Abstract
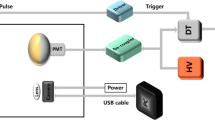
Inter-crystal scattering (ICS) events cause degradation of the contrast in PET images. We developed the X’tal cube PET detector with submillimeter spatial resolution, which consisted of a segmented LYSO scintillator and 96 MPPCs. For this high spatial resolution PET detector, the ICS event was not negligible. In this study, we proposed a method to discriminate the ICS events and showed its feasibility by the following method. For each 96 MPPC, we measured the mean and standard deviation of the peak in the pulse height distribution obtained by the photoabsorption events in a scintillator pixel. Every time a newly detected event was identified as the segment, we monitored the reduced chi-square value that was calculated with the pulse height and the prepared mean and the standard deviation for each 96 MPPC. Since the pulse height caused by the photoabsorption event resulted in a small reduced chi-square value, we could eliminate the ICS events by setting a threshold on the reduced chi-square value. We carried out both a Monte Carlo simulation and a scanning experiment. By the simulation, we confirmed that the threshold of the reduced chi square significantly discriminated the ICS event. We obtained the response function by a scanning experiment with a 0.2 mm slit beam of 511 keV gamma-ray. The standard deviation of the response function was improved from 1.6 to 1.06 mm by eliminating the ICS events. The proposed method could significantly eliminate the ICS events and retain the true events.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ota R, Omura T, Yamada R, Miwa T, Watanabe M. Evaluation of a sub-millimeter resolution pet detector with a 12 mm pitch TSV-MPPC array one-to-one coupled to lFS scintillator crystals and inter-crystal scatter studies with individual signal readout. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2017;1(1):15–22.
Park S-J, Rogers WL, Clinthorne NH. Effect of inter-crystal Compton scatter on efficiency and image noise in small animal PET module. In: Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record IEEE, 2003;4: 2272–77.
Stickel JR, Cherry SR. High-resolution PET detector design: modelling components of intrinsic spatial resolution. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:179–95.
Ghazanfari N, Ay MR, Zeraatkar N, Sarkar S, Loudos G. Quantitative assessment of the influence of crystal material and size on the inter crystal scattering and penetration effect in pixilated dual head small animal PET scanner. IFMBE Proceedings. 2011;35:712–5.
Surti S, Scheuermann R, Werner ME, Karp JS. Improved spatial resolution in PET scanners using sampling techniques. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2009;56:596–601.
Lam CF, Hagiwara N, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, Yamaya T, Murayama H. An inter-crystal scatter correction method for DOI PET image reconstruction. Jpn J Med Phys. 2006;26:118–30.
Daghighian F, Shenderov P, Pentlow KS, Graham MC, Eshaghian B. Evaluation of cerium doped lutetium oxyorthosilicate (LSO) scintillation crystal for PET. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1992;40:1045–7.
Melcher CL, Schweitzer JS. Cerium-doped lutetium oxyorthosilicate: a fast, efficient new scintillator. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1992;39:502–5.
Cooke DW, McClellan KJ, Bennett BL, Roper JM, Whittaker MT, Muenchausen RE. Crystal growth and optical characterization of cerium-doped Lu Y SiO. J Appl Phys. 2000;88:7360–2.
Kimble T, Chou M, Chai BHT. Scintillation properties of LYSO crystals. Proc IEEE Nuclear Science Symp Conf. 2002;3:1434–7.
Shimizu S, Pepin CM, Lecomte R. Assessment of (LGSO) scintillators with APD readout for PET/SPECT/CT detectors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2010;57:1512–7.
https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Xcom/html/xcom1.html. Accessed Oct 2017
Yazaki Y, Inadama N, Nishikido F, Mitsuhashi T, Suga M, Shibuya K, Watanabe M, Yamashita T, Yoshida E, Murayama H, Yamaya T. Development of the X’tal cube: a 3D position-sensitive radiation detector with all-surface MPPC readout. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2012;59:462–8.
Yamaya T, Mitsuhashi T, Matsumoto T, et al. A SiPM-based isotropic-3D PET detector X’tal cube with a three-dimensional array of 1 mm3 crystals. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:6793–807.
Naoko I, Takahiro M, et al. X’tal cube PET detector composed of a stack of scintillator plates segmented by laser processing. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014;59:53–9.
Nitta M, Inadama N, Hirano Y, Nishikido F, Yoshida E, Tashima H, Kawai H, Yamaya T. Development of the X’tal cube PET detector with segments of (0.77 mm). IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2018;2:564–73.
Vandenbroucke A, Foudray AMK, Olcott PD, Levin CS. Performance characterization of a new high-resolution PET scintillation detector. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:5895–911.
Moriya T, Fukumitsu K, Yamashita T, Watanabe M. Fabrication of finely pitched LYSO arrays using subsurface laser engraving technique with picosecond and nanosecond pulse lasers. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014;61:1032–8.
Agostinelli S, et al. Geant4—a simulation toolkit Nucl. Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 2003;506:250–303.
van der Laan DJ, Schaart DR, Maas MC, Beekman FJ, Bruyndonckx P, van Eijk CW. Optical simulation of monolithic scintillator detectors using GATE/GEANT4. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:1659–75.
Mao R, Zhang L, Zhu R-Y. Emission spectra of LSO and LYSO crystals excited by UV Light, X-ray and -ray. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2008;55:1759–66.
Ogata Y, Ohnishi T, Moriya T, Inadama N, Nishikido F, Yoshida E, Murayama H, Yamaya T. Hideaki Haneishi “GPU-based optical propagation simulator of a laser-processed crystal block for the X’tal cube PET detector.” Radiol Phys Technol. 2014;7:35–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Ethics approval
No ethical approval from patients was needed for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Nitta, M., Nishikido, F., Inadama, N. et al. Discrimination of inter-crystal scattering events by signal processing for the X'tal cube PET detector. Radiol Phys Technol 16, 516–531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00740-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00740-3