Abstract
Purpose
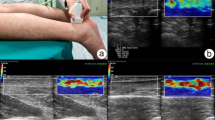
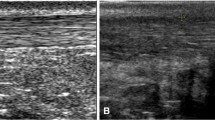
To seek differences of Achilles tendon hardness between insertional tendinopathy (IT) and asymptomatic controls by using computer-assisted quantification on axial-strain sonoelastography (ASE).
Methods
The study consisted of 37 non-athletic patients presenting with Achilles tendon pain in one or two tendons. Both tendons were examined clinically. Among the 74 tendons, 16 were diagnosed and categorized into an IT group and 29 into an asymptomatic group. The remaining 29 tendons were excluded due to non-insertional tendinopathy, ruptures, previous surgery or mixed disorders. The tendons in the IT and asymptomatic groups were examined with both ASE and conventional ultrasound. Computer-assisted quantification on ASE was conducted to extract parameters of tendon hardness, including the 20th percentile (H20), median (H50) and skewness (Hsk) of the hardness within tendon, as well as the ratio of the mean hardness within tendon to that outside tendon (Hratio).
Results
The H20 (p = 0.003), H50 (p = 0.004) and Hratio (p = 0.002) were larger and Hsk (p = 0.001) was smaller at distal thirds of IT tendons than those of asymptomatic tendons. For differentiation between two groups, the Hsk achieved the best value (0.815) of area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, with a sensitivity of 81.3 %, a specificity of 86.2 % and an accuracy of 84.4 %.
Conclusions
Computer-assisted quantification on ASE shows that IT tendons are harder than asymptomatic tendons. It might act as a potentially useful technique for identification and risk stratification of IT patients and thus be valuable in day-by-day clinical practice for monitoring IT progression and for evaluating therapeutic effects.
Level of evidence
III.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubry S, Nueffer J-P, Tanter M, Becce F, Vidal C, Michel F (2015) Viscoelasticity in achilles tendonopathy: quantitative assessment by using real-time shear-wave elastography. Radiology 274(3):821–829
Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich C, Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F, Cantisani V, Correas J, D’Onofrio M, Drakonaki E (2013) Efsumb guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med 34(2):169–184
Brown PG, Alsousou J, Cooper A, Thompson MS, Noble JA (2013) The AutoQual ultrasound elastography method for quantitative assessment of lateral strain in post-rupture achilles tendons. J Biomech 46(15):2695–2700
Campbell MJ, Julious SA, Altman DG (1995) Estimating sample sizes for binary, ordered categorical, and continuous outcomes in two group comparisons. BMJ 311(7013):1145–1148
Chen X-M, Cui L-G, He P, Shen W-W, Qian Y-J, Wang J-R (2013) Shear wave elastographic characterization of normal and torn achilles tendons a pilot study. J Ultrasound Med 32(3):449–455
Currey JD (1999) The design of mineralised hard tissues for their mechanical functions. J Exp Biol 202(23):3285–3294
De Zordo T, Chhem R, Smekal V, Feuchtner G, Reindl M, Fink C, Faschingbauer R, Jaschke W, Klauser AS (2010) Real-time sonoelastography: findings in patients with symptomatic achilles tendons and comparison to healthy volunteers. Ultraschall Med 31(4):394–400
De Zordo T, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Smekal V, Reindl M, Klauser AS (2009) Real-time sonoelastography findings in healthy achilles tendons. Am J Roentgenol 193(2):W134–W138
DeWall RJ, Jiang J, Wilson JJ, Lee KS (2014) Visualizing tendon elasticity in an ex vivo partial tear model. Ultrasound Med Biol 40(1):158–167
DeWall RJ, Slane LC, Lee KS, Thelen DG (2014) Spatial variations in achilles tendon shear wave speed. J Biomech 47(11):2685–2692
Doschak MR, Zernicke RF (2005) Structure, function and adaptation of bone-tendon and bone-ligament complexes. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 5(1):35–40
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ (2012) Ultrasound elastography for musculoskeletal applications. Br J Radiol 85(1019):1435–1445
Evranos B, Idilman I, Ipek A, Polat SB, Cakir B, Ersoy R (2015) Real-time sonoelastography and ultrasound evaluation of the achilles tendon in patients with diabetes with or without foot ulcers: a cross sectional study. J Diabetes Complicat 29(8):1124–1129
Gehmert S, Jung E, Kügler T, Klein S, Gehmert S, Zeitler K, Loibl M, Prantl L (2012) Sonoelastography can be used to monitor the restoration of achilles tendon elasticity after injury. Ultraschall Med 33(6):581
Klauser AS, Faschingbauer R, Jaschke WR (2010) Is sonoelastography of value in assessing tendons? Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 14(3):323–333
Klauser AS, Miyamoto H, Bellmann-Weiler R, Feuchtner GM, Wick MC, Jaschke WR (2014) Sonoelastography: musculoskeletal applications. Radiology 272(3):622–633
Klauser AS, Miyamoto H, Tamegger M, Faschingbauer R, Moriggl B, Klima G, Feuchtner GM, Kastlunger M, Jaschke WR (2013) Achilles tendon assessed with sonoelastography: histologic agreement. Radiology 267(3):837–842
Lee KS (2012) Musculoskeletal sonography of the tendon. J Ultrasound Med 31(12):1879–1884
Martin JA, Biedrzycki AH, Lee KS, DeWall RJ, Brounts SH, Murphy WL, Markel MD, Thelen DG (2015) In vivo measures of shear wave speed as a predictor of tendon elasticity and strength. Ultrasound Med Biol 41(10):2722–2730
Masala S, Manenti G, Antonicoli M, Morosetti D, Claroni G, Guglielmi G, Simonetti G (2014) Real time evaluation of monolateral clubfoot with sonoelastography. Radiol Med 119(8):601–606
Masala S, Manenti G, Antonicoli M, Morosetti D, Claroni G, Simonetti G (2012) Real time evaluation of monolateral clubfoot with sonoelastography. Preliminary results. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J 2(1):49–52
Mautner K, Colberg RE, Malanga G, Borg-Stein JP, Harmon KG, Dharamsi AS, Chu S, Homer P (2013) Outcomes after ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for chronic tendinopathy: a multicenter, retrospective review. PM&R 5(3):169–175
Ooi CC, Malliaras P, Schneider ME, Connell DA (2014) “Soft, hard, or just right?” Applications and limitations of axial-strain sonoelastography and shear-wave elastography in the assessment of tendon injuries. Skelet Radiol 43(1):1–12
Ooi CC, Schneider ME, Malliaras P, Chadwick M, Connell DA (2015) Diagnostic performance of axial-strain sonoelastography in confirming clinically diagnosed achilles tendinopathy: comparison with b-mode ultrasound and color doppler imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 41(1):15–25
Ooi CC, Schneider ME, Malliaras P, Jones D, Saunders S, McMahon A, Connell D (2016) Sonoelastography of the achilles tendon: prevalence and prognostic value among asymptomatic elite australian rules football players. Clin J Sport Med. doi:10.1097/JSM.0000000000000265
Ophir J, Alam SK, Garra BS, Kallel F, Konofagou EE, Krouskop T, Merritt CR, Righetti R, Souchon R, Srinivasan S (2002) Elastography: imaging the elastic properties of soft tissues with ultrasound. J Med Ultrason 29(4):155–171
Reeves ND (2006) Adaptation of the tendon to mechanical usage. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 6(2):174–180
Ruan Z, Zhao B, Qi H, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wu M, Shao G (2015) Elasticity of healthy achilles tendon decreases with the increase of age as determined by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(1):1043–1050
Schepull T, Aspenberg P (2015) Healing of human achilles tendon ruptures: radiodensity reflects mechanical properties. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(3):884–889
Sconfienza LM, Silvestri E, Cimmino MA (2010) Sonoelastography in the evaluation of painful achilles tendon in amateur athletes. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(3):373–378
Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, Hall TJ, Bamber JC, Barr RG, Castera L, Choi BI, Chou Y-H, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Ding H, Amy D, Farrokh A, Ferraioli G, Filice C, Friedrich-Rust M, Nakashima K, Schafer F, Sporea I, Suzuki S, Wilson S, Kudo M (2015) Wfumb guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol 41(5):1126–1147
Tan S, Kudas S, Ozcan AS, Ipek A, Karaoglanoglu M, Arslan H, Bozkurt M (2012) Real-time sonoelastography of the achilles tendon: pattern description in healthy subjects and patients with surgically repaired complete ruptures. Skelet Radiol 41(9):1067–1072
Thorpe CT, Udeze CP, Birch HL, Clegg PD, Screen HR (2013) Capacity for sliding between tendon fascicles decreases with ageing in injury prone equine tendons: a possible mechanism for age-related tendinopathy. Eur Cells Mater 25:48–60
Tudisco C, Bisicchia S, Stefanini M, Antonicoli M, Masala S, Simonetti G (2015) Tendon quality in small unilateral supraspinatus tendon tears. Real-time sonoelastography correlates with clinical findings. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(2):393–398
Turan A, Teber MA, Yakut ZI, Unlu HA, Hekimoglu B (2015) Sonoelastographic assessment of the age-related changes of the achilles tendon. Med Ultrason 17(1):58–61
Turan A, Tufan A, Mercan R, Teber MA, Tezcan ME, Bitik B, Goker B, Haznedaroglu S (2013) Real-time sonoelastography of achilles tendon in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Skelet Radiol 42(8):1113–1118
van Dijk CN, van Sterkenburg MN, Wiegerinck JI, Karlsson J, Maffulli N (2011) Terminology for achilles tendon related disorders. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(5):835–841
Wiegerinck JI, Kerkhoffs GM, van Sterkenburg MN, Sierevelt IN, van Dijk CN (2013) Treatment for insertional achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(6):1345–1355
Wu Z, Hua Y, Li H, Chen S, Li Y (2015) Biomechanical comparison of three methods for distal achilles tendon reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(12):3756–3760
Zhang Q, Li CL, Han H, Yang LJ, Wang YY, Wang WP (2014) Computer-aided quantification of contrast agent spatial distribution within atherosclerotic plaque in contrast-enhanced ultrasound image sequences. Biomed Signal Process Control 13:50–61
Zhang Q, Li CL, Zhou ML, Liao Y, Huang CC, Shi J, Wang YY, Wang WP (2015) Quantification of carotid plaque elasticity and intraplaque neovascularization using contrast-enhanced ultrasound and image registration-based elastography. Ultrasonics 62:253–262
Zhang Q, Xiao Y, Chen S, Wang C, Zheng H (2015) Quantification of elastic heterogeneity using contourlet-based texture analysis in shear-wave elastography for breast tumor classification. Ultrasound Med Biol 41(2):588–600
Zhang X, Xiao Y, Zeng J, Qiu W, Qian M, Wang C, Zheng R, Zheng H (2014) Computer-assisted assessment of ultrasound real-time elastography: initial experience in 145 breast lesions. Eur J Radiol 83(1):e1–e7
Zhang ZJ, Ng GY, Lee WC, Fu SN (2014) Changes in morphological and elastic properties of patellar tendon in athletes with unilateral patellar tendinopathy and their relationships with pain and functional disability. Plos One 9(10):e108337
Zhou B, Zhou Y, Tang K (2014) An overview of structure, mechanical properties, and treatment for age-related tendinopathy. J Nutr Health Aging 18(4):441–448
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61401267 and 61471231). The authors wish to thank Dr. Liangjun Zhang for his editorial contributions and the anonymous referees for their careful review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Cai, Y., Hua, Y. et al. Sonoelastography shows that Achilles tendons with insertional tendinopathy are harder than asymptomatic tendons. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 1839–1848 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4197-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4197-8