Abstract
Purpose
Drawing on prospective longitudinal data, this paper examines the intergenerational transmission of childhood conduct problems in a sample of 209 parents and their 331 biological offspring studied as part of the Christchurch Health and Developmental Study. The aims were to estimate the association between parental and offspring conduct problems and to examine the extent to which this association could be explained by (a) confounding social/family factors from the parent’s childhood and (b) intervening factors reflecting parental behaviours and family functioning.
Methods
The same item set was used to assess childhood conduct problems in parents and offspring. Two approaches to data analysis (generalised estimating equation regression methods and latent variable structural equation modelling) were used to examine possible explanations of the intergenerational continuity in behaviour.
Results
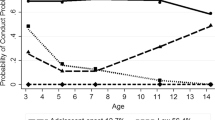
Regression analysis suggested that there was moderate intergenerational continuity (r = 0.23, p < 0.001) between parental and offspring conduct problems. This continuity was not explained by confounding factors but was partially mediated by parenting behaviours, particularly parental over-reactivity. Latent variable modelling designed to take account of non-observed common genetic and environmental factors underlying the continuities in problem behaviours across generations also suggested that parenting behaviour played a role in mediating the intergenerational transmission of conduct problems.
Conclusions
There is clear evidence of intergenerational continuity in conduct problems. In part this association reflects a causal chain process in which parental conduct problems are associated (directly or indirectly) with impaired parenting behaviours that in turn influence risks of conduct problems in offspring.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capaldi DM, Stoolmiller M (1999) Co-occurrence of conduct problems and depressive symptoms in early adolescent boys. III. Prediction to young-adult adjustment. Dev Psychopathol 11:59–84
Caspi A (2000) The child is the father of man: personality continuities from childhood to adulthood. J Pers Soc Psychol 78(1):158–172
Farrington DP (1995) The development of offending and antisocial behaviour from childhood: key findings from the Cambridge study in delinquent development. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 36:929–964
Putkonen A, Ryynanen OP, Eronen M, Tiihonen J (2007) Transmission of violent offending and crime across three generations. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 42(2):94–99. doi:10.1007/s00127-006-0139-y
Bailey JA, Hill KG, Oesterle S, Hawkins JD (2009) Parenting practices and problem behavior across three generations: monitoring, harsh discipline, and drug use in the intergenerational transmission of externalizing behavior. Dev Psychol 45(5):1214–1226. doi:10.1037/a0016129
Capaldi DM, Pears KC, Patterson GR, Owen LD (2003) Continuity of parenting practices across generations in an at-risk sample: a prospective comparison of direct and mediated associations. J Abnorm Child Psychol 31(2):127–140
Thornberry TP, Freeman-Gallant A, Lizotte AJ, Krohn MD, Smith CA (2003) Linked lives: the intergenerational transmission of antisocial behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 31(2):171–184
Van Meurs I, Reef J, Verhulst FC, Van Der Ende J (2009) Intergenerational transmission of child problem behaviors: a longitudinal, population-based study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48(2):138–145
Rhee SH, Waldman ID (2002) Genetic and environmental influences on antisocial behavior: a meta-analysis of twin and adoption studies. Psychol Bull 128(3):490–529
Moffitt TE (2005) The new look of behavioral genetics in developmental psychopathology: gene-environment interplay in antisocial behaviors. Psychol Bull 131(4):533–554. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.131.4.533
Beaver KM, DeLisi M, Vaughn MG, Wright JP (2010) The intersection of genes and neuropsychological deficits in the prediction of adolescent delinquency and low self-control. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol 54(1):22–42. doi:10.1177/0306624x08325349
Yeh MT, Coccaro EF, Jacobson KC (2010) Multivariate behavior genetic analyses of aggressive behavior subtypes. Behav Genet 40(5):603–617. doi:10.1007/s10519-010-9363-z
Tuvblad C, Narusyte J, Grann M, Sarnecki J, Lichtenstein P (2011) The genetic and environmental etiology of antisocial behavior from childhood to emerging adulthood. Behav Genet 41(5):629–640. doi:10.1007/s10519-011-9463-4
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Ridder E (2005) Show me the child at seven: the consequences of conduct problems in childhood for psychosocial functioning in adulthood. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 46(8):837–849
Giordano P, Millhollin TJ, Cernkovich SA, Rudolph JL (1999) Delinquency, identity and women’s involvement in relationship violence. Criminology 37(1):17–39
Capaldi DM, Clark S (1998) Prospective family predictors of aggression toward female partners for at-risk young men. Dev Psychol 34(6):1175–1188
Merikangas KR, Stolar M, Stevens DE, Goulet J, Preisig MA, Fenton B, Zhang H, O’Malley SS, Rounsaville BJ (1998) Familial transmission of substance use disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55(11):973–979
Ritter J, Stewart M, Bernet C, Coe M, Brown SA (2002) Effects of childhood exposure to familial alcoholism and family violence on adolescent substance use, conduct problems, and self-esteem. J Trauma Stress 15(2):113–122. doi:10.1023/a:1014803907234
Clark DB, Cornelius JR, Kirisci L, Tarter RE (2005) Childhood risk categories for adolescent substance involvement: a general liability typology. Drug Alcohol Depend 77(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.06.008
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (1998) Early conduct problems and later life opportunities. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 39(8):1097–1108
Black C, DeBlassie ER (1985) Adolescent pregnancy: contributing factors: consequence, treatment and plausible solutions. Adolescence 20:281–290
Zuckerman BS, Waller DK, Frank DA, Chase C, Hamburg B (1984) Adolescent pregnancy: biobehavioral determinants of outcome. J Pediatr 105(6):857–863
Henry B, Feehan M, McGee R, Stanton W, Moffitt TE, Silva P (1993) The importance of conduct problems and depressive symptoms in predicting adolescent substance use. J Abnorm Child Psychol 21(5):469–480
Baumrind D (1966) Effects of authoritative parental control on child behavior. Child Dev 37:887–907
Wakschlag LS, Gordon RA, Lahey BB, Loeber R, Green SM, Leventhal BL (2000) Maternal age at first birth and boys’ risk for conduct disorder. J Res Adolesc 10(4):417–441
Kemppinen K, Ebeling H, Raita-Hasu J, Toivonen-Falck A, Paavola L, Moilanen I, Kumpulainen K (2007) Early maternal sensitivity and child behaviour at toddler age: does low maternal sensitivity hinder identification of behavioural problems? J Reprod Infant Psychol 25(4):270–284. doi:10.1080/02646830701692044
Christ MA, Lahey BB, Frick PJ, Russo MF, McBurnett K, Loeber R, Stouthamer-Loeber M, Green S (1990) Serious conduct problems in the children of adolescent mothers: disentangling confounded correlations. J Consult Clin Psychol 58(6):840–844
Côté SM, Boivin M, Nagin DS, Japel C, Xu Q, Zoccolillo M, Junger M, Tremblay RE (2007) The role of maternal education and nonmaternal care services in the prevention of children’s physical aggression problems. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(11):1305–1312. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.64.11.1305
Najman JM, Williams GM, Nikles J, Spence S, Bor W, O’Callaghan M, Le Brocque R, Andersen MJ (2000) Mothers’ mental illness and child behavior problems: cause-effect association or observation bias? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(5):592–602. doi:10.1097/00004583-200005000-00013
Raudino A, Woodward LJ, Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (2012) Childhood conduct problems are associated with increased partnership and parenting difficulties in adulthood. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40(2):251–263. doi:10.1007/s10802-011-9565-8
Fergusson DM, Lynskey MT (1993) Maternal age and cognitive and behavioural outcomes in middle childhood. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 7(1):77–91
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (2001) The Christchurch Health and Development Study: review of findings on child and adolescent mental health. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 35(3):287–296
Rutter M, Tizard J, Whitmore K (1970) Education, health and behaviour. Longmans, London
Conners CK (1970) Symptom patterns in hyperkinetic, neurotic and normal children. Child Dev 41(3):667–682
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Lloyd M (1991) Confirmatory factor models of attention deficit and conduct disorder. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 32(2):257–274
Elley WB, Irving JC (1976) Revised socio-economic index for New Zealand. NZJ Educ Stud 11(1):25–36
Straus MA, Hamby SL, Boney-McCoy S, Sugarman DB (1996) The revised conflict tactics scales (CTS2). Development and preliminary psychometric data. J Fam Issues 17(3):283–316
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (1998) Exposure to interparental violence in childhood and psychosocial adjustment in young adulthood. Child Abuse Negl 22(5):339–357
Fergusson DM, Boden JM, Horwood LJ (2008) Exposure to childhood sexual and physical abuse and adjustment in early adulthood. Child Abuse Negl 32:607–619
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Boden JM (2008) The transmission of social inequality: examination of the linkages between family socioeconomic status in childhood and educational achievement in young adulthood. Res Soc Stratif Mobil 26:277–295
Friesen MD, Woodward LJ, Horwood LJ, Fergusson DM (2010) Childhood exposure to sexual abuse and partnership outcomes at age 30. Psychol Med 40(4):679–688
World Health Organization (1993) Composite international diagnostic interview (CIDI). World Health Organization, Geneva
Zeger SL, Liang KY, Albert PS (1988) Models for longitudinal data: a generalized estimating equation approach. Biometrics 44:1049–1060
Sobel ME (1986) Some new results on indirect effects and their standard errors in covariance structure models. In: Tuma N (ed) Sociological Methodology 1986. American Sociological Association, Washington, pp 159–186
StataCorp (2007) Stata statistical software: release 10.0. Stata Corporation, Texas
Muthen LK, Muthen BO (2007) Mplus user’s guide, 5th edn. Muthen and Muthen, Los Angeles
Schermelleh-Engel K, Moosbrugger H, Müller H (2003) Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Psychol Res 8(2):23–74
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51(6):1173–1182
Patterson GR, DeBaryshe BD, Ramsey E (1989) A developmental perspective on antisocial behavior. Am Psychol 44(2):329–335
Brestan EV, Eyberg SM (1998) Effective psychosocial treatments of conduct-disordered children and adolescents: 29 years, 82 studies, and 5,272 kids. J Clin Child Psychol 27(2):180–189
Sanders MR (1999) Triple P-positive parenting program: towards an empirically validated multilevel parenting and family support strategy for the prevention of behavior and emotional problems in children. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 2(2):71–90
Scott S (2008) An update on interventions for conduct disorder. Adv Psychiatr Treat 14(1):61–70. doi:10.1192/apt.bp.106.002626
Dishion TJ, Patterson GR (1996) Preventive parenting with love, encouragement and limits. Castalia, Eugene
Acknowledgments
This research has been funded by grants from the Health Research Council of New Zealand, the National Child Health Research Foundation, the Canterbury Medical Research Foundation and the New Zealand Lottery Grants Board.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raudino, A., Fergusson, D.M., Woodward, L.J. et al. The intergenerational transmission of conduct problems. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 48, 465–476 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-012-0547-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-012-0547-0