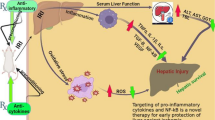
Abstract
Liver injury is a common pathological basis for various liver diseases. Chronic liver injury is often an important initiating factor in liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Currently, hepatitis A and E infections are the most common causes of acute liver injury worldwide, whereas drug toxicity (paracetamol overdose) in the USA and part of Western Europe. In recent years, chronic liver injury has become a common disease that harms human health. Meanwhile, the main causes of chronic liver injury are viral hepatitis (B, C) and long-term alcohol consumption worldwide. During the process of liver injury, massive inflammatory cytokines are stimulated by these hazardous factors, leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome, followed by a compensatory anti-inflammatory response, which causes immune cell dysfunction and sepsis, subsequent multi-organ failure. Cytokine release and immune cell infiltration-mediated aseptic inflammation are the most important features of the pathobiology of liver failure. From this perspective, diminishing the onset and progression of liver inflammation is of clinical importance in the treatment of liver injury. Although many studies have hinted at the critical role of nerves in regulating inflammation, there largely remains undetermined how hepatic nerves mediate immune inflammation and how the inflammatory factors released by these nerves are involved in the process of liver injury. Therefore, the purpose of this article is to summarize previous studies in the field related to hepatic nerve and inflammation as well as future perspectives on the aforementioned questions. Our findings were presented in three aspects: types of nerve distribution in the liver, how these nerves regulate immunity, and the role of liver nerves in hepatitis and liver failure.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Miller, B.M., I.M. Oderberg, and W. Goessling. 2021. Hepatic nervous system in development, regeneration, and disease. Hepatology 74: 3513–3522.
Pereira, M.R., and P.E. Leite. 2016. The involvement of parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve in the inflammatory reflex. Journal of Cellular Physiology 231: 1862–1869.
Terrando, N., T. Yang, J.K. Ryu, P.T. Newton, C. Monaco, M. Feldmann, et al. 2015. Stimulation of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protects against neuroinflammation after tibia fracture and endotoxemia in mice. Molecular Medicine 20: 667–675.
Sanchez-Aleman, E., A. Quintanar-Stephano, G. Escobedo, R. Campos-Esparza Mdel, R. Campos-Rodriguez, and J. Ventura-Juarez. 2015. Vagotomy induces deregulation of the inflammatory response during the development of amoebic liver abscess in hamsters. NeuroImmunoModulation 22 (3): 166–180.
de Jonge, W.J., E.P. van der Zanden, F.O. The, M.F. Bijlsma, D.J. van Westerloo, R.J. Bennink, et al. 2005. Stimulation of the vagus nerve attenuates macrophage activation by activating the Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Nature Immunology 6: 844–851.
Nishio, T., K. Taura, K. Iwaisako, Y. Koyama, K. Tanabe, G. Yamamoto, et al. 2017. Hepatic vagus nerve regulates Kupffer cell activation via alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology 52: 965–976.
Leroux, A., G. Ferrere, V. Godie, F. Cailleux, M.L. Renoud, F. Gaudin, et al. 2012. Toxic lipids stored by Kupffer cells correlates with their pro-inflammatory phenotype at an early stage of steatohepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 57: 141–149.
Diehl, A.M., and C. Day. 2017. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 377: 2063–2072.
Lau, J.K., X. Zhang, and J. Yu. 2017. Animal models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current perspectives and recent advances. The Journal of Pathology 241: 36–44.
Tilg, H., and A.R. Moschen. 2010. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 52: 1836–1846.
Pavlov, V.A., and K.J. Tracey. 2012. The vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex–linking immunity and metabolism. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology 8: 743–754.
Lambert, G.W., N.E. Straznicky, E.A. Lambert, J.B. Dixon, and M.P. Schlaich. 2010. Sympathetic nervous activation in obesity and the metabolic syndrome–causes, consequences and therapeutic implications. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 126: 159–172.
Hurr, C., H. Simonyan, D.A. Morgan, K. Rahmouni, and C.N. Young. 2019. Liver sympathetic denervation reverses obesity-induced hepatic steatosis. Journal of Physiology 597: 4565–4580.
Lyudmila, V., S.I. Borovikova. 2019.Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 458–62.
Torres, H., C. Huesing, D.H. Burk, A.J.R. Molinas, W.L. Neuhuber, H.R. Berthoud, et al. 2021. Sympathetic innervation of the mouse kidney and liver arising from prevertebral ganglia. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 321: R328–R337.
Jensen, K.J., G. Alpini, and S. Glaser. 2013. Hepatic nervous system and neurobiology of the liver. Comprehensive Physiology 3: 655–665.
McCuskey, R.S. 2004. Anatomy of efferent hepatic nerves. The Anatomical Record. Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology 280: 821–826.
Pavlov, V.A., and K.J. Tracey. 2017. Neural regulation of immunity: Molecular mechanisms and clinical translation. Nature Neuroscience 20: 156–166.
Metz, C.N., and V.A. Pavlov. 2018. Vagus nerve cholinergic circuitry to the liver and the gastrointestinal tract in the neuroimmune communicatome. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 315: 651–658.
Chavan, S.S., V.A. Pavlov, and K.J. Tracey. 2017. Mechanisms and therapeutic relevance of neuro-immune communication. Immunity 46: 927–942.
Rosas-Ballina, M., and K.J. Tracey. 2009. Cholinergic control of inflammation. Journal of Internal Medicine 265 (6): 663–679.
Bonaz, B., V. Sinniger, S. Pellissier. 2019. Vagus nerve stimulation at the interface of brain-gut interactions. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 9(8).
Fonseca, R.C., G.S. Bassi, C.C. Brito, L.B. Rosa, B.A. David, A.M. Araujo, et al. 2019. Vagus nerve regulates the phagocytic and secretory activity of resident macrophages in the liver. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 81: 444–454.
Fernandez, R., G. Nardocci, C. Navarro, E.P. Reyes, C. Acuna-Castillo, P.P. Cortes. 2014. Neural reflex regulation of systemic inflammation: potential new targets for sepsis therapy. Frontiers in Physiology 5:489–98.
Kim, H.H., Y.R. Shim, S.E. Choi, M.H. Kim, G. Lee, H.J. You, et al. 2023. Catecholamine induces Kupffer cell apoptosis via growth differentiation factor 15 in alcohol-associated liver disease. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 55: 158–170.
Chida, Y., N. Sudo, A. Takaki, and C. Kubo. 2005. The hepatic sympathetic nerve plays a critical role in preventing Fas induced liver injury in mice. Gut 54: 994–1002.
Pavlov, V.A., S.S. Chavan, and K.J. Tracey. 2018. Molecular and functional neuroscience in immunity. Annual Review of Immunology 36: 783–812.
Stoyanova, I.I., and M.V. Gulubova. 1998. Peptidergic nerve fibres in the human liver. Acta Histochemica 100: 245–256.
Streba, L.A., C.C. Vere, A.G. Ionescu, C.T. Streba, and I. Rogoveanu. 2014. Role of intrahepatic innervation in regulating the activity of liver cells. World Journal of Hepatology 6: 137–143.
Stoyanova, I.I., and M.V. Gulubova. 2000. Immunocytochemical study on the liver innervation in patients with cirrhosis. Acta Histochemica 102: 391–402.
Marra, F., and F. Tacke. 2014. Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology 147: 577–594.
Liu, M., S. Cao, L. He, J. Gao, J.P. Arab, H. Cui, et al. 2021. Super enhancer regulation of cytokine-induced chemokine production in alcoholic hepatitis. Nature Communications 12: 14.
Heydtmann, M., P.F. Lalor, J.A. Eksteen, S.G. Hubscher, M. Briskin, and D.H. Adams. 2005. CXC chemokine ligand 16 promotes integrin-mediated adhesion of liver-infiltrating lymphocytes to cholangiocytes and hepatocytes within the inflamed human liver. The Journal of Immunology 174: 1055–1062.
Nagata, N., G. Chen, L. Xu, and H. Ando. 2022. An update on the chemokine system in the development of NAFLD. Medicina (Kaunas) 58(761–771).
Landsman, L., L. Bar-On, A. Zernecke, K.W. Kim, R. Krauthgamer, E. Shagdarsuren, et al. 2009. CX3CR1 is required for monocyte homeostasis and atherogenesis by promoting cell survival. Blood 113: 963–972.
Roh, Y.S., and E. Seki. 2018. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in the development of NAFLD. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 1061: 45–53.
Aoyama, T., S. Inokuchi, D.A. Brenner, and E. Seki. 2010. CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 52: 1390–1400.
Chaudhry, S., J. Emond, and A. Griesemer. 2019. Immune cell trafficking to the liver. Transplantation 103: 1323–1337.
Kandilis, A.N., I.P. Papadopoulou, J. Koskinas, G. Sotiropoulos, and D.G. Tiniakos. 2015. Liver innervation and hepatic function: New insights. Journal of Surgical Research 194: 511–519.
Ishii, K., M. Shimizu, H. Karube, A. Shibuya, H. Shibata, M. Okudaira, H. Nagata, and M. Tsuchiya. 1992. Inhibitory effect of noradrenaline on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in the rat. Journal of Autonomic Nervous System.
Lin, J.C., Y.J. Peng, S.Y. Wang, M.J. Lai, T.H. Young, D.M. Salter, et al. 2016. Sympathetic nervous system control of carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in liver through alpha-adrenergic signaling. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2016: 3190617.
Lin, J.C., Y.J. Peng, S.Y. Wang, T.H. Young, D.M. Salter, and H.S. Lee. 2015. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and systemic inflammation. PLoS ONE 10: 18.
Lin, J.C., Y.J. Peng, S.Y. Wang, M.J. Lai, T.H. Young, D.M. Salter, et al. 2016. Sympathetic nervous system control of carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in liver through alpha-adrenergic signaling. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2016: 11.
Lee, S.B., H.G. Kim, J.S. Lee, W.Y. Kim, M.M. Lee, Y.H. Kim, et al. 2019. Intermittent restraint-induced sympathetic activation attenuates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in a high-fat diet-fed mouse model. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 317: G811–G823.
Nakade, Y., M. Yoneda, K. Nakamura, I. Makino, A. Terano. 2002. Involvement of endogenous CRF in carbon tetrachlorideinduced acute liver injury in rats. The American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 282:1782–8.
Zhang, J., L. Zhang, X. Sun, Y. Yang, L. Kong, C. Lu, et al. 2016. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease treatment ameliorate acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via central cholinergic system regulation. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 359: 374–382.
Akinci, S.B., N. Ulu, O.Z. Yondem, P. Firat, M.O. Guc, M. Kanbak, et al. 2005. Effect of neostigmine on organ injury in murine endotoxemia: Missing facts about the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. World Journal of Surgery 29: 1483–1489.
Steinebrunner, N., C. Mogler, S. Vittas, B. Hoyler, C. Sandig, W. Stremmel, et al. 2014. Pharmacologic cholinesterase inhibition improves survival in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in the mouse. BMC Gastroenterology 14: 148–156.
Abdel-Salam, O.M.E., E.R. Youness, R.S.E. Esmail, N.A. Mohammed, Y.A. Khadrawy, A.A. Sleem, et al. 2018. Protection by neostigmine and atropine against brain and liver injury induced by acute malathion exposure. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 18: 510–521.
Waldburger, J.M., D.L. Boyle, M. Edgar, L.S. Sorkin, Y.A. Levine, V.A. Pavlov, et al. 2008. Spinal p38 MAP kinase regulates peripheral cholinergic outflow. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58: 2919–2921.
Maldifassi, M.C., C. Martin-Sanchez, G. Atienza, J.L. Cedillo, F. Arnalich, A. Bordas, et al. 2018. Interaction of the alpha7-nicotinic subunit with its human-specific duplicated dupalpha7 isoform in mammalian cells: Relevance in human inflammatory responses. Journal of Biological Chemistry 293: 27.
Hur, M.H., W. Song, D.H. Cheon, Y. Chang, Y.Y. Cho, Y.B. Lee, et al. 2023. Chemogenetic stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system lowers hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model. Life Sciences 321: 121533.
Ologunde, R., H. Zhao, K. Lu, and D. Ma. 2014. Organ cross talk and remote organ damage following acute kidney injury. International Urology and Nephrology 46: 2337–2345.
Lai, Y., J. Deng, M. Wang, M. Wang, L. Zhou, G. Meng, et al. 2019. Vagus nerve stimulation protects against acute liver injury induced by renal ischemia reperfusion via antioxidant stress and anti-inflammation. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 117: 9.
Sha, J., X. Feng, Y. Chen, H. Zhang, B. Li, X. Hu, et al. 2019. Dexmedetomidine improves acute stress-induced liver injury in rats by regulating MKP-1, inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway and cell apoptosis. Journal of Cellular Physiology 234: 1–11.
Mukhopadhyay, B., K. Holovac, K. Schuebel, P. Mukhopadhyay, R. Cinar, S. Iyer, et al. 2023. The endocannabinoid system promotes hepatocyte progenitor cell proliferation and maturation by modulating cellular energetics. Cell Death Discov. 9: 104.
Oben, J.A., and A.M. Diehl. 2004. Sympathetic nervous system regulation of liver repair. The Anatomical Record. Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology 280: 874–883.
Oben, J.A., T. Roskams, S. Yang, H. Lin, N. Sinelli, Z. Li, et al. 2003. Sympathetic nervous system inhibition increases hepatic progenitors and reduces liver injury. Hepatology 38: 664–673.
Kiba, T. 2002. The role of the autonomic nervous system in liver regeneration and apoptosis–recent developments. Digestion 66: 79–88.
Kamimura, K., R. Inoue, T. Nagoya, N. Sakai, R. Goto, M. Ko, Y. Niwa, and S. Terai. 2018. Autonomic nervous system network and liver regeneration. World Journal of Gastroenterology 24:1583–678.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Hunan Key Laboratory of Viral Hepatitis laboratory, especially Yinghui Xiong, for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81970523, 81800506), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China, (2018ZX10723203), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (2020JJ4877, 2020JJ5886, 2019JJ40494, 2021JJ70148, 2020JJ4906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingwang Hu designed the study. Kaili Yang collected and analyzed the data, and Kaili Yang, Xingwang Hu, and Jun Quan wrote the manuscript. Zebing Huang and Yayu Chen modified the manuscript. Panpan Yi, Meifang Xiao, Shuyi Wang, and Zhihong Zhao checked the data. All authors contributed to the revision of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, K., Huang, Z., Wang, S. et al. The Hepatic Nerves Regulated Inflammatory Effect in the Process of Liver Injury: Is Nerve the Key Treating Target for Liver Inflammation?. Inflammation 46, 1602–1611 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01854-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01854-x