Abstract
Key message
The Raso2 , novel QTL for Korea biotype foxglove aphid resistance in soybean from PI 366121 was identified on chromosome 7 using GoldenGate SNP microarray.
Abstract
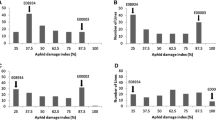
Foxglove aphid, Aulacorthum solani (Kaltenbach), is a hemipteran insect that infects a wide variety of plants worldwide and causes serious yield losses in crops. The objective of this study was to identify the putative QTL for foxglove aphid resistance in wild soybean, PI 366121, (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.). One hundred and forty-one F4-derived F8 recombinant inbred lines developed from a cross of susceptible Williams 82 and PI 366121 were used. The phenotyping of antibiosis and antixenosis resistance was done through choice and no-choice tests with total plant damage and primary infestation leaf damage; a genome-wide molecular linkage map was constructed with 504 single-nucleotide polymorphism markers utilizing a GoldenGate assay. Using inclusive composite interval mapping analysis for foxglove aphid resistance, one major candidate QTL on chromosome 7 and three minor QTL regions on chromosomes 3, 6 and 18 were identified. The major QTL on chromosome 7 showed both antixenosis and antibiosis resistance responses. However, the minor QTLs showed only antixenosis resistance response. The major QTL mapped to a different chromosome than the previously identified foxglove aphid resistance QTL, Raso1, from the cultivar Adams. Also, the responses to the Korea biotype foxglove aphid were different for Raso1, and the gene from PI 366121 against the Korea biotype foxglove aphid was different. Thus, the foxglove aphid resistance gene from PI 366121 was determined to be an independent gene from Raso1 and was designated as Raso2. This result could be useful in breeding for new foxglove aphid-resistant soybean cultivars.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- TPD:
-
Total plant damage
- PLD:
-
Primary infestation leaf damage
- RILs:
-
Recombinant inbred lines
- DAI:
-
Days after infestation
References
Bansal R, Jun T-H, Mian MAR, Michel AP (2013) Developing host-plant resistance for hemipteran soybean pests: lessons from soybean aphid and stink bugs. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Bernard RL, Cremeens CR (1988) REGISTRATION OF WILLIAMS 82 SOYBEAN. Crop Sci 28:1027–1028
Bradshaw HD Jr, Otto KG, Frewen BE, McKay JK, Schemske DW (1998) Quantitative trait loci affecting differences in floral morphology between two species of monkeyflower (Mimulus). Genetics 149:367–382
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2010) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D843–D846
Hullé M, Cœur d’Acier A, Bankhead-Dronnet S, Harrington R (2010) Aphids in the face of global changes. CR Biol 333:497–503
Hyten DL, Choi I-Y, Song Q, Specht JE, Carter TE, Shoemaker RC, Hwang E-Y, Matukumalli LK, Cregan PB (2010) A High density integrated genetic linkage map of soybean and the development of a 1536 Universal Soy Linkage panel for quantitative trait locus mapping. Crop Sci 50:960–968
Jandricic SE, Wraight SP, Bennett KC, Sanderson JP (2010) Developmental Times and Life Table Statistics of Aulacorthum solani (Hemiptera: Aphididae) at Six Constant Temperatures, With Recommendations on the Application of Temperature-Dependent Development Models. Environ Entomol 39:1631–1642
Jandricic SE, Mattson NS, Wraight SP, Sanderson JP (2014) Within-plant distribution of Aulacorthum solani (Hemiptera: Aphididae), on various greenhouse plants with implications for control. J Econ Entomol 107:697–707
Jun TH, Rouf Mian MA, Michel AP (2012) Genetic mapping revealed two loci for soybean aphid resistance in PI 567301B. Theor Appl Genet 124:13–22
Kang YJ, Kim KH, Shim S, Yoon MY, Sun S, Kim MY, Van K, Lee SH (2012) Genome-wide mapping of NBS-LRR genes and their association with disease resistance in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12:139
Kim K-S, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Mian MAR, Diers BW (2008) Discovery of soybean aphid biotypes. Crop Sci 48:923–928
Kim K-S, Bellendir S, Hudson K, Hill C, Hartman G, Hyten D, Hudson M, Diers B (2010a) Fine mapping the soybean aphid resistance gene Rag1 in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 120:1063–1071
Kim KS, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Hyten DL, Hudson ME, Diers BW (2010b) Fine mapping of the soybean aphid-resistance gene Rag2 in soybean PI 200538. Theor Appl Genet 121:599–610
Kogan M, Ortman EF (1978) Antixenosis–a new term proposed to define painter’s “Nonpreference” Modality of Resistance. Bull Entomol Soc Am 24(2):175–176
Lenis JM (2011) Genetics of soybean seed lipoxygenases and linolenic acid content in seeds of the soybean wild ancestor. University of Missouri-Columbia, Agronomy
Li Y, Hill C, Carlson S, Diers B, Hartman G (2007) Soybean aphid resistance genes in the soybean cultivars Dowling and Jackson map to linkage group M. Mol Breeding 19:25–34
Li H, Ribaut JM, Li Z, Wang J (2008) Inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) for digenic epistasis of quantitative traits in biparental populations. Theor Appl Genet 116:243–260
Masuda T, Goldsmith PD (2009) World soybean production: area harvested, yield, and long-term projections. Int Food Agribus Manag Rev 12:143–162
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Nelson RL, Wang D (2005) Resistance to soybean aphid in early maturing soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:2228–2233
Mian MAR, Kang ST, Beil SE, Hammond RB (2008) Genetic linkage mapping of the soybean aphid resistance gene in PI 243540. Theor Appl Genet 117:955–962
Nagano T, Umetsu Y, Hoshi N, Kidokoro T (2001) Outbreak of the foxglove aphid, Aulacorthum solani (Kaltenbach), in Soybean Fields of Miyagi Prefecture. Annu Rep Soc Plant Prot N Jpn 52:175–177
Oerke E-C (2006) Crop losses to pests. J Agricult Sci 144:31–43
Ohnishi S, Miyake N, Takeuchi T, Kousaka F, Hiura S, Kanehira O, Saito M, Sayama T, Higashi A, Ishimoto M, Tanaka Y, Fujita S (2012) Fine mapping of foxglove aphid (Aulacorthum solani) resistance gene Raso1 in soybean and its effect on tolerance to Soybean dwarf virus transmitted by foxglove aphid. Breed Sci 61:618–624
Painter RH (1951) Insect resistance in crop plants. Macmillan. 72(6):481
Pan Q, Wendel J, Fluhr R (2000) Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J Mol Evol 50:203–213
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Sato D, Akashi H, Sugimoto M, Tomita M, Soga T (2013) Metabolomic profiling of the response of susceptible and resistant soybean strains to foxglove aphid, Aulacorthum solani Kaltenbach. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 925:95–103
Sato D, Sugimoto M, Akashi H, Tomita M, Soga T (2014) Comparative metabolite profiling of foxglove aphids (Aulacorthum solani Kaltenbach) on leaves of resistant and susceptible soybean strains. Mol BioSyst 10:909–915
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang XC, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Song F, Swinton SM, DiFonzo C, O’Neal M, Ragsdale DW (2006) Profitability Analysis Of Soybean Aphid Control Treatments In Three North-Central States. Michigan State University, Department of Agricultural, Food, and Resource Economics
Tilmon KJ, Hodgson EW, O’Neal ME, Ragsdale DW (2011) Biology of the Soybean Aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the United States. J Integr Pest Manag 2:A1–A7
Wang X, Fang Y, Lin S, Zhang L, Wang H (1994) A study on the damage and economic threshold of the soybean aphid at the seedling stage. Plant Prot 20:12–13
Weiss MG (1953) Registration of Soybean Varieties.3. Agron J 45:326–330
Xiao L, Hu Y, Wang B, Wu T (2013) Genetic mapping of a novel gene for soybean aphid resistance in soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) line P203 from China. Theor Appl Genet 126:2279–2287
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2009) Molecular mapping of soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567541B. Theor Appl Genet 118:473–482
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2010) A novel locus for soybean aphid resistance. Theor Appl Genet 120:1183–1191
Zheng C, Chen P, Hymowitz T, Wickizer S, Gergerich R (2005) Evaluation of Glycine species for resistance to Bean pod mottle virus. Crop Protection 24:49–56
Acknowledgment
This work was carried out with the support of ‘Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ009771)’ Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. A. Lightfoot.
J. S. Lee and M. Yoo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.S., Yoo, Mh., Jung, J.K. et al. Detection of novel QTLs for foxglove aphid resistance in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 128, 1481–1488 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2519-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2519-8