C, Miczek K (2007) Effect of 5-HT1B receptor agonists injected into the prefrontal cortex on maternal aggression in rats. Brazilian J 40:825–830
Walker DL, Toufexis DJ, Davis M (2003) Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis versus the amygdala in fear, stress, and anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 463:199–216. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(03)01282-2
Walsh SL, Cunningham KA (1997) Serotonergic mechanisms involved in the discriminative stimulus, reinforcing and subjective effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 130:41–58
Watson S, Man MS (2000) Serotonin, stress and corticoids. J Psychopharmacol 14:419–421. doi:10.1177/026988110001400415
Wenzel JM, Cotten SW, Dominguez HM, Lane JE, Shelton K, Su Z-I, Ettenberg A (2014) Noradrenergic β-receptor antagonism within the central nucleus of the amygdala or bed nucleus of the stria terminalis attenuates the negative/anxiogenic effects of cocaine. J Neurosci 34:3467–3474. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3861-13.2014
Wenzel JM, Waldroup SA, Haber ZM, Su Z-I, Ben-Shahar O, Ettenberg A (2011) Effects of lidocaine-induced inactivation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, the central or the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala on the opponent-process actions of self-administered cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 217:221–230. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2267-7
Williamson S, Gossop M, Powis B, Griffiths P, Fountain J, Strang J (1997) Adverse effects of stimulant drugs in a community sample of drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend 44:87–94. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(96)01324-5
Yang XM, Gorman AL, Dunn AJ, Goeders NE (1992) Anxiogenic effects of acute and chronic cocaine administration: neurochemical and behavioral studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:643–650
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Kerisa Shelton for her assistance throughout the project. This work was funded by NIDA grant DA03370 awarded to AE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, A.K., Brito, M.A., Akhavan, S. et al. Attenuation of the anxiogenic effects of cocaine by 5-HT1B autoreceptor stimulation in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of rats. Psychopharmacology 234, 485–495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4479-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4479-3