Abstract
Background
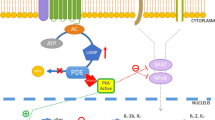
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic pruritic inflammatory dermatosis. Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are a superfamily of enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of cyclic AMP (cAMP), a second messenger that controls key cellular functions, into its inactive forms. Selective inhibitors of PDE4, a cAMP-specific PDE, serve as potent antiinflammatory agents.
Objectives
To measure PDE4 gene expression in patients with AD before and after treatment with topical mometasone cream, in comparison to controls.
Materials & Methods
Twenty patients with acute and subacute AD were investigated. Skin biopsies before and after treatment were obtained for evaluation of PDE4 expression level by RT-PCR.
Results
The level of PDE4 mRNA was significantly higher in AD patients either before or after treatment compared to controls (p < 0.001), and the level of PDE4 mRNA in AD patients significantly decreased following treatment (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our study indicates that there is an increased level of PDE4 in AD lesions, suggesting that PDE4 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD. Targeting PDE4 (using PDE4 inhibitors) may herald a new era in the treatment of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulos S, Yan AC. Current concepts in the prevention of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol 2018; 36: 668–71.
Simpson EL, Irvine AD, Eichenfield LF, et al. Update on epidemiology, diagnosis and disease course of atopic dermatitis. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2016; 35: S84–8.
Hong J, Buddenkotte J, Berger TG. Management of itch in atopic dermatitis. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2011; 30: 71–86.
Chang Y-S, Chiang B-L. Mechanism of sleep disturbance in children with atopic dermatitis and the role of the circadian rhythm and melatonin. Int J Mol Sci 2016; 17: 462.
Hanifin JM, Chan SC. Monocyte phosphodiesterase abnormalities and dysregulation of lymphocyte function in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 1995; 105: 84S–8S.
Houslay MD, Miles D, David RA. PDE4 cAMP phosphodiesterases: modular enzymes that orchestrate signalling cross-talk, desensitization and compartmentalization. Biochem J 2003; 370: 1–18.
Ahmad F, Murata T, Simizu K, Degerman E, Maurice D, Manganiello V. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiestrases: important signaling modulators and therapeutic targets. Oral Dis 2015; 21: e25–50.
Arellano FM, Arana A, Wentworth CE, et al. Lymphoma among patients with atopic dermatitis and/or treated with topical immunosuppressants in the United Kingdom. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 123: 1111–6, 116.e1–13.
Hanifin JM, Chan SC, Cheng JB, et al. Type 4 phosphodiesterase inhibitors have clinical and in vitro anti-inflammatory effects in atopic dermatitis. J Investig Dermatol 1996; 107: 51–6.
Levy J, Zhou DM, Zippin JH. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate signaling in inflammatory skin disease. J Clin Exp Dermatol Res 2016; 7: 326–32.
Udkoff J, Waldman A, Ahluwalia J, et al. Current and emerging topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol 2017; 35: 375–82.
Kunz BIF, Ring J. Clinical features and diagnostic criteria of atopic dermatitis. In: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N, editors. Textbook of pediatric dermatology (2nd edition). Oxford: Blackwell, 2006, p. 227–44.
Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allerg Clin Immunol 2000; 105: 860–76.
Samrao A, Berry TM, Goreshi R, et al. A pilot study of an oral phosphodiesterase inhibitor (apremilast) for atopic dermatitis in adults. Arch Dermatol 2012; 148: 890–7.
Volf E, Au S, Dumont N, et al. A phase 2, open-label, investigator-initiated study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of apremilast in subjects with recalcitrant allergic contact or atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol 2012; 11: 341.
Furue M, Kitahara Y, Akama H, Hojo S, Hayashi N, Nakagawa H. Safety and efficacy of topical E6005, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in Japanese adult patients with atopic dermatitis: Results of a randomized, vehicle-controlled, multicenter clinical trial. J Dermatol 2014; 41: 577–85.
Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Antipruritic mechanisms of topical E6005, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor: inhibition of responses to proteinase-activated receptor 2 stimulation mediated by increase in intracellular cyclic AMP. J Dermatol Sci 2014; 76: 206–13.
Hanifin JM, Ellis CN, Frieden IJ, et al. OPA-15406, a novel, topical, nonsteroidal, selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in the treatment of adult and adolescent patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD): a phase-II randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016; 75: 297–305.
Zane LT, Chanda S, Jarnagin K, Nelson DB, Spelman L, Gold LS. Crisaborole and its potential role in treating atopic dermatitis: overview of early clinical studies. Immunotherapy 2016; 8: 853–66.
Eichenfield LF, Call RS, Forsha DW, et al. Long-term safety of crisaborole ointment 2% in children and adults with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017; 77(4): 641–9.e5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial support
none.
Conflicts of interest
none.
About this article
Cite this article
Nada, H.R., Rashed, L.A., Shehada, J. et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) gene expression in atopic dermatitis patients, before and after treatment with topical mometasone cream. Eur J Dermatol 32, 19–23 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2022.4194
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2022.4194