Summary
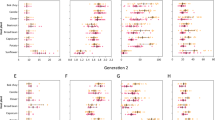
Resistance of Pteridium aquilinum to insect attack was studied by incorporating air dried bracken leaf meal and extracts of bracken leaf meal into an artificial diet for Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). When larvae are reared on diets containing 6% bracken leaf meal, they do not mature past the second instar and after 16 days the average weight is approximately 1 mg compared to 70 mg for control larvae. Feeding initiation studies indicate that a feeding deterrent is present in bracken fern but feeding rates and food utilization efficiency studies suggest that either the deterrent or another compound also functions as a toxin. This toxin does not affect growth, feeding rates, or utilization efficiency for the first 4 days after third instar larvae are transferred to a diet containing the water extract of bracken leaf meal; thereafter growth is terminated and feeding is greatly reduced. The active factor is water soluble, heat labile, and non-volatile and this partial characterization indicates that neither the bracken ecdysones or the anti-thiamine factor of bracken is involved in the resistance of this fern to insect attack by T. ni.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlisle, D., Ellis, P.: The effects of Pteridium aquilinum on the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria. Science 159, 1472–1473 (1968)
Fenton, F.: The spread of bracken (Pteris aquilina L.) in Scotland and its ecological significance. Agric. Prog. 13, 66–72 (1936)
Freeland, W., Janzen, D.: Strategies in herbivory by mammals. The role of 2° compounds. Amer. Nat. 108, 269–289 (1974)
Galbraith, M., Horn, D.: An insect molting hormone from a plant. Chem. Commun. 24, 905–906 (1966)
Henneberry, T., Kishaba, A.: Cabbage loopers. In: Insect colonization and mass production, pp. 461–478 (C.N. Smith, ed.). New York: Academic Press 1966
Horn, D. The ecdysones. In: Naturally occurring insecticides, pp. 333–459 (M. Jacobson, D. Crosby, eds.). New York: Dekker 1971
Inoue, H.: Checklist of the Lepidoptera of Japan. V. Tokyo:Rikusuisha 1958
Jermy, T.: Feeding inhibitors and food preferences in chewing phytophagous insects. Entomol. Exp. and Appl., 9, 1–12 (1966)
Kaplanis, J., Thompson, M., Robbins, W., Bryce, B.: Insect hormones: Alpha-ecdysone and 20-hydroxyecdysone in bracken fern. Science 157, 1436–1438 (1967)
Karlson, P., Bode, P.: Die Inaktivierung des Ecdysons bei der Schmeissfliege Calliphora erythrocephala Meigen. J. Insect Physiol. 15, 111–118 (1969)
Kingsbury, J.: Poisonous plants of the United States and Canada, 626 pp Englewood: Prentice-Hall 1964
Lawton, J.: The structure of the arthropod community of bracken (Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn. In: The ecology of bracken (F. Perring, ed.). London: Academic Press (in press)
Mathavan, S., Pandian, T.: Use of fecal weight as an indicator of food consumption in some lepidopterans. Oecologia (Berl.). 15, 177–185 (1974)
Mathur, L.: On the food utilization and digestion of major nutrients in lepidopterous larvae feeding on cauliflower. Zool. Anz. 178, 82–89 (1967)
McKinney, K.: The cabbage loope as a pest of lettuce in the Southwest, 30 pp. USDA, Tech. Bull. 846 (1944)
Moon, F., Pal, A.: The composition and nutritive value of bracken. J. Ag. Sci. 39, 296–301 (1949)
Muenscher, W.: Poisonous plants of the United States, 206 pp New York: Macmillian 1939
Rees, H.: Ecdysones. In: Aspects of terpenoid chemistry and biochemistry, pp. 181–222 (T. Goodwin, ed.). London: Academic Press 1971
Robbins, W., Kaplanis, J., Thompson, M., Shortino, T., Cohen, C., Joyner, S.: Ecdysones and analogues: effects on development and reproduction of insects. Science 161, 1158–1160 (1968)
Shigematsu, H., Moriyama, H., Arai, N.: Growth and silk formation of silkworm larvae influenced by phytoecdysones. J. Insect Physiol. 20, 867–875 (1974)
Shorey, H.: A simple artificial diet for the cabbage looper. J. Econ. Entomol. 56, 536–537 (1963)
Somoygi, J.: Inactivation of anerin by extracts of animal and plant tissues. Int. Z. Vitaminforsch. 21, 341–346 (1949)
Somoygi, J.: On antithiamine factors of ferns. J. Vitaminol. (Kyoto). 17, 165–174 (1971)
Soo Hoo, C., Fraenkel, G.: The resistance of ferns to the feeding of Prodenia eridana larvae. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer. 57, 788–792 (1964)
Swain, T., Cooper-Driver, G.: Biochemical systematics in the filcopsida, pp. 111–134 (A. Mermy, T. Crabbe, B. Thomas, eds.). In: The phylogeny and classification of ferns. London: Academic Press 1973
Takemoto, T., Arihara, S., Hikino, H.: Structure of ponasteroside A, a novel glycoside of insect molting substance from Pteridium aquilinum var. latiusculum. Tetrahedron Letters 39, 4199–4202 (1968)
Tanada, Y., Chang, G.: Resistance of the alfalfa caterpillar, polyhedrosis virus and thermal inactivation point of the virus. J. Invert. Path. 10, 79–83 (1968)
Tanada, Y., Hukuhara, T., Chang, G.: A strain of nuclear polyhedrosis virus causing extensive cellular hypertrophy. J. Invert. Path. 13, 394–409 (1969)
Tryon, R.: A revision of the genus Pteridium. Rhodora 43, 1–31, 37–67 (1941)
Weiczorek, H.: Zur Kenntnis der Alderfarninsekten: Ein Beitrag zum Problem der biologischen Bekaempfung von Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn in Mitteleuropa. A. Ang. Entomol. 72, 337–358 (1973)
Wesig, P., Freed, A., Haag, J.: Antithiamine activities of plant materials. J. biol. Chem. 165, 737–738 (1946)
Wigglesworth, V.B.: The principles of insect physiology, 741 pp. London: Metheum 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hendrix, S.D. The resistance of Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn to insect attack by Trichoplusia ni (Hübn.). Oecologia 26, 347–361 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345534
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345534