Abstract
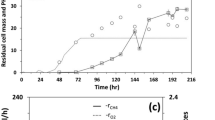
In this study, the ability of microalgae Chlorella kessleri to remove nutrients, biofix CO2, and generate valuable biomass was investigated. For this purpose, CO2 at different concentrations was added to the synthetic tertiary municipal wastewater for cultivating C. kessleri in batch photobioreactors. The concentration of biomass increases gradually during the cultivation period for the tested CO2 concentrations of 2%, 6%, and 10%, except 0% CO2. The highest biomass concentration found was 607 mg/L, and the highest biomass productivity is 46 mg/L/day, at a CO2 concentration of 2%. Monod growth kinetic model based on a single substrate factor was used, and the experimental findings agree well with the predictions by the model for all feed concentrations except 0% CO2. Biofixation of CO2 depends on the optimal CO2 concentration supplied to the culture. The maximum biofixation rate of CO2 achieved at 2% CO2 is 83.88 mg/L/day. The maximum removal of total nitrogen of 99% was achieved for both 2% and 10% CO2, while the total nitrogen removal is negligible by microalgae cultured with air without CO2 enrichment, which confirms the beneficial effect of CO2 on the removal of nutrients from wastewater media. These findings indicate the possibility of nutrient removal from tertiary municipal wastewater using microalgae C. kessleri along with CO2 biofixation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OD:
-
Optical density
- BBM:
-
Bold’s Basal Medium
- \( \mu_{\text{g}} \) :
-
Specific growth rate
- \( \mu_{\text{m}} \) :
-
Maximum specific growth rate
- \( P_{\text{B}} \) :
-
Biomass productivity (mg/L/day)
- \( X_{1} \;{\text{and}}\;X_{2} \) :
-
Biomass weight (mg/L) at the time \( t_{1} \) and \( t_{2} \)
- \( X_{0} \;{\text{and}}\;X_{t} \) :
-
Biomass weight (mg/L) at the initial time, \( t_{0} \) and at the end of the cultivation period \( t_{t} \)
- \( R_{{{\text{CO}}_{2} }} \) :
-
CO2 biofixation rate (mg/L/day)
- \( C_{\text{carbon}} \) :
-
Carbon content
- \( M_{{{\text{CO}}_{2} }} \) :
-
Molecular weight of CO2
- \( M_{\text{c}} \) :
-
Atomic weight of carbon
- d:
-
Day
References
Abdelaziz AEM, Leite GB, Hallenbeck PC (2013) Addressing the challenges for sustainable production of algal biofuels: I. Algal strains and nutrient supply. Environ Technol (United Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.827748
Abreu AP, Fernandes B, Vicente AA et al (2012) Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using industrial dairy waste as organic carbon source. Bioresour Technol 118:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.055
Ajayan KV, Selvaraju M, Unnikannan P, Sruthi P (2015) Phycoremediation of tannery wastewater using microalgae Scenedesmus species. Int J Phytoremediation 17:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2014.989313
Akpor OB, Muchie M (2010) Remediation of heavy metals in drinking water and wastewater treatment systems: processes and applications. Int J Phys, Sci
Aksu Z, Açikel Ü (1999) A single-staged bioseparation process for simultaneous removal of copper(II) and chromium(VI) by using C. vulgaris. Process Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00130-7
Álvarez-Díaz PD, Ruiz J, Arbib Z et al (2017) Freshwater microalgae selection for simultaneous wastewater nutrient removal and lipid production. Algal Res 24:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.02.006
Andruleviciute V, Makareviciene V, Skorupskaite V, Gumbyte M (2014) Biomass and oil content of Chlorella sp., Haematococcus sp., Nannochloris sp. and Scenedesmus sp. under mixotrophic growth conditions in the presence of technical glycerol. J Appl Phycol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0048-x
Arbib Z, Ruiz J, Álvarez-Díaz P et al (2014) Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res 49:465–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.036
Azov Y (1982) Effect of pH on inorganic carbon uptake in algal cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:1300–1306
Becker EW (1994) Microalgae : biotechnology and microbiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bhola V, Swalaha F, Ranjith Kumar R et al (2014) Overview of the potential of microalgae for CO2 sequestration. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:2103–2118
Chan A, Salsali H, McBean E (2014) Heavy metal removal (copper and zinc) in secondary effluent from wastewater treatment plants by microalgae. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400289z
Chi Z, O’Fallon JV, Chen S (2011) Bicarbonate produced from carbon capture for algae culture. Trends Biotechnol 29:537–541
Chinnasamy S, Bhatnagar A, Hunt RW, Das KC (2010) Microalgae cultivation in a wastewater dominated by carpet mill effluents for biofuel applications. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.026
Cho S, Luong TT, Lee D et al (2011) Reuse of effluent water from a municipal wastewater treatment plant in microalgae cultivation for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.037
Das P, Lei W, Aziz SS, Obbard JP (2011) Enhanced algae growth in both phototrophic and mixotrophic culture under blue light. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.102
de Morais MG, Costa JAV (2007) Isolation and selection of microalgae from coal fired thermoelectric power plant for biofixation of carbon dioxide. Energy Convers Manag 48:2169–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2006.12.011
Demirbas MF (2011) Biofuels from algae for sustainable development. Appl Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.01.059
Eze VC, Velasquez-Orta SB, Hernández-García A et al (2018) Kinetic modelling of microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and carbon dioxide sequestration. Algal Res 32:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.03.015
Francisco ÉC, Neves DB, Jacob-Lopes E, Franco TT (2010) Microalgae as feedstock for biodiesel production: carbon dioxide sequestration, lipid production and biofuel quality. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2338
García J, Green BF, Lundquist T et al (2006) Long term diurnal variations in contaminant removal in high rate ponds treating urban wastewater. Bioresour Technol 97:1709–1715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.07.019
Goldman JC, Shapiro J (1973) Carbon dioxide and pH: effect on species succession of algae. Science (80-) 182:306–307. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.182.4109.306
Iasimone F, De Felice V, Panico A, Pirozzi F (2017) Experimental study for the reduction of CO2 emissions in wastewater treatment plant using microalgal cultivation. J CO2 Util 22:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2017.09.004
Jaafari J, Yaghmaeian K (2019a) Response surface methodological approach for optimizing heavy metal biosorption by the blue-green alga Chroococcus dispersus. Desalin Water Treat 142:225–234. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23406
Jaafari J, Yaghmaeian K (2019b) Optimization of heavy metal biosorption onto freshwater algae (Chlorella coloniales) using response surface methodology (RSM). Chemosphere 217:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2018.10.205
Jaafari J, Seyedsalehi M, Safari GH et al (2017) Simultaneous biological organic matter and nutrient removal in an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2O) moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) integrated system. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1206-x
Kasiri S, Abdulsalam S, Ulrich A, Prasad V (2015) Optimization of CO2 fixation by Chlorella kessleri using response surface methodology. Chem Eng Sci 127:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2015.01.008
Kassim MA, Meng TK (2017) Carbon dioxide (CO2) biofixation by microalgae and its potential for biorefinery and biofuel production. Sci Total Environ 584–585:1121–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.172
Kong QX, Li L, Martinez B et al (2010) Culture of microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in wastewater for biomass feedstock production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8670-4
Lee K, Lee CG (2001) Effect of light/dark cycles on wastewater treatments by microalgae. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 6:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932550
Lee E, Jalalizadeh M, Zhang Q (2015) Growth kinetic models for microalgae cultivation: a review. Algal Res 12:497–512
Li Y, Zhou W, Hu B et al (2012) Effect of light intensity on algal biomass accumulation and biodiesel production for mixotrophic strains Chlorella kessleri and Chlorella protothecoide cultivated in highly concentrated municipal wastewater. Biotechnol Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24491
Loladze I, Elser JJ (2011) The origins of the Redfield nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio are in a homoeostatic protein-to-rRNA ratio. Ecol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01577.x
Mohsenpour SF, Richards B, Willoughby N (2012) Spectral conversion of light for enhanced microalgae growth rates and photosynthetic pigment production. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.072
Molazadeh M, Ahmadzadeh H, Pourianfar HR et al (2019) The use of microalgae for coupling wastewater treatment with CO2 biofixation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00042
Monod J (1949) The growth of bacterial cultures. Annu Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.03.100149.002103
Nayak M, Karemore A, Sen R (2016) Performance evaluation of microalgae for concomitant wastewater bioremediation, CO2 biofixation and lipid biosynthesis for biodiesel application. Algal Res 16:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.020
Razzak SA (2019) In situ biological CO 2 fixation and wastewater nutrient removal with Neochloris oleoabundans in batch photobioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-2017-x
Razzak SA, Hossain MM, Lucky RA et al (2013) Integrated CO2 capture, wastewater treatment and biofuel production by microalgae culturing—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 27:622–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.063
Razzak SA, Ilyas M, Ali SAM, Hossain MM (2015) Effects of CO2 concentration and pH on mixotrophic growth of Nannochloropsis oculata. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176:1290–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1646-7
Razzak SA, Ali SAM, Hossain MM, deLasa H (2017) Biological CO2 fixation with production of microalgae in wastewater—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.02.038
Ruiz-Martinez A, Martin Garcia N, Romero I et al (2012) Microalgae cultivation in wastewater: nutrient removal from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent. Bioresour Technol 126:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.022
Sheng PX, Tan LH, Chen JP, Ting YP (2004) Biosorption performance of two brown marine algae for removal of chromium and cadmium. J Dispers Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1081/DIS-200027327
Stephens E, Ross IL, Mussgnug JH et al (2010) Future prospects of microalgal biofuel production systems. Trends Plant Sci 15:554–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.003
Sydney EB, da Silva TE, Tokarski A et al (2011) Screening of microalgae with potential for biodiesel production and nutrient removal from treated domestic sewage. Appl Energy 88:3291–3294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.11.024
Tang D, Han W, Li P et al (2011) CO2 biofixation and fatty acid composition of Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to different CO2 levels. Bioresour Technol 102:3071–3076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.047
Wang Y, Chen T, Qin S (2014) Heterotrophic cultivation of Chlorella kessleri for fatty acids production by carbon and nitrogen supplements. Biomass Bioenerg 47:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.09.018
Wilbanks TJ, Fernandez SJ (2014) Climate change and infrastructure, urban systems, and vulnerabilities. Technical Report for the US Department of Energy in Support of the National Climate Assessment national Climate assessment regional technical input report series
Yadav G, Sen R (2017) Microalgal green refinery concept for biosequestration of carbon-dioxide vis-à-vis wastewater remediation and bioenergy production: Recent technological advances in climate research. J CO2 Util 17:188–206
Zhao B, Su Y (2014) Process effect of microalgal-carbon dioxide fixation and biomass production: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 31:121–132
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the support received from King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals (KFUPM) along with internal direct funding grant and financial support for this work through Project No. DF191050.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faruque, M.O., Mohammed, K.A., Hossain, M.M. et al. Influence of elevated CO2 concentrations on growth, nutrient removal, and CO2 biofixation using Chlorella kessleri cultivation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 913–926 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02909-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02909-4