Abstract
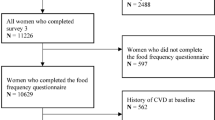
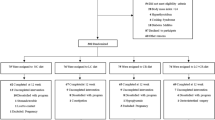
A growing number of observational studies have been carried out on the relationship between serum magnesium and risk of dyslipidemia, but their results were conflicting. This study aimed to investigate the association between serum magnesium levels and risk of dyslipidemia in Chinese adult residents. We used data from the China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) in the wave of 2009 to conduct a cross-sectional study. A total of 8,457 participants (47.2% male) with a mean age of 50.5 years were assessed and divided into 4 groups based on quartiles of serum magnesium levels. We found that higher quartiles of serum magnesium were associated with increased prevalence of dyslipidemia. After adjustment for confounders, the results of logistic regression analyses indicated that there was an increased trend in dyslipidemia risk as quartiles of serum magnesium increased. The restricted cubic spline model revealed a nonlinear relationship between serum magnesium levels and dyslipidemia. In subgroup analyses, the positive relationship between serum magnesium levels and dyslipidemia was more significant in females than in males. Our study suggested that serum magnesium levels were positively associated with risk of dyslipidemia in Chinese adult population. Further research is needed to provide a deep understanding of the underlying mechanism of magnesium on lipid metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available at the website (http://www.cpc.unc.edu/projects/china/home.html).
References
Pirillo A, Casula M, Olmastroni E, Norata G-D, Catapano A-L (2021) Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias. Nat Rev Cardiol 18:689–700
Ference B-A, Graham I, Tokgozoglu L, Catapano A-L (2018) Impact of Lipids on Cardiovascular Health: JACC Health Promotion Series. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:1141–1156
Mehta A, Shapiro M-D (2022) Apolipoproteins in vascular biology and atherosclerotic disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 19:168–179
National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on Chinese Nutrition and Chronic Diseases (2020) National Health Commission Bureau for Disease Control and Prevention. Beijing, China, p 5
Opoku S, Gan Y, Yobo E-A, Tenkorang-Twum D, Yue W, Wang Z, Lu Z et al (2021) Awareness, treatment, control, and determinants of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Sci Rep 11:10056
Fiorentini D, Cappadone C, Farruggia G, Prata C (2021) Magnesium: biochemistry, nutrition, detection, and social impact of diseases linked to its deficiency. Nutrients 13(4):1136
Elin R-J (1988) Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Dis Mon 34:161–218
Zhang Q, Zhou P-H, Zhou X-L, Zhang D-L, Gu Q, Zhang S-J, Qian Z-Y et al (2018) Effect of magnesium gluconate administration on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, and related gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet. Magnes Res 31:117–130
Chen S, Luo S, Zou B, Xie J, Li J, Zeng Y et al (2023) Magnesium supplementation stimulates autophagy to reduce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 201:3311–3322
Kurstjens S, van Diepen J-A, Overmars-Bos C, Alkema W, Bindels RJM, Ashcroft F-M, de Baaij JHF et al (2018) Magnesium deficiency prevents high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice. Diabetologia 61:2030–2042
Găman M-A, Dobrică E-C, Cozma M-A, Antonie N-I, Stănescu AMA, Găman A-M, Diaconu C-C et al (2021) Crosstalk of magnesium and serum lipids in dyslipidemia and associated disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients 13(5):1411
Zhao S-P (2016) [Key points and comments on the 2016 Chinese guideline for the management of dyslipidemia in adults]. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 44:827–829
Randell E-W, Mathews M, Gadag V, Zhang H, Sun G (2008) Relationship between serum magnesium values, lipids and anthropometric risk factors. Atherosclerosis 196:413–419
Cao Y, Wang C, Guan K, Xu Y, Su Y-X, Chen Y-M et al (2016) Association of magnesium in serum and urine with carotid intima-media thickness and serum lipids in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: a community-based cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr 55:219–26
Liu A, Xu P, Gong C, Zhu Y, Zhang H, Nie W, Zhou J-C et al (2020) High serum concentration of selenium, but not calcium, cobalt, copper, iron, and magnesium, increased the risk of both hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in adults: A health examination center based cross-sectional study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 59:126470
Alkazemi D, Alsouri N, Zafar T, Kubow S (2022) Hypomagnesemia and the metabolic syndrome among apparently healthy Kuwaiti adults: a cross-sectional study. Nutrients 14(24):5257
Corica F, Corsonello A, Ientile R, Cucinotta D, Di Benedetto A, Perticone F, Barbagallo M et al (2006) Serum ionized magnesium levels in relation to metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. J Am Coll Nutr 25:210–5
Barragán R, Llopis J, Portolés O, Sorlí J-V, Coltell O, Rivas-García L, Sánchez-González C et al (2020) Influence of demographic and lifestyle variables on plasma magnesium concentrations and their associations with cardiovascular risk factors in a Mediterranean population. Nutrients 12(4):1018
Liu M, Dudley SC-Jr, (2020) Magnesium, oxidative stress, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(10):907
Oost L-J, Tack C-J, de Baaij JHF (2023) Hypomagnesemia and cardiovascular risk in Type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 44:357–378
Rooney M-R, Alonso A, Folsom A-R, Michos E-D, Rebholz C-M, Misialek J-R, Lutsey P-L et al (2020) Serum magnesium and the incidence of coronary artery disease over a median 27 years of follow-up in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study and a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 111:52–60
Song Y, He K, Levitan E-B, Manson J-E, Liu S (2006) Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on glycaemic control in Type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled trials. Diabet Med 23:1050–6
Salehidoost R, Taghipour Boroujeni G, Feizi A, Aminorroaya A, Amini M (2022) Effect of oral magnesium supplement on cardiometabolic markers in people with prediabetes: a double blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Sci Rep 12:18209
Sadeghian M, Azadbakht L, Khalili N, Mortazavi M, Esmaillzadeh A (2020) Oral magnesium supplementation improved lipid profile but increased insulin resistance in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 193:23–35
Nartea R, Mitoiu B-I, Ghiorghiu I (2023) The link between magnesium supplements and statin medication in dyslipidemic patients. Curr Issues Mol Biol 45:3146–3167
Schutten J-C, Joris P-J, Groendijk I, Eelderink C, Groothof D, van der Veen Y, Bakker SJL et al (2022) Effects of magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide, and magnesium sulfate supplementation on arterial stiffness: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial. J Am Heart Assoc 11:e021783
Bressendorff I, Hansen D, Schou M, Kragelund C, Svensson M, Hashemi B, Brandi L et al (2023) The effect of magnesium supplementation on vascular calcification in CKD: a randomized clinical trial (MAGiCAL-CKD). J Am Soc Nephrol 34:886–894
Rosanoff A, West C, Elin R-J, Micke O, Baniasadi S, Barbagallo M, Wolf F et al (2022) Recommendation on an updated standardization of serum magnesium reference ranges. Eur J Nutr 61:3697–3706
Costello R-B, Elin R-J, Rosanoff A, Wallace T-C, Guerrero-Romero F, Hruby A, Van Horn L-V et al (2016) Perspective: the case for an evidence-based reference interval for serum magnesium: the time has come. Adv Nutr 7:977–993
Rosanoff A, Seelig M-S (2004) Comparison of mechanism and functional effects of magnesium and statin pharmaceuticals. J Am Coll Nutr 23:501S-505S
Rosner M-H, Ha N, Palmer B-F, Perazella M-A (2023) Acquired disorders of hypomagnesemia. Mayo Clin Proc 98:581–596
Huijgen H-J, Soesan M, Sanders R, Mairuhu W-M, Kesecioglu J, Sanders G-T et al (2000) Magnesium levels in critically ill patients. What should we measure? Am J Clin Pathol 114:688–695
Casal H-L, Mantsch H-H, Hauser H (1989) Infrared and 31P-NMR studies of the interaction of Mg2+ with phosphatidylserines: effect of hydrocarbon chain unsaturation. Biochim Biophys Acta 982:228–36
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express sincere appreciation to the Institutional Review Board of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the National Institute for Nutrition and Food safety at China Center for Disease Control and Prevention for providing original data publicly available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both Yang Liu and Shizhen Li contributed to the design, methodology, interpretation, and writing of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, S. Association between Serum Magnesium Levels and Risk of Dyslipidemia: A Cross-Sectional Study from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 2410–2418 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03846-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03846-2