Abstract
Background
The ultimate goal in the management of paediatric ileocolic intussusception is to achieve non-operative reduction and therefore patient cure. The standard non-surgical treatment consists of enema (air or liquid media).
Objective
The purpose of this study is to present external manual reduction for paediatric ileocolic intussusception. We present a new manoeuvre that is standardised, simple, safe and effective for the radiologist in the non-surgical management of this pathology.
Materials and methods
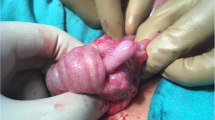
External manual reduction is performed under sedation. Execution of the manoeuvre is detailed and illustrated. The procedure was carried out 15 times in 13 paediatric patients with idiopathic ileocolic intussusception.
Results
Complete reduction exclusively by external manual reduction was accomplished on 12 occasions (80%). In the remaining three procedures, partial reduction to the cecum was obtained. Subsequent enema achieved complete reduction in two. Overall non-surgical reduction rate was 93%.
Conclusion
External manual reduction is a radiation-free, safe and effective procedure. In case of incomplete reduction, it facilitates enema performance. External manual reduction incorporates and additional initial step in the non-surgical reduction of intussusception and should be considered a first-line procedure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applegate KE (2009) Intussusception in children: evidence-based diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Radiol 39(Suppl 2):S140–S143
Applegate KE (2008) Intussusception in children: imaging choices. Semin Roentgenol 43:15–21
Huppertz HI, Soriano-Gabarro M, Grimprel E et al (2006) Intussusception among young children in Europe. Pediatr Infect Dis J 25:S22–S29
DiFiore JW (1999) Intussusception. Semin Pediatr Surg 8:214–220
Daneman A, Navarro O (2003) Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol 33:79–85
Ko HS, Schenk JP, Troger J et al (2007) Current radiological management of intussusception in children. Eur Radiol 17:2411–2421
Stringer MD, Pablot SM, Brereton RJ (1992) Paediatric intussusception. Br J Surg 79:867–876
Waseem M, Rosenberg HK (2008) Intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care 24:793–800
Littlewood Teele R, Vogel SA (1998) Intussusception: the paediatric radiologist's perspective. Pediatr Surg Int 14:158–162
Byrne AT, Geoghegan T, Govender P et al (2005) The imaging of intussusception. Clin Radiol 60:39–46
Williams H (2008) Imaging and intussusception. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 93:30–36
Collins DL, Pinckney LE, Miller KE et al (1989) Hydrostatic reduction of ileocolic intussusception: a second attempt in the operating room with general anesthesia. J Pediatr 115:204–207
Shekherdimian S, Lee SL (2011) Management of pediatric intussusception in general hospitals: diagnosis, treatment, and differences based on age. World J Pediatr 7:70–73
Henrikson S, Blane CE, Koujok K et al (2003) The effect of screening sonography on the positive rate of enemas for intussusception. Pediatr Radiol 33:190–193
Schmit P, Rohrschneider WK, Christmann D (1999) Intestinal intussusception survey about diagnostic and nonsurgical therapeutic procedures. Pediatr Radiol 29:752–761
Hooker RL, Hernanz-Schulman M, Yu C et al (2008) Radiographic evaluation of intussusception: utility of left-side-down decubitus view. Radiology 248:987–994
Daneman A, Alton DJ (1996) Intussusception. Issues and controversies related to diagnosis and reduction. Radiol Clin North Am 34:743–756
Weihmiller SN, Buonomo C, Bachur R (2011) Risk stratification of children being evaluated for intussusception. Pediatrics 127:e296–e303
Daneman A, Navarro O (2004) Intussusception. Part 2: an update on the evolution of management. Pediatr Radiol 34:97–108, quiz 187
Rohrschneider W, Troger J, Betsch B (1994) The post-reduction donut sign. Pediatr Radiol 24:156–160
Navarro O, Daneman A (2004) Intussusception. Part 3: diagnosis and management of those with an identifiable or predisposing cause and those that reduce spontaneously. Pediatr Radiol 34:305–312, quiz 369
del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D et al (1999) Intussusception in children: current concepts in diagnosis and enema reduction. Radiographics 19:299–319
del-Pozo G, Gonzalez-Spinola J, Gomez-Anson B et al (1996) Intussusception: trapped peritoneal fluid detected with US – relationship to reducibility and ischemia. Radiology 201:379–383
Lim HK, Bae SH, Lee KH et al (1994) Assessment of reducibility of ileocolic intussusception in children: usefulness of color Doppler sonography. Radiology 191:781–785
Koumanidou C, Vakaki M, Pitsoulakis G et al (2002) Sonographic detection of lymph nodes in the intussusception of infants and young children: clinical evaluation and hydrostatic reduction. AJR 178:445–450
Kong MS, Wong HF, Lin SL et al (1997) Factors related to detection of blood flow by color Doppler ultrasonography in intussusception. J US Med 16:141–144
Stranzinger E, Dipietro MA, Yarram S et al (2009) Intramural and subserosal echogenic foci on US in large-bowel intussusceptions: prognostic indicator for reducibility? Pediatr Radiol 39:42–46
Gartner RD, Levin TL, Borenstein SH et al (2011) Interloop fluid in intussusception: what is its significance? Pediatr Radiol 41:727–731
Caro P, Iqbal A, Donoghue V et al (2011) Interloop fluid in intussusception. Pediatr Radiol 41:1483
Markowitz RI, Meyer JS (1992) Pneumatic versus hydrostatic reduction of intussusception. Radiology 183:623–624
Somekh E, Serour F, Goncalves D et al (1996) Air enema for reduction of intussusception in children: risk of bacteremia. Radiology 200:217–218
Kirks DR, Griscom NT (1998) Practical pediatric imaging: diagnostic radiology of infants and children. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Meyer JS (1992) The current radiologic management of intussusception: a survey and review. Pediatr Radiol 22:323–325
Couloures KG, Beach M, Cravero JP et al (2011) Impact of provider specialty on pediatric procedural sedation complication rates. Pediatrics 127:e1154–e1160
American Academy of P, American Academy of Pediatric D, Coté CJ et al (2006) Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: an update. Pediatrics 118:2587–2602
Sirinelli D, Guilley C, Lardy H et al (2003) Reduction of acute intestinal intussusception: when and how? J Radiol 84:269–274
Touloukian RJ, O'Connell JB, Markowitz RI et al (1987) Analgesic premedication in the management of ileocolic intussusception. Pediatrics 79:432–434
Lee JH, Jeong YK, Hwang JC et al (2002) Graded compression sonography with adjuvant use of a posterior manual compression technique in the sonographic diagnosis of acute appendicitis. AJR 178:863–868
Lee JH, Jeong YK, Park KB et al (2005) Operator-dependent techniques for graded compression sonography to detect the appendix and diagnose acute appendicitis. AJR 184:91–97
Khong PL, Peh WC, Lam CH et al (2000) US-guided hydrostatic reduction of childhood intussusception: technique and demonstration. Radiographics 20:E1
McAlister WH (1998) Intussusception: even Hippocrates did not standardize his technique of enema reduction. Radiology 206:595–598
Fiorito ES, Recalde Cuestas LA (1959) Diagnosis and treatment of acute intestinal intussusception with controlled insufflation of air. Pediatrics 24:241–244
Monrad S (1926) Acute invagination of the intestine in small children. Arch Dis Child 1:323–338
Ravitch MM, McCune RM (1948) Reduction of intussusception by barium enema: a clinical and experimental study. Ann Surg 128:904–917
Kirks DR (1995) Air intussusception reduction: ‘the winds of change’. Pediatr Radiol 25:89–91
Khanna G, Applegate K (2008) US guided intussusception reduction: are we there yet? Abdom Imaging 33:38–40
Shiels WE 2nd, Kirks DR, Keller GL et al (1993) John Caffey Award. Colonic perforation by air and liquid enemas: comparison study in young pigs. AJR 160:931–935
Daneman A, Alton DJ, Ein S et al (1995) Perforation during attempted intussusception reduction in children—a comparison of perforation with barium and air. Pediatr Radiol 25:81–88
Grasso SN, Katz ME, Presberg HJ et al (1994) Transabdominal manually assisted reduction of pediatric intussusception: reappraisal of this historical technique. Radiology 191:777–779
Ravitch MM (1966) Diagnosis and treatment intussusception—a surgical condition. Pediatrics 38:122–123
Katz ME, Kolm P (1992) Intussusception reduction 1991: an international survey of pediatric radiologists. Pediatr Radiol 22:318–322
Kirks DR (1994) Diagnosis and treatment of pediatric intussusception: how far should we push our radiologic techniques? Radiology 191:622–623
Grasso SN, Katz ME, Presberg HJ et al (1994) Manual assistance in air reduction of intussusceptions. Radiology 193:283
Swischuk LE (2004) Imaging of the newborn, infant, and young child. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Sargent MA, Wilson BP (1991) Are hydrostatic and pneumatic methods of intussusception reduction comparable? Pediatr Radiol 21:346–349
Hase T, Kodama M, Mizukuro T et al (1998) Manual reduction with the index finger for infantile intussusception. A modification of Hutchinson’s maneuver. Pediatr Surg Int 13:223–225
Hutchinson J (1874) A successful case of abdominal section for intussusception, with remarks on this and other methods of treatment. Med Chir Trans 57:31–75
Paterson CA, Langer JC, Somers S et al (1994) Pneumatic reduction of intussusception using carbon dioxide. Pediatr Radiol 24:296–297
Ilivitzki A, Shtark LG, Arish K et al (2012) Deep sedation during pneumatic reduction of intussusception. Pediatr Radiol 42:562–565
Evrard M (1973) Problems facing the anesthesiologist in acute intestinal intussusception in infants. Anesth Analg (Paris) 30:1085–1091
Hoffman RD, Levine HA, Baram S et al (1992) Painless intussusception. Giving conservative treatment another chance. Postgrad Med 91:283–284
del Palomar P, Chavarri R, Rodriguez de Benito JF et al (1984) [Anesthesia in intestinal invagination]. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 31:231–233
Suzuki M, Hayakawa K, Nishimura K et al (1999) Intussusception: the role of general anesthesia during hydrostatic barium reduction. Radiat Med 17:121–124
Brenn BR, Katz A (1997) General anaesthesia may improve the success rate of hydrostatic reductions of intussusception. Paediatr Anaesth 7:77–81
Diaz-Aldagalan Gonzalez R, Perez-Martinez A, Pison-Chacon J et al (2011) Rescue by pneumoenema under general anaesthesia of apparently non-reducible intestinal intussusception. Eur J Pediatr 171:189–191
Shekherdimian S, Lee SL, Sydorak RM et al (2009) Contrast enema for pediatric intussusception: is reflux into the terminal ileum necessary for complete reduction? J Pediatr Surg 44:247–249, discussion 249-250
Bajaj L, Roback MG (2003) Postreduction management of intussusception in a children's hospital emergency department. Pediatrics 112:1302–1307
Connolly B, Alton DJ, Ein SH et al (1995) Partially reduced intussusception: when are repeated delayed reduction attempts appropriate? Pediatr Radiol 25:104–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was honored with the Jacques Lefebvre Award at the 2012 ESPR meeting in Athens.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(MP4 20570 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vazquez, J.L., Ortiz, M., Doniz, M.C. et al. External manual reduction of paediatric idiopathic ileocolic intussusception with US assistance: a new, standardised, effective and safe manoeuvre. Pediatr Radiol 42, 1197–1204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2424-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2424-0