Abstract
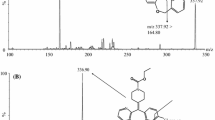
A simple, sensitive, and selective liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method was validated for the identification and quantification of mavoglurant (AFQ056) in human plasma. The chromatographic separation was performed using a Cosmosil 5 C18 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) column at 40 ± 0.5 °C with a mobile phase consisting of acetic acid in water (0.1 %, v/v)/methanol (10:90, v/v) with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min followed by quantification with tandem mass spectrometry, operating with electrospray ionization in positive ion mode and applying multiple reaction monitoring. The validated method described in this paper presents high absolute recovery with precision and accuracy meeting the acceptance criteria. The method was precise and accurate for 2- and 10-fold dilution of samples. The method was validated using sodium heparin as specific anticoagulant, and the anticoagulant effect was tested by lithium heparin and K3EDTA. The method was successfully cross-validated between two bioanalytical sites. The method was specific for mavoglurant within the given criteria for acceptance (apparent peak area at the retention time of mavoglurant in zero samples was less than 20 % compared with the mean peak area at LLOQ) in human plasma. The method was fully validated for the quantitative determination of mavoglurant in human plasma between the range of 2.00 and 2,500 ng/mL.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole P (2012) Mavoglurant. Drugs Future 37:7–12
Meldrum BS (2000) Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr 130(4S, Suppl):1007S–1015S
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
Dölen G, Bear MF (2008) Role for metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) in the pathogenesis of fragile X syndrome. J Physiol 586(6):1503–1508
Levenga J, Hayashi S, de Vrij FM, Koekkoek SK, van der Linde HC, Nieuwenhuizen I, Song C, Buijsen RA, Pop AS, Gomez-Mancilla B, Nelson DL, Willemsen R, Gasparini F, Oostra BA (2011) AFQ056, a new mGluR5 antagonist for treatment of fragile X syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 42(3):311–317
Gregoire L, Morin N, Ouattara B, Gasparini F, Bilbe G, Johns D, Vranesic I, Sahasranaman S, Gomez-Mancilla B, Di Paolo T (2011) The acute antiparkinsonian and antidyskinetic effect of AFQ056, a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 antagonist, in l-dopa-treated parkinsonian monkeys. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17(4):270–276
Berg D, Godau J, Trenkwalder C, Eggert K, Csoti I, Storch A, Gasparini F, Hariry S, Vandemeulebroecke M, Johns D, Gomez-Mancilla B (2010) AFQ056 treatment of severe levodopa- induced dyskinesias: proof of concept study. Mov Disord 25(suppl2):321 [14th Int Congr Parkinson’s Dis Mov Disord (June 13–17, Buenos Aires) 2010]
Berg D, Godau J, Trenkwalder C, Eggert K, Csoti I, Storch A, Huber H, Morelli-Canelo M, Stamelou M, Ries V, Wolz M, Schneider C, Di Paolo T, Gasparini F, Hariry S, Vandemeulebroecke M, Abi-Saab W, Cooke K, Johns D, Gomez-Mancilla B (2011) AFQ056 treatment of levodopainduced dyskinesias: results of 2 randomized controlled trials. Mov Disord 26(7):1243–1250
Jacquemont S, Curie A, Portes V, Torrioli MG, Berry-Kravis E, Hagerman RJ, Ramos FJ, Cornish K, He Y, Paulding C, Neri G, Chen F, Hadjikhani N, Martinet D, Meyer J, Beckmann JS, Delange K, Brun A, Bussy G, Gasparini F, Hilse T, Floesser A, Branson J, Bilbe G, Johns D, Gomez-Mancilla B (2011) Epigenetic modification of the FMR1 gene in fragile X syndrome is associated with differential response to the mGluR5 antagonist AFQ056. Sci Transl Med 3(64):64ra1
Walles M, Wolf T, Gschwind HP, Krauser J, Woessner R, Chakraborty A, Ufer M, Swart P (2012) Absorption and disposition of mavoglurant (AFQ056) in healthy volunteers (The 19th International Symposium on Microsomes and Drug Oxidations and 12th European ISSX Meeting (June 17–21, 2012) P195
Chakraborty A, Ufer M, Bhad P, Vandemeulebroecke M, Gomez-Mancilla B, Bell D, Winter S (2012) Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between the novel mGluR5 antagonist AFQ056 and levodopa/carbidopa in healthy volunteers. Mov Disord 27(Suppl 1):456
FDA guidance for industry, bioanalytical method validation, US department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) (2001)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the assistance of Phaninatha Sarma Ayalavajjala, Novartis Healthcare Private Limited, in the development of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Disclosure
This study was funded by Novartis Pharma AG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jakab, A., Winter, S., Raccuglia, M. et al. Validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantitative determination of mavoglurant (AFQ056) in human plasma. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 215–223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6456-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6456-y