Abstract
Introduction
Aggressive prolactinomas are life-limiting tumors without a standard of care treatment option after the oral alkylator, temozolomide, fails to provide tumor control.
Methods
We reviewed an institutional database of pituitary tumors for patients with aggressive prolactinomas who progressed following treatment with a dopamine receptor agonist, radiotherapy and temozolomide. Within this cohort, we identified four patients who were treated with everolimus and we report their response to this therapy. Treatment response was determined by a neuroradiologist, who manually performed volumetric assessment and determined treatment response by Response Assessments in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria.
Results
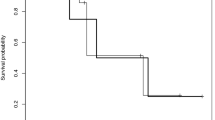
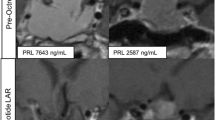
Three of four patients who were treated with everolimus had a biochemical response to therapy and all patients derived a clinically meaningful benefit based upon suppression of tumor growth. While the best overall response as assessed by RANO criteria was stable disease for the four patients, a minor regression in tumor size was appreciated in two of the four patients.
Conclusion
Everolimus is an active agent in the treatment of prolactinomas that warrants further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data and materials availability
Not applicable.
References
Melmed S et al (2011) Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(2):273–288. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-1692
McCormack A et al (2018) Treatment of aggressive pituitary tumours and carcinomas: results of a European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) survey 2016. Eur J Endocrinol 178(3):265–276. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-17-0933
Bengtsson D et al (2015) Long-term outcome and MGMT as a predictive marker in 24 patients with atypical pituitary adenomas and pituitary carcinomas given treatment with temozolomide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1689–1698. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-4350
Burman P et al (2022) Aggressive pituitary tumours and carcinomas, characteristics and management of 171 patients. Eur J Endocrinol 187(4):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-22-0440
Yao JC et al (2011) Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med 364(6):514–523. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1009290
Baselga J et al (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366(6):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1109653
Monsalves E et al (2014) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the pathophysiology and treatment of pituitary adenomas. Endocr Relat Cancer 21(4):R331–R344. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-14-0188
Zhang D et al (2019) Effect of everolimus in treatment of aggressive prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104(6):1929–1936. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-02461
Wen PY et al (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28(11):1963–1972. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.26.3541
Mete O, Lopes MB (2017) Overview of the 2017 WHO classification of pituitary tumors. Endocr Pathol 28(3):228–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-017-9498-z
Asa SL et al (2022) Overview of the 2022 WHO classification of pituitary tumors. Endocr Pathol 33(1):6–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-022-09703-7
Trouillas J et al (2013) A new prognostic clinicopathological classification of pituitary adenomas: a multicentric case-control study of 410 patients with 8 years post-operative follow-up. Acta Neuropathol 126(1):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1084-y
Motzer RJ et al (2010) Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma : final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer 116(18):4256–4265. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25219
White DA et al (2010) Noninfectious pneumonitis after everolimus therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182(3):396–403. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200911-1720OC
Rugo HS et al (2017) Prevention of everolimus-related stomatitis in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer using dexamethasone mouthwash (SWISH): a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(5):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30109-2
Cooper O et al (2014) Prolactinoma ErbB receptor expression and targeted therapy for aggressive tumors. Endocrine 46(2):318–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0093-x
Ben-Jonathan N et al (2009) Estrogen receptor-alpha mediates the epidermal growth factor-stimulated prolactin expression and release in lactotrophs. Endocrinology 150(2):795–802. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-0756
Fukuoka H et al (2011) HER2/ErbB2 receptor signaling in rat and human prolactinoma cells: strategy for targeted prolactinoma therapy. Mol Endocrinol 25(1):92–103. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2010-0353
Cooper O et al (2021) EGFR/ErbB2-targeting lapatinib therapy for aggressive prolactinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106(2):e917–e925. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa805
Gadgeel SM et al (2013) Phase I study evaluating the combination of lapatinib (a Her2/Neu and EGFR inhibitor) and everolimus (an mTOR inhibitor) in patients with advanced cancers: South West Oncology Group (SWOG) Study S0528. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72(5):1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2297-4
Funding
This research was funded in part through the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grand P30 CA008748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of the data. AL—wrote the main manuscript text and prepared the figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Andrew L. Lin reports that he has received funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Robert J. Young reports that he has consulted for Olea Sphere and ICON plc, unrelated to this work. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted using a waiver of informed consent that was approved by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, A.L., Geer, E.B., Lala, N. et al. The treatment of aggressive prolactinomas with everolimus. Pituitary 26, 474–481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-023-01340-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-023-01340-5