Abstract
Introduction
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is the fifth most common cancer globally. Diagnosis at early stages are critical to reduce mortality and improve functional and esthetic outcomes associated with HNC. Metabolomics is a promising approach for discovery of biomarkers and metabolic pathways for risk assessment and early detection of HNC.
Objectives
To summarize and consolidate the available evidence on metabolomics and HNC in plasma/serum, saliva, and urine.
Methods
A systematic search of experimental research was executed using PubMed and Web of Science. Available data on areas under the curve was extracted. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis were performed to identify metabolic pathways altered in HNC. Fifty-four studies were eligible for data extraction (33 performed in plasma/serum, 15 in saliva and 6 in urine).
Results
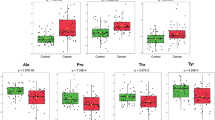
Metabolites with high discriminatory performance for detection of HNC included single metabolites and combination panels of several lysoPCs, pyroglutamate, glutamic acid, glucose, tartronic acid, arachidonic acid, norvaline, linoleic acid, propionate, acetone, acetate, choline, glutamate and others. The glucose-alanine cycle and the urea cycle were the most altered pathways in HNC, among other pathways (i.e. gluconeogenesis, glycine and serine metabolism, alanine metabolism, etc.). Specific metabolites that can potentially serve as complementary less- or non-invasive biomarkers, as well as metabolic pathways integrating the data from the available studies, are presented.
Conclusion
The present work highlights utility of metabolite-based biomarkers for risk assessment, early detection, and prognostication of HNC, as well as facilitates incorporation of available metabolomics studies into multi-omics data integration and big data analytics for personalized health.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aemaimanan, P., Sattayasai, N., Wara-aswapati, N., Pitiphat, W., Suwannarong, W., Prajaneh, S., & Taweechaisupapong, S. (2009). Alanine aminopeptidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in saliva of chronic periodontitis patients. Journal of Periodontology, 80(11), 1809–1814. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.090233
Allen, T. W. (1991). Guide to clinical preventive services. Report of the US Preventive Services Task Force. Journal of American Osteopathic Association, 91(3), 281–289.
Ananieva, E. A., & Wilkinson, A. C. (2018). Branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 21(1), 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000430
Arlauckas, S. P., Popov, A. V., & Delikatny, E. J. (2016). Choline kinase alpha-putting the ChoK-hold on tumor metabolism. Progress in Lipid Research, 63, 28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2016.03.005
Armitage, E. G., & Barbas, C. (2014). Metabolomics in cancer biomarker discovery: Current trends and future perspectives. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 87, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.08.041
Askari, M., Darabi, M., Zare Mahmudabadi, R., Oboodiat, M., Fayezi, S., Mostakhdemin Hosseini, Z., & Pirzadeh, A. (2015). Tissue fatty acid composition and secretory phospholipase-A2 activity in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical and Translational Oncology, 17(5), 378–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1242-2
Aversa, Z., Costelli, P., & Muscaritoli, M. (2017). Cancer-induced muscle wasting: Latest findings in prevention and treatment. Therapeutic Advances Medical Oncology, 9(5), 369–382. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758834017698643
Badawy, A. A. (2017). Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: Regulatory and functional aspects. International Journal of Tryptophan Research, 10, 1178646917691938. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646917691938
Bag, S., Banerjee, D. R., Basak, A., Das, A. K., Pal, M., Banerjee, R., & Chatterjee, J. (2015). NMR ((1)H and (13)C) based signatures of abnormal choline metabolism in oral squamous cell carcinoma with no prominent Warburg effect. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 459(4), 574–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.149
Boguszewicz, Ł, Bieleń, A., Ciszek, M., Wendykier, J., Szczepanik, K., Skorupa, A., & Sokół, M. (2021a). NMR-based metabolomics in investigation of the radiation induced changes in blood serum of head and neck cancer patients and its correlation with the tissue volumes exposed to the particulate doses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126310
Boguszewicz, Ł, Bieleń, A., Jarczewski, J. D., Ciszek, M., Skorupa, A., Składowski, K., & Sokół, M. (2021b). Molecular response to induction chemotherapy and its correlation with treatment outcome in head and neck cancer patients by means of NMR-based metabolomics. BMC Cancer, 21(1), 410. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08137-4
Boguszewicz, Ł, Bieleń, A., Mrochem-Kwarciak, J., Skorupa, A., Ciszek, M., Heyda, A., & Sokół, M. (2019). NMR-based metabolomics in real-time monitoring of treatment induced toxicity and cachexia in head and neck cancer: a method for early detection of high risk patients. Metabolomics, 15(8), 110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1576-4
Boguszewicz, Ł., Hajduk, A., Mrochem-Kwarciak, J., Skorupa, A., Ciszek, M., Heyda, A., Składowski, K., & Sokół, M. (2016). 1H NMR based metabolomic approach to monitoring of the head and neck cancer treatment toxicity. Metabolomics, 12, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1043-4
Borin, T. F., Angara, K., Rashid, M. H., Achyut, B. R., & Arbab, A. S. (2017). Arachidonic acid metabolite as a novel therapeutic target in breast cancer metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18, 2661.
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 68(6), 394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Cadoni, G., Giraldi, L., Chiarla, C., Gervasoni, J., Persichilli, S., Primiano, A., & Almadori, G. (2020). Prognostic role of serum amino acids in head and neck cancer. Disease Markers, 2020, 2291759. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2291759
Chen, J., Hou, H., Chen, H., Luo, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., & Hu, Q. (2019). Urinary metabolomics for discovering metabolic biomarkers of laryngeal cancer using UPLC-QTOF/MS. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 167, 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.01.035
Chen, X., & Yu, D. (2019). Metabolomics study of oral cancers. Metabolomics, 15(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1483-8
Chen, Z., Gao, Y., Huang, X., Yao, Y., Chen, K., Zeng, S., & Mao, W. (2021). Tissue-based metabolomics reveals metabolic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 197, 113937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2021.113937
Cheng, J., Jin, H., Hou, X., Lv, J., Gao, X., & Zheng, G. (2017). Disturbed tryptophan metabolism correlating to progression and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 486(3), 781–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.120
Chiarugi, A., Dölle, C., Felici, R., & Ziegler, M. (2012). The NAD metabolome—a key determinant of cancer cell biology. Nature Reviews Cancer, 12(11), 741–752. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3340
Chong, J., Soufan, O., Li, C., Caraus, I., Li, S., Bourque, G., & Xia, J. (2018). MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 46, W486–W494. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky310
Christou, C. N., Tiblom Ehrsson, Y., Lampa, E., Risérus, U., & Laurell, G. (2021). Circulating fatty acids in patients with head and neck cancer after treatment: An explorative study with a one-year perspective. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 141(9), 878–884. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2021.1959950
Da, M., Zhuang, J., Zhou, Y., Qi, Q., & Han, S. (2021). Role of long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 in cancers. Molecular Medicine, 27(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00312-4
Daniel, C. R., McCullough, M. L., Patel, R. C., Jacobs, E. J., Flanders, W. D., Thun, M. J., & Calle, E. E. (2009). Dietary intake of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids and risk of colorectal cancer in a prospective cohort of U.S. men and women. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 18(2), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0750
de Sá Alves, M., de Sá Rodrigues, N., Bandeira, C. M., Chagas, J. F. S., Pascoal, M. B. N., Nepomuceno, G. L. J. T., & Almeida, J. D. (2021). Identification of possible salivary metabolic biomarkers and altered metabolic pathways in South American patients diagnosed with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11100650
DeFelice, B. C., Fiehn, O., Belafsky, P., Ditterich, C., Moore, M., Abouyared, M., & Anderson, J. D. (2022). Polyamine metabolites as biomarkers in head and neck cancer biofluids. Diagnostics, 12(4), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040797
Diamant, A., Chatterjee, A., Vallières, M., Shenouda, G., & Seuntjens, J. (2019). Deep learning in head & neck cancer outcome prediction. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39206-1
Du, E., Mazul, A. L., Farquhar, D., Brennan, P., Anantharaman, D., Abedi-Ardekani, B., & Zevallos, J. P. (2019). Long-term survival in head and neck cancer: Impact of site, stage, smoking, and human papillomavirus status. The Laryngoscope, 129(11), 2506–2513. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27807
Dupertuis, Y. M., Meguid, M. M., & Pichard, C. (2007). Colon cancer therapy: New perspectives of nutritional manipulations using polyunsaturated fatty acids. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 10(4), 427–432. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e3281e2c9d4
Eldridge, R. C., Uppal, K., Hayes, D. N., Smith, M. R., Hu, X., Qin, Z. S., & Xiao, C. (2021). Plasma metabolic phenotypes of HPV-associated versus smoking-associated head and neck cancer and patient survival. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 30(10), 1858–1866. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0576
Elmore, L. W., Greer, S. F., Daniels, E. C., Saxe, C. C., Melner, M. H., Krawiec, G. M., & Phelps, W. C. (2021). Blueprint for cancer research: Critical gaps and opportunities. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(2), 107–139. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21652
Enomoto, Y., Kimoto, A., Suzuki, H., Nishiumi, S., Yoshida, M., & Komori, T. (2018). Exploring a novel screening method for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: A plasma metabolomics analysis. Kobe Journal of Medical Sciences, 64(1), E26–E35.
Felig, P. (1973). The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism, 22(2), 179–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0495(73)90269-2
Feng, Z., & Pepe, M. S. (2020). Adding rigor to biomarker evaluations-EDRN experience. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 29(12), 2575–2582. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-0240
Gaál Kovalčíková, A., Pančíková, A., Konečná, B., Klamárová, T., Novák, B., Kovaľová, E., & Tóthová, Ľ. (2019). Urea and creatinine levels in saliva of patients with and without periodontitis. European Journal of Oral Sciences, 127(5), 417–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/eos.12642
Gibellini, F., & Smith, T. K. (2010). The Kennedy pathway–De novo synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. IUBMB Life, 62(6), 414–428. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.337
Gomes, J. M., Almeida, T. F. A., da Silva, T. A., de Lourdes Cardeal, Z., & Menezes, H. C. (2020). Saliva biomonitoring using LPME-GC/MS method to assess dentistry exposure to plasticizers. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 412(28), 7799–7810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02908-x
Grapov, D., Fahrmann, J., Wanichthanarak, K., & Khoomrung, S. (2018). Rise of deep learning for genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data integration in precision medicine. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 22(10), 630–636. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2018.0097
Grapov, D., Wanichthanarak, K., & Fiehn, O. (2015). MetaMapR: Pathway independent metabolomic network analysis incorporating unknowns. Bioinformatics, 31(16), 2757–2760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv194
Guasch-Ferré, M., Hruby, A., Toledo, E., Clish, C. B., Martínez-González, M. A., Salas-Salvadó, J., & Hu, F. B. (2016). Metabolomics in prediabetes and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 39(5), 833–846. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-2251
Gupta, A., Gupta, S., & Mahdi, A. A. (2015). 1H NMR-derived serum metabolomics of leukoplakia and squamous cell carcinoma. Clinica Chimica Acta, 441, 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.12.003
Halczy-Kowalik, L., Drozd, A., Stachowska, E., Drozd, R., Żabski, T., & Domagała, W. (2019). Fatty acids distribution and content in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and its adjacent microenvironment. PLoS ONE, 14(6), e0218246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218246
Hao, Y., Li, D., Xu, Y., Ouyang, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Qin, G. (2019). Investigation of lipid metabolism dysregulation and the effects on immune microenvironments in pan-cancer using multiple omics data. BMC Bioinformatics, 20(Suppl 7), 195. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-2734-4
Harrigan, G. G., & Goodacre, R. (Eds.). (2003). Metabolic profiling: its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis: Its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis. Springer Science & Business Media.
Hayden, J. A., Côté, P., & Bombardier, C. (2006). Evaluation of the quality of prognosis studies in systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine, 144(6), 427–437. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-144-6-200603210-00010
He, X., Liu, S., Lai, W., Yan, B., Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Liu, S., Chen, L., Shi, Y., & Tao, Y. (2016). The simultaneous determination of tricarboxylic acid cycle acids and 2-hydroxyglutarate in serum from patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma via gc–MS. Chromatographia, 79, 501–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3061-9
Huang, Y., Liang, J., Hu, W., Liang, Y., Xiao, X., Zhao, W., & Cai, Y. (2022). Integration profiling between plasma lipidomics, epstein-barr virus and clinical phenomes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Frontiers in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.919496
Huxtable, R. J. (1992). Physiological actions of taurine. Physiological Reviews, 72(1), 101–163. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1992.72.1.101
Ishikawa, S., Sugimoto, M., Kitabatake, K., Sugano, A., Nakamura, M., Kaneko, M., & Iino, M. (2016). Identification of salivary metabolomic biomarkers for oral cancer screening. Science and Reports, 6, 31520. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31520
Ishikawa, S., Sugimoto, M., Kitabatake, K., Tu, M., Sugano, A., Yamamori, I., & Iino, M. (2017). Effect of timing of collection of salivary metabolomic biomarkers on oral cancer detection. Amino Acids, 49(4), 761–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2378-5
Ishikawa, S., Wong, D. T. W., Sugimoto, M., Gleber-Netto, F. O., Li, F., Tu, M., Zhang, Y., Akin, D. & Iino, M. (2019). Identification of salivary metabolites for oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral epithelial dysplasia screening from persistent suspicious oral mucosal lesions. Clinical Oral Investigations, 23, 3557–3563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2777-3
Jelonek, K., Krzywon, A., Jablonska, P., Slominska, E. M., Smolenski, R. T., Polanska, J., & Widlak, P. (2020). Systemic effects of radiotherapy and concurrent chemo-radiotherapy in head and neck cancer patients-comparison of serum metabolome profiles. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10020060
Jelonek, K., Krzywon, A., Papaj, K., Polanowski, P., Szczepanik, K., Skladowski, K., & Widlak, P. (2021). Dose-dependence of radiotherapy-induced changes in serum levels of choline-containing phospholipids; the importance of lower doses delivered to large volumes of normal tissues. Strahlentherapie Und Onkologie, 197(10), 926–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-021-01802-4
Jelonek, K., Pietrowska, M., Ros, M., Zagdanski, A., Suchwalko, A., Polanska, J., & Widlak, P. (2014). Radiation-induced changes in serum lipidome of head and neck cancer patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(4), 6609–6624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046609
Kamarajan, P., Rajendiran, T. M., Kinchen, J., Bermúdez, M., Danciu, T., & Kapila, Y. L. (2017). Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metabolism draws on glutaminolysis, and stemness is specifically regulated by glutaminolysis via aldehyde dehydrogenase. Journal of Proteome Research, 16(3), 1315–1326. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00936
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., & Yamanishi, Y. (2008). KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, 480–484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm882
Kim, D. H., Kim, S. W., Lee, J., & Hwang, S. H. (2021). Narrow-band imaging for screening of oral premalignant or cancerous lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Otolaryngology, 46(3), 501–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/coa.13724
Kunkel, M., Reichert, T. E., Benz, P., Lehr, H. A., Jeong, J. H., Wieand, S., & Whiteside, T. L. (2003). Overexpression of Glut-1 and increased glucose metabolism in tumors are associated with a poor prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer, 97(4), 1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.11159
Lash, T. L., Rothman, K. J., et al. (2021). Modern epidemiology (4th ed.). Dordrecht: Wolters Kluwer.
Lasisi, T. J., Raji, Y. R., & Salako, B. L. (2016). Salivary creatinine and urea analysis in patients with chronic kidney disease: A case control study. BMC Nephrology, 17, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-016-0222-x
Laus, A. C., da Silva, I. D. C. G., Cordeiro, F. B., Lo Turco, E. G., de Souza Viana, L., & Carvalho, A. L. (2018). Is Lipidomic the answer to the search of a biomarker for organ preservation protocol in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma? Pathology & Oncology Research, 24(4), 931–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0336-x
Li, W., Li, Y., Chen, Z., Lam, A. K. Y., Li, Z., Liu, X., & Qiao, B. (2022). Analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics data in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.14125
Liao, Z., Zhao, L., Zhong, F., Zhou, Y., Lu, T., Liu, L., & Rao, J. (2023). Serum and urine metabolomics analyses reveal metabolic pathways and biomarkers in relation to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.9469
Lima, I. F. P., Brand, L. M., de Figueiredo, J. A. P., Steier, L., & Lamers, M. L. (2021). Use of autofluorescence and fluorescent probes as a potential diagnostic tool for oral cancer: A systematic review. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 33, 102073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102073
Lohavanichbutr, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Gu, H., Nagana Gowda, G. A., Djukovic, D., & Chen, C. (2018). Salivary metabolite profiling distinguishes patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma from normal controls. PLoS ONE, 13(9), e0204249. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204249
Ma, C., Fan, L., Wang, J., Hao, L., & He, J. (2019). Hippo/Mst1 overexpression induces mitochondrial death in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via activating β-catenin/Drp1 pathway. Cell Stress and Chaperones, 24(4), 807–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-01008-9
Marcinkiewicz, J., & Kontny, E. (2014). Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids, 46(1), 7–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1361-4
Mayers, J. R., Wu, C., Clish, C. B., Kraft, P., Torrence, M. E., Fiske, B. P., & Wolpin, B. M. (2014). Elevation of circulating branched-chain amino acids is an early event in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma development. Nature Medicine, 20(10), 1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3686
Mikkonen, J. J. W., Singh, S. P., Akhi, R., Salo, T., Lappalainen, R., González-Arriagada, W. A., & Myllymaa, S. (2018). Potential role of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to identify salivary metabolite alterations in patients with head and neck cancer. Oncology Letters, 16(5), 6795–6800. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9419
Miller, B. L. (1991). A review of chemical issues in 1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-l-aspartate, creatine and choline. NMR in Biomedicine, 4(2), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1940040203
Nakamura, Y., Kodama, H., Satoh, T., Adachi, K., Watanabe, S., Yokote, Y., & Sakagami, H. (2010). Diurnal changes in salivary amino acid concentrations. In Vivo, 24(6), 837–842.
Ohshima, M., Sugahara, K., Kasahara, K., & Katakura, A. (2017). Metabolomic analysis of the saliva of Japanese patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology Reports, 37(5), 2727–2734. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5561
Opitz, P., & Herbarth, O. (2018). The volatilome—investigation of volatile organic metabolites (VOM) as potential tumor markers in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Journal of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery, 47(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0288-5
Perez-Castro, L., Garcia, R., Venkateswaran, N., Barnes, S., & Conacci-Sorrell, M. (2021). Tryptophan and its metabolites in normal physiology and cancer etiology. FEBS Journal. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16245
Pires, F. R., Ramos, A. B., Oliveira, J. B., Tavares, A. S., Luz, P. S., & Santos, T. C. (2013). Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological features from 346 cases from a single oral pathology service during an 8-year period. Journal of Applied Oral Science, 21(5), 460–467. https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-775720130317
Rahman, M. A., Haron, D. E. M., Hollows, R. J., Ghani, Z. D. F. A., Mohd, M. A., Chai, W. L., Ng, C. C., Lye, M. S., Karsani, S. A., Yap, L. F., & Paterson, I. C. (2020). Profiling lysophosphatidic acid levels in plasma from head and neck cancer patients. PeerJ, 8, e9304. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9304
Ripps, H., & Shen, W. (2012). Review: Taurine: A “very essential” amino acid. Molecular Vision, 18, 2673–2686.
Rodríguez-Tomàs, E., Arguís, M., Arenas, M., Fernández-Arroyo, S., Murcia, M., Sabater, S., & Joven, J. (2020). Alterations in plasma concentrations of energy-balance-related metabolites in patients with lung, or head & neck, cancers: Effects of radiotherapy. Journal of Proteomics, 213, 103605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103605
Roś-Mazurczyk, M., Wojakowska, A., Marczak, Ł., Polański, K., Pietrowska, M., Jelonek, K., Widłak, P. (2017). Ionizing radiation affects profile of serum metabolites: increased level of 3-hydroxybutyric acid in serum of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Acta Biochim Pol, 64(1), 189–193. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2016_1301
Sanchez-Cespedes, M., Esteller, M., Wu, L., Nawroz-Danish, H., Yoo, G. H., Koch, W. M., & Sidransky, D. (2000). Gene promoter hypermethylation in tumors and serum of head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Research, 60(4), 892–895.
Sasaki, E., Masago, K., Fujita, S., Hanai, N., & Yatabe, Y. (2020). Frequent KRAS and HRAS mutations in squamous cell papillomas of the head and neck. J Pathol Clin Res, 6(2), 154–159. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjp2.157
Shah, J. P. S., & Singh, B. (2019). Jatin Shah’s head and neck surgery and oncology (5th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Shahid, N., Iqbal, A., Siddiqui, A. J., Shoaib, M., & Musharraf, S. G. (2019). Plasma metabolite profiling and chemometric analyses of tobacco snuff dippers and patients with oral cancer: Relationship between metabolic signatures. Head and Neck, 41(2), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25511
Šimundić, A. M. (2009). Measures of diagnostic accuracy: Basic definitions. EJIFCC, 19(4), 203–211.
Sivanand, S., & Vander Heiden, M. G. (2020). Emerging roles for branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer. Cancer Cell, 37(2), 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.12.011
Sridharan, G., Ramani, P., Patankar, S., & Vijayaraghavan, R. (2019). Evaluation of salivary metabolomics in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine, 48(4), 299–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12835
Stipanuk, M. H., & Caudill, M. A. (2018). Biochemical, physiological, and molecular aspects of human nutrition. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Sugimoto, M., Wong, D. T., Hirayama, A., Soga, T., & Tomita, M. (2010). Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics, 6(1), 78–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0178-y
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., & Viant, M. R. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics, 3, 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2
Szlasa, W., Zendran, I., Zalesińska, A., Tarek, M., & Kulbacka, J. (2020). Lipid composition of the cancer cell membrane. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 52(5), 321–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09846-4
Taherizadeh, M., Khoshnia, M., Shams, S., Hesari, Z., & Joshaghani, H. (2020). Clinical significance of plasma levels of gluconeogenic amino acids in esophageal cancer patients. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 21(8), 2463–2468. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.8.2463
Tamás, L., Szentkúti, G., Eros, M., Dános, K., Brauswetter, D., Szende, B., & Krenács, T. (2011). Differential biomarker expression in head and neck cancer correlates with anatomical localization. Pathology Oncology Research, 17(3), 721–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9376-9
Tang, F., Xie, C., Huang, D., Wu, Y., Zeng, M., Yi, L., & Sun, L. (2011). Novel potential markers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma for diagnosis and therapy. Clinical Biochemistry, 44(8–9), 711–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.03.025
Tannapfel, A., & Weber, A. (2001). Tumor markers in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Clinical effectiveness and prognostic value. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 258(2), 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050000303
Taware, R., Taunk, K., Pereira, J. A. M., Dhakne, R., Kannan, N., Soneji, D., Câmara, J. S., & Nagarajaram, H. A. (2017). Investigation of urinary volatomic alterations in head and neck cancer: A non-invasive approach towards diagnosis and prognosis. Metabolomics, 13, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1251-6
Taware, R., Taunk, K., Pereira, J. A. M., Shirolkar, A., Soneji, D., Câmara, J. S., & Rapole, S. (2018). Volatilomic insight of head and neck cancer via the effects observed on saliva metabolites. Science and Reports, 8(1), 17725. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35854-x
Thiébaut, A. C., Chajès, V., Gerber, M., Boutron-Ruault, M. C., Joulin, V., Lenoir, G., & Clavel-Chapelon, F. (2009). Dietary intakes of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and the risk of breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 124(4), 924–931. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23980
Tiziani, S., Lopes, V., & Günther, U. L. (2009). Early stage diagnosis of oral cancer using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Neoplasia, 11(3), 269–276, 264. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.81396
Totan, A., Greabu, M., Totan, C., & Spinu, T. (2006). Salivary aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase: Possible markers in periodontal diseases? Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 44(5), 612–615. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2006.096
Troisi, J., Sarno, L., Landolfi, A., Scala, G., Martinelli, P., Venturella, R., & Guida, M. (2018). Metabolomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer. Journal of Proteome Research, 17(2), 804–812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00503
Ueland, P. M. (2011). Choline and betaine in health and disease. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 34(1), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9088-4
Vander Heiden, M. G., & DeBerardinis, R. J. (2017). Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer biology. Cell, 168(4), 657–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.039
Volpe, S., Pepa, M., Zaffaroni, M., Bellerba, F., Santamaria, R., Marvaso, G., & Jereczek-Fossa, B. A. (2021). Machine learning for head and neck cancer: A safe bet?—a clinically oriented systematic review for the radiation oncologist. Frontiers in Oncology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.772663
Wang, L., Wang, X., Li, Y., Hou, Y., Sun, F., Zhou, S., Zhang, B. (2017). Plasma lipid profiling and diagnostic biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget, 8(54), 92324–92332. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21289
Wang, Q., Gao, P., Wang, X., & Duan, Y. (2014). The early diagnosis and monitoring of squamous cell carcinoma via saliva metabolomics. Science and Reports, 4, 6802. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06802
Wang, X. L., Li, C. J., Xing, Y., Yang, Y. H., & Jia, J. P. (2015). Hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia caused by mutations in the branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase gene. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 38(5), 855–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9814-z
Wang, Y., Luo, X., Zhang, G. H., & Li, S. L. (2016). Nuclear magnetic resonance-based study reveals the metabolomics profile of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Genetics and Molecular Research. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15027796
Wang, X., & Li, B. B. (2021). Deep learning in head and neck tumor multiomics diagnosis and analysis: review of the literature. Frontiers in Genetics, 12, 624820. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.624820
Wang, H., Luo, Y., Chen, H., Hou, H., Hu, Q., & Ji, M. (2022). Non-targeted serum lipidomics analysis and potential biomarkers of laryngeal cancer based on UHPLC-QTOF-MS. Metabolites, 12(11), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111087
Wei, J., Xie, G., Zhou, Z., Shi, P., Qiu, Y., Zheng, X., & Jia, W. (2011). Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia. International Journal of Cancer, 129(9), 2207–2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25881
Wojakowska, A., Zebrowska, A., Skowronek, A., Rutkowski, T., Polanski, K., Widlak, P., & Pietrowska, M. (2020). Metabolic profiles of whole serum and serum-derived exosomes are different in head and neck cancer patients treated by radiotherapy. Journal of Personalized Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040229
Xia, Y., Peng, C., Zhou, Z., Cheng, P., Sun, L., Peng, Y., & Xiao, P. (2012). Clinical significance of saliva urea, creatinine, and uric acid levels in patients with chronic kidney disease. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban, 37(11), 1171–1176. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2012.11.016
Xie, G., Chen, T. L., Jia, W., Qiu, Y. P., Shi, P., Xiao, J. Z., Su, M. M., Zhao, A. H., & Zhou, T. Z. (2012). Urine metabolite profiling offers potential early diagnosis of oral cancer. Metabolomics, 8, 220–231.
Xu, Y., Wang, J., Qiu, M., Xu, L., Li, M., Jiang, F., & Yin, R. (2015). Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biology, 36(3), 1643–1651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2763-6
Yatsuoka, W., Ueno, T., Miyano, K., Enomoto, A., Ota, S., Sugimoto, M., & Uezono, Y. (2021). Time-course of salivary metabolomic profiles during radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122631
Yi, L., Dong, N., Shi, S., Deng, B., Yun, Y., Yi, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. RSC advances, 4(103), 59094–59101.https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA09860A
Yi, L., Song, C., Hu, Z., Yang, L., Xiao, L., Yi, B., Jiang, W., Cao, Y. & Sun, L. (2013). A metabolic discrimination model for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its potential role in the therapeutic evaluation of radiotherapy. Metabolomics, 10, 697–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0606-x
Yonezawa, K., Nishiumi, S., Nishiumii, S., Kitamoto-Matsuda, J., Fujita, T., Morimoto, K., Nibu, K. (2013). Serum and tissue metabolomics of head and neck cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 10(5), 233–238.
Yu, B., & Wang, J. (2021). Lipidomics identified lyso-phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of laryngeal cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 646779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.646779
Yu, K. H., & Snyder, M. (2016). Omics profiling in precision oncology. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 15(8), 2525–2536. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.O116.059253
Zabokova Bilbilova, E., Sotirovska Ivkovska, A., & Ambarkova, V. (2012). Correlation between salivary urea level and dental caries. Prilozi, 33(1), 289–302.
Zhang, E., He, X., Yin, D., Han, L., Qiu, M., Xu, T., & De, W. (2016). Increased expression of long noncoding RNA TUG1 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p57. Cell Death & Disease, 7, e2109. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.356
Zhang, H., Wang, L., Hou, Z., Ma, H., Mamtimin, B., Hasim, A., & Sheyhidin, I. (2017). Metabolomic profiling reveals potential biomarkers in esophageal cancer progression using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry platform. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 491(1), 119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.060
Zhang, J., Bowers, J., Liu, L., Wei, S., Gowda, G. A., Hammoud, Z., & Raftery, D. (2012). Esophageal cancer metabolite biomarkers detected by LC-MS and NMR methods. PLoS ONE, 7(1), e30181. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030181
Zhang, X., Hou, H., Chen, H., Liu, Y., Wang, A., & Hu, Q. (2018a). Serum metabolomics of laryngeal cancer based on liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomedical Chromatography, 32(5), e4181. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4181
Zhang, X., Xu, L., Shen, J., Cao, B., Cheng, T., Zhao, T., & Zhang, H. (2013). Metabolic signatures of esophageal cancer: NMR-based metabolomics and UHPLC-based focused metabolomics of blood serum. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1832(8), 1207–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.009
Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Cao, S., Han, X., Wang, Z., Zhao, X., & Lei, D. (2018b). The Long Noncoding RNA TUG1 Promotes Laryngeal Cancer Proliferation and Migration. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 49(6), 2511–2520. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493876
Zhou, J., Xu, B., Huang, J., Jia, X., Xue, J., Shi, X., & Li, W. (2009). 1H NMR-based metabonomic and pattern recognition analysis for detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clinica Chimica Acta, 401(1–2), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2008.10.030
Zhou, W., Feng, X., Ren, C., Jiang, X., Liu, W., Huang, W., & Yao, K. (2013). Over-expression of BCAT1, a c-Myc target gene, induces cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Molecular Cancer, 12, 53. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-53
Funding
The work was financed by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of state support for the creation and development of World-Class Research Centers “Digital Biodesign and Personalized Healthcare” Nº075-15–2022-304. ACC received funding from the Millennium Science Initiative Program, Nº NCS2021_003 and Nº NCS2021_013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author responsibilities: NC and AB conceptualized the review, participated in the design, execution and interpretation of data and drafted the manuscript. NC, HNN, AC-C and AB executed the systematic search. JL, IAL, IRC, DG, JF, MRL, SAA and AB run data analysis on metabolomics and/or interpreted metabolomics data. AC-C provided input on epidemiological aspects. IR-C advised on proper execution of the systematic search and assessed potential for meta-analysis. FC, VF, EK, VS, IR, YR, KS, NM, CM and RP provided general input, with particular emphasis on clinical aspects. All authors read, provided input and approved the final version of the manuscript. AB has final responsibility for all parts of this review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chuchueva, N., Carta, F., Nguyen, H.N. et al. Metabolomics of head and neck cancer in biofluids: an integrative systematic review. Metabolomics 19, 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02038-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02038-2