Abstract
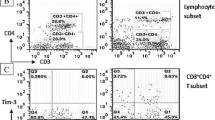
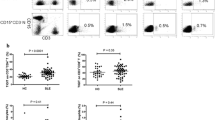
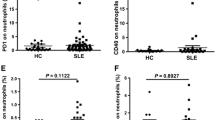
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototypic systemic autoimmune disease. The T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain (TIM) family is associated with autoimmune diseases, but its level of expression in the immune cells of patients with SLE is still uncertain. The aim of this study was to examine whether TIM-3 and Galectin-9 (Gal-9) contribute to the pathogenesis of SLE. In total, 30 patients with SLE and 30 healthy controls were recruited, and their levels of TIM-3 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were examined via flow cytometry. Meanwhile, the levels of Gal-9 expression in serum and in PBMCs were measured via an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit and immunofluorescence staining, respectively. The relation between the level of TIM-3 or Gal-9 expression and the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) was also studied. Finally, the function of the TIM-3 and Gal-9 pathway in the pathogenesis of SLE was explored. Our results showed that the levels of expression of TIM-3 and Gal-9 on CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, CD56+ T cells and in serum in patients with SLE were significantly higher than those of healthy controls. We found that the level of Gal-9 expression was significantly higher in both serum and PMBCs of patients with SLE than in healthy controls. The up-regulation of TIM-3 and Gal-9 expression in patients with SLE was closely related to the SLEDAI scores. In addition, Gal-9 blocking antibody significantly inhibited CD3-stimulated PBMC proliferation and Th1-derived cytokines (IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α), Th2-derived cytokines (IL-4, IL-10), a Th17-derived cytokine (IL-17A), and release of a pro-inflammatory factor (IL-6) in patients with SLE. The results suggest that increased expression of TIM-3 and Gal-9 may be a biomarker for SLE diagnosis and that the TIM-3 pathway may be a target for SLE treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alunno A, Bartoloni E, Bistoni O, Nocentini G, Ronchetti S, Caterbi S, Valentini V, Riccardi C, Gerli R (2012) Balance between regulatory T and Th17 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: the old and the new. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:823085
Anderson AC (2012) Tim-3, a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):213–216
Arikawa T, Saita N, Oomizu S, Ueno M, Matsukawa A, Katoh S, Kojima K, Nagahara K, Miyake M, Yamauchi A, Kohrogi H, Hirashima M (2010) Galectin-9 expands immunosuppressive macrophages to ameliorate T-cell-mediated lung inflammation. Eur J Immunol 40(2):548–558
Bazso A, Szappanos A, Patocs A, Poor G, Shoenfeld Y, Kiss E (2015) The importance of glucocorticoid receptors in systemic lupus erythaematosus. A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 14(4):349–351
Cai XZ, Huang WY, Qiao Y, Chen Y, Du SY, Chen D, Yu S, Liu N, Dou LY, Jiang Y (2015) Downregulation of TIM-3 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Braz J Med Biol Res 48(1):77–82
Chae SC, Park YR, Shim SC, Yoon KS, Chung HT (2004) The polymorphisms of Th1 cell surface gene Tim-3 are associated in a Korean population with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Lett 95(1):91–95
de Kivit S, Lempsink LJ, Plants J, Martinson J, Keshavarzian A, Landay AL (2015) Modulation of TIM-3 expression on NK and T cell subsets in HIV immunological non-responders. Clin Immunol 156(1):28–35
Du WT, Zhao HF, Xu JH, Gu DS, Xue F, Ge J, Dong XW, Chen ZP, Zhou ZP, Yang RC (2009) The role of T-cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 polymorphisms in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hum Immunol 70(6):398–402
Ferris RL, Lu B, Kane LP (2014) Too much of a good thing? Tim-3 and TCR signaling in T cell exhaustion. J Immunol 193(4):1525–1530
Fujita T, Burwitz BJ, Chew GM, Reed JS, Pathak R, Seger E, Clayton KL, Rini JM, Ostrowski MA, Ishii N, Kuroda MJ, Hansen SG, Sacha JB, Ndhlovu LC (2014) Expansion of dysfunctional Tim-3-expressing effector memory CD8+ T cells during simian immunodeficiency virus infection in rhesus macaques. J Immunol 193(11):5576–5583
Gleason MK, Lenvik TR, McCullar V, Felices M, O’Brien MS, Cooley SA, Verneris MR, Cichocki F, Holman CJ, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Niki T, Hirashima M, Blazar BR, Miller JS (2012) Tim-3 is an inducible human natural killer cell receptor that enhances interferon gamma production in response to galectin-9. Blood 119(13):3064–3072
Guo L, Yang X, Xia Q, Zhen J, Zhuang X, Peng T (2014) Expression of human T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin-3 (TIM-3) on kidney tissue from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Clin Exp Med 14(4):383–388
Hanly JG (2014) Diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10(6):338–347
Ju Y, Hou N, Meng J, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhao D, Liu Y, Zhu F, Zhang L, Sun W, Liang X, Gao L, Ma C (2010) T cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3) mediates natural killer cell suppression in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 52(3):322–329
Khaitan A, Unutmaz D (2011) Revisiting immune exhaustion during HIV infection. Curr HIV 8(1):4–11
Koguchi K, Anderson DE, Yang L, O’Connor KC, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA (2006) Dysregulated T cell expression of TIM3 in multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 203(6):1413–1418
Konya C, Paz Z, Tsokos GC (2014) The role of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol 26(5):493–501
Li S, Peng D, He Y, Zhang H, Sun H, Shan S, Song Y, Zhang S, Xiao H, Song H, Zhang M (2014) Expression of TIM-3 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis. APMIS 122(10):899–904
Li WX, Chen GM, Yuan H, Yao YS, Li RJ, Pan HF, Li XP, Xu JH, Tao JH, Ye DQ (2011) Polymorphisms of the TIM-1 and TIM-3 genes are not associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese population. Mutagenesis 26(4):507–511
Li Y, Feng J, Geng S, Geng S, Wei H, Chen G, Li X, Wang L, Wang R, Peng H, Han G, Shen B, Li Y (2011) The N- and C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domains of galectin-9 contribute differently to its multiple functions in innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Mol Immunol 48(4):670–677
Li Z, Ju Z, Frieri M (2013) The T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain (Tim) gene family in asthma, allergy, and autoimmunity. Allergy Asthma Proc 34(1):e21–e26
Mak A, Kow NY (2014) The pathology of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res 2014:419029
Martin JC, Baeten DL, Josien R (2014) Emerging role of IL-17 and Th17 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol 154(1):1–12
Maurya N, Gujar R, Gupta M, Yadav V, Verma S, Sen P (2014) Immunoregulation of dendritic cells by the receptor T cell Ig and mucin protein-3 via Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and c-Src. J Immunol 193(7):3417–3425
Mikolajczyk TP, Skiba D, Batko B, Krezelok M, Wilk G, Osmenda G, Pryjma JR, Guzik TJ (2014) Characterization of the impairment of the uptake of apoptotic polymorphonuclear cells by monocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 23(13):1358–1369
Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, Ryu A, Waldner H, Chernova T, Manning S, Greenfield EA, Coyle AJ, Sobel RA, Freeman GJ, Kuchroo VK (2002) Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 415(6871):536–541
Pan HF, Zhang N, Li WX, Tao JH, Ye DQ (2010) TIM-3 as a new therapeutic target in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 37(1):395–398
Pieterse E, van der Vlag J (2014) Breaking immunological tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 5:164
Sakuishi K, Jayaraman P, Behar SM, Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK (2011) Emerging Tim-3 functions in antimicrobial and tumor immunity. Trends Immunol 32(8):345–349
Seki M, Oomizu S, Sakata KM, Sakata A, Arikawa T, Watanabe K, Ito K, Takeshita K, Niki T, Saita N, Nishi N, Yamauchi A, Katoh S, Matsukawa A, Kuchroo V, Hirashima M (2008) Galectin-9 suppresses the generation of Th17, promotes the induction of regulatory T cells, and regulates experimental autoimmune arthritis. Clin Immunol 127(1):78–88
Seki M, Sakata KM, Oomizu S, Arikawa T, Sakata A, Ueno M, Nobumoto A, Niki T, Saita N, Ito K, Dai SY, Katoh S, Nishi N, Tsukano M, Ishikawa K, Yamauchi A, Kuchroo V, Hirashima M (2007) Beneficial effect of galectin 9 on rheumatoid arthritis by induction of apoptosis of synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 56(12):3968–3976
Shin MS, Lee N, Kang I (2011) Effector T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update focusing on Th17 cells. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23(5):444–448
Song YW, Im CH, Park JH, Lee YJ, Lee EY, Lee EB, Park K (2011) T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 genetic polymorphisms are associated with rheumatoid arthritis independent of a shared epitope status. Hum Immunol 72(8):652–655
Wang Y, Meng J, Wang X, Liu S, Shu Q, Gao L, Ju Y, Zhang L, Sun W, Ma C (2008) Expression of human TIM-1 and TIM-3 on lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Scand J Immunol 67(1):63–70
Xu J, Yang Y, Liu X, Wang Y (2012) Genetic variation and significant association of polymorphism rs7700944 G > A of TIM-4 gene with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Chinese Han and Hui populations. Int J Immunogenet 39(5):409–413
Zhang Q, Luan H, Wang L, He F, Zhou H, Xu X, Li X, Xu Q, Niki T, Hirashima M, Xu G, Lv Y, Yuan J (2014) Galectin-9 ameliorates anti-GBM glomerulonephritis by inhibiting Th1 and Th17 immune responses in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306(8):F822–F832
Zhang ZY, Schluesener HJ, Zhang Z (2011) Distinct expression of Tim-3 during different stages of rat experimental autoimmune neuritis. Brain Res Bull 86(3–4):229–234
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31170834 and 81402597) and the Science and Technology Project of Suzhou (Grant No. SYS201331). The authors express their appreciation to the enrolled patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Q. Jiao and Q. Qian contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, Q., Qian, Q., Zhao, Z. et al. Expression of human T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin-3 (TIM-3) and TIM-3 ligands in peripheral blood from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res 308, 553–561 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1665-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1665-4