Abstract
Purpose
Assess the effect of fat deposition on the MRI diffusion coefficients in lipid emulsion-based phantoms and patients with proven isolated liver steatosis.
Materials and methods
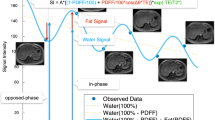
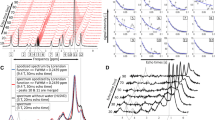
Diffusion-weighted MRI with 11 b values from 0–500 s/mm2 was performed in phantoms (fat fractions 0–18 %) with and without fat suppression and in 19 patients with normal liver (n = 14) or isolated liver steatosis (n = 5) proven by histopathology. The apparent, pure and perfusion-related diffusion coefficients and the perfusion fraction were measured. Spearman correlation coefficient and Mann–Whitney U test were used for comparisons.
Results
A strong correlation between the apparent and pure diffusion coefficients and fat fractions was seen in phantoms. The pure diffusion coefficient decreased significantly in patients with liver steatosis (0.96 ± 0.16 × 10-3 mm2/s versus 1.18 ± 0.09 × 10-3 mm2/s in normal liver, P = 0.005), whereas the decrease in apparent diffusion coefficient did not reach statistical significance (1.26 ± 0.25 × 10-3 mm2/s versus 1.41 ± 0.14 × 10-3 mm2/s in normal liver, P = 0.298).
Conclusions
Fat deposition decreases the apparent and pure diffusion coefficients in lipid emulsion-based phantoms and patients with isolated liver steatosis proven by histopathology.
Key Points
• Magnetic resonance imaging is increasingly used to quantify hepatic fibrosis.
• Lipid phantoms show inverse correlations between diffusion coefficients and fat fractions.
• The pure diffusion coefficient decreases in patients with isolated liver steatosis.
• Steatosis may be a confounding factor when measuring the liver diffusion parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roulot D, Costes JL, Buyck JF et al (2011) Transient elastography as a screening tool for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in a community-based population aged over 45 years. Gut 60:977–984
Szczepaniak LS, Nurenberg P, Leonard D et al (2005) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E462–E468
Stefan N, Kantartzis K, Haring HU (2008) Causes and metabolic consequences of fatty liver. Endocr Rev 29:939–960
Wang Y, Ganger DR, Levitsky J, Sternick LA, McCarthy RJ, Chen ZE et al (2011) Assessment of chronic hepatitis and fibrosis: comparison of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Am J Roentgenol 196:553–561
Bonekamp S, Torbenson MS, Kamel IR (2011) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:885–892
Taouli B, Chouli M, Martin AJ, Qayyum A, Coakley FV, Vilgrain V (2008) Chronic hepatitis: role of diffusion-weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and inflammation. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:89–95
Lewin M, Poujol-Robert A, Boelle P-Y et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 46:658–665
Annet L, Peeters F, Abarca-Quinones J, Leclercq I, Moulin P, Van Beers BE (2007) Assessment of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in liver fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:122–128
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M et al (2008) Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging-pilot study. Radiology 249:891–899
Pais R, Pascale A, Fedchuck L, Charlotte F, Poynard T, Ratziu V (2011) Progression from isolated steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 35:23–28
Sirlin CB (2009) Non invasive imaging biomarkers for steatosis assessment. Liver Transpl 15:1389–1391
d’Assignies G, Ruel M, Khiat A et al (2009) Noninvasive quantitation of human liver steatosis using magnetic resonance and bioassay methods. Eur Radiol 19:2033–2040
Lee JT, Liau J, Murphy P, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Bydder M (2012) Cross-sectional investigation of correlation between hepatic steatosis and IVIM perfusion on MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 30:572–578
Anderson SW, Soto JA, Milch HN et al (2011) Effect of diffusion progression on liver apparent diffusion coefficient values in a murine model of NASH at 11.7 Tesla MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:882–888
Poyraz AK, Onur MR, Kocakoç E, Ogur E (2012) Diffusion-weighted MRI of fatty liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:1108–1111
Gimsberg HN, Goldberg IJ (2001) Disorders of the lipoprotein metabolism. In: Braunvald E, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL (eds) Disorders of the intermediary metabolism. (Harrison’s principals of internal medicine), 15th edn. Mc Graw-Hill, USA, p 2246
Crawford JM (2007) Basic mechanisms in hepatopathology. In: Burt AD, Portmann BC, Ferrell LD (eds) MacSween’s pathology of the liver, 5th edn. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Philadelphia, Philadelphia, p 85
Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG (2010) Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 16:5286–5296
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin M-L, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Kim SY, Lee SS, Byun JH et al (2010) Malignant hepatic tumors: short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients with breath-hold and respiratory-triggered diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 255:815–823
Ababneh ZQ, Beloeil H, Berde CB, Ababneh AM, Maier SE, Mulkern RV (2009) In vivo lipid diffusion coefficient measurements in rat bone marrow. Magn Reson Imaging 27:859–864
Qiao Y, Ronen I, Viereck J, Ruberg FL, Hamilton JA (2007) Identification of atherosclerotic lipid deposits by diffusion-weighted imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1440–1446
Reeder SB, Cruite I, Hamilton G, Sirlin CB (2011) Quantitative assessment of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging 34:729–749
Wenkel E, Geppert C, Schulz-Wendtland R et al (2007) Diffusion weighted imaging in breast MRI: comparison of two different pulse sequences. Acad Radiol 14:1077–1083
Baron P, Dorrius MD, Kappert P, Oudkerk M, Sijens PE (2010) Diffusion-weighted imaging of normal fibroglandular breast tissue: influence of microperfusion and fat suppression technique on the apparent diffusion coefficient. NMR Biomed 23:399–405
O’Reagan DP, Callaghan MF, Wylezinska-Arridge M, Fitzpatrick J, Naoumova RP, Hajnal JV et al (2008) Liver fat content and T2*: simultaneous measurements by using breath-hold multiecho MR imaging at 3.0 T—feasibility. Radiology 247:550–557
Hussain HK, Chenevert TL, Londy FJ, Gulani V, Swanson SD, McKenna BJ et al (2005) Hepatic fat fraction: MR imaging for quantitative measurement and display—early experience. Radiology 237:1048–1055
Marsman H, Matsushita T, Dierkhising R, Kremers W, Rosen C, Burgart L (2004) Assessment of donor liver steatosis: pathologist or automated software. Hum Pathol 35:430–435
Farrell GC, Teoh NC, McCuskey RS (2008) Hepatic microcirculation in fatty liver disease. Anat Rec 291:684–692
King MD, van Bruggen N, Busza AL, Houseman J, Williams SR, Gadian DG (1992) Perfusion and diffusion MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 24:288–301
McCuskey RS, Ito Y, Robertson GR, McCuskey MK, Perry M, Farrell GC (2004) Hepatic microvascular dysfunction during evolution of dietary steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 40:386–393
Yokoo T, Bydder M, Hamilton G et al (2009) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: diagnostic and fat-grading accuracy of low-flip-angle multiecho gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology 251:67–76
Annet L, Materne R, Danse E, Jamart J, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE (2003) Hepatic flow parameters measured with MR imaging and Doppler US: correlations with degree of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Radiology 229:409–414
Paradis V, Bedossa P (2008) Definition and natural history of metabolic steatosis: histology and cellular aspects. Diabetes Metab 34:638–642
Padhani AR, Liu G, Mu-Koh D et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M, Babb JS, Taouli B (2010) Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone and in combination: preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:589–600
Acknowledgements
Helena S Leitão received a grant (SFRH/BD/33893/2009) from the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT, Portugal).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leitão, H.S., Doblas, S., d’Assignies, G. et al. Fat deposition decreases diffusion parameters at MRI: a study in phantoms and patients with liver steatosis. Eur Radiol 23, 461–467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2626-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2626-8