Abstract
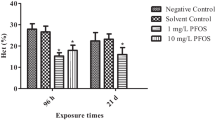
Highly persistent perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) is an industrial fluorinated organic chemical with significant bioaccumulation and biomagnification properties. The purpose of this study was to determine the toxic effects of sublethal PFOS on the aquatic invertebrate organism, narrow-clawed crayfish [Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823]. The 96 h LC50 value was determined as 48.81 mg/L (34.19–63.68 mg/L) with probit analysis. The sublethal experimental design was formed into four groups solvent control (DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide), non-treated control group, and 1/10 (5 mg/L) and 1/100 (0.5 mg/L) of 96 h LC50 of PFOS, and crayfish were exposed for 48 h, 7 d, and 21 d under laboratory conditions. Total haemocyte counts (THCs) decreased, while the haemolymph total antioxidant status (TAS) values increased (p < 0.05) after exposure to 0.5 and 5 mg/L PFOS for 48 h, 7 d, and 21 d. Haemolymph total oxidative stress (TOS) levels significantly increased at 5 mg/L PFOS concentration (p < 0.05). Catalase (CAT) activities increased at both concentrations after 48 h and 7 d and then returned to control levels after 21 d; whereas superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) activities did not change in muscle tissue (p > 0.05). GPX and CAT activities decreased, but SOD activity increased in hepatopancreas tissue (p < 0.05). SOD activity at both concentrations and CAT activity at 5 mg/L PFOS exposure decreased in gill tissue, while GPX activity increased at both concentrations of 48 h and 7 d and returned to control values on day 21 of exposure. Histopathological alterations were detected in hepatopancreas and gill tissues. Lamellar deformations, epithelial hyperplasia, and haemocytic infiltrations were observed in the gill tissues, whereas tubular degeneration, tubule loss, necrosis, and lesions in the hepatopancreas tissues were the major recorded alterations. As a result, the sublethal concentrations of PFOS have toxic effects on crayfish and histologically cause tissue damage. Our findings also support a better understanding of the early toxicological effects of PFOS in freshwater ecosystems. Also, it could be concluded that A. leptodactylus is a reliable model for examining histopathological alterations and differences in enzyme activities together with the haemolymph findings in toxicology studies amid aquatic species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott BD (2009) Review of the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha (PPARα), beta (PPARβ), and gamma (PPARγ) in rodent and human development. Reproduc Tox 27(3–4):246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2008.10.001
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Amraoui I, Khalloufi N, Touaylia S (2018) Effects to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on the mollusk Unio ravoisieri under laboratory exposure. Chem Ecol 34:324–339. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2018.1433168
Ankley GT, Kuehl DW, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Linnum A, Leino RL, Villeneuve DA (2005) Reproductive and developmental toxicity and bioconcentration of perfluorooctanesulfonate in a partial life-cycle test with the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 24(9):2316–2324. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-634R.1
Arslan, P (2022) Determinations of the effects of cyfluthrin on the hemocytes parameters of freshwater mussel (Unio delicatus). Ege J Fish Aquat Sci 39(1):39–45. Retrieved from http://www.egejfas.org/tr/pub/issue/68550/988408
Austin ME, Kasturi BS, Barber M, Kannan K, MohanKumar PS, MohanKumar SMJ (2003) Neuroendocrine effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate in rats. Environ Health Perspect 111(12):1485–1489. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6128
Bal A, Panda F, Pati SG, Das K, Agrawal PK, Paital B (2021) Modulation of physiological oxidative stress and antioxidant status by abiotic factors especially salinity in aquatic organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 241:108971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108971
Balık S, Ustaoglu MR, Sarı HM, Berber S (2005) Determination of traits some growth and morphometric of crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823) at Demirkopru Dam Lake (Manisa). Ege J Fish Aquat Sci 22:83–89
Bell TA, Lightner DV (1988) A handbook of normal penaeid shrimp histology. Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Benli ACK, Şahin D, Koçak B, Sepici Dinçel A (2012) Determination of antioxidant enzyme levels of narrow clawed crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823) exposed to carbaryl. Turk J Bioch 37(2):162–166
Benli ACK (2015) The influence of etofenprox on narrow clawed crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823): acute toxicity and sublethal effects on histology, hemolymph parameters, and total hemocyte counts. Environ Toxicol 30:887–894. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.21963
Benli ACK, Sahin D, Selvi M, Sarıkaya R, Memmi BK, Dinçel AS (2016) The sublethal effects of (2,4-dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid (2,4-D) on narrow-clawed crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823). Arch Ind Hy. Toxicol 67:289–296
Borkovic SS, Pavlovic SZ, Kovacevic TB, Stajn AS, Petrovic VM, Saicic ZS (2008) Antioxidant defence enzyme activities in hepatopancreas, gills and muscle of Spiny cheek crayfish (Orconectes limosus) from the River Danube. Comp Biochem Phys C 147:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.08.006
Bossi R, Riget FF, Dietz R, Sonne C, Fauser P, Dam M, Vorkamp K (2005) Preliminary screening of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and other fluorochemicals in fish, birds and marine mammals from Greenland and the Faroe Islands. Environ Pollut 136(2):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.12.020
Boudreau TM, Sibley PK, Mabury SA, Muir DG, Solomon KR (2003) Laboratory evaluation of the toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on Selenastrum capricornutum, Chlorella vulgaris, Lemna gibba, Daphnia magna, and Daphnia pulicaria. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:0307–0313
Brittle SW, Paluri SLA, Foose DP, Ruis MT, Amato MT, Lam NH, Buttigieg B, Gagnon ZE, Sizemore IE (2016) Freshwater crayfish: a potential benthic-zone indicator of nanosilver and ionic silver pollution. Environ Sci Technol 50:7056–7065. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00511
CEAM (Center for Exposure Assessment Modeling) (1999) U.S.E.P.A. LC50 Software Program, Version 1.00. CEAM Distribution Center, Athens, GA
Chabera J, Stara A, Kubec J, Buric M, Zuskova E, Kouba A, Velisek J (2021) The effect of chronic exposure to chloridazon and its degradation product chloridazon-desphenyl on signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. Ecotoxicol and Environ Saf 208:111645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111645
Chen H, Han J, Zhang C, Cheng J, Sun R, Wang X, Han G, Yang W, He X (2017) Occurrence and seasonal variations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) including fluorinated alternatives in rivers, drain outlets and the receiving Bohai Sea of China. Environ Pollut 231:1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.068
Chen J, Zheng L, Tian L, Wang N, Lei L, Wang Y, Dong Q, Huang C, Yang D (2018) Chronic PFOS exposure disrupts thyroid structure and function in zebrafish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2359-8
Cheng J, Lv S, Nie S, Liu J, Tong S, Kang N, Xiao Y, Dong Q, Huang C, Yang D (2016) Chronic perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure induces hepatic steatosis in zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 176:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.04.013
Cui L, Zhou QF, Liao CY, Fu JJ, Jiang GB (2009) Studies on the toxicological effects of PFOA and PFOS on rats using histological observation and chemical analysis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9194-6
Cui Y, Lv S, Liu J, Noe S, Chen J, Dong Q, Huang C, Yang D (2017) Chronic perfluorooctanesulphonic acid (PFOS) exposure disrupts lipid metabolism in zebrafish model. Hum Exp Toxicol 36:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327116646615
Desouky MMA, Abdel Gawad H, Hegazi B (2013) Distribution, fate and histopathological effects of ethion insecticide on selected organs of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Food Chem Toxicol 52:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.10.029
DeWitt JC, Shnyra A, Badr MZ, Loveless SE, Hoban D, Frame SR, Cunard R, Anderson SE, Meade BJ, Peden Adams MM, Luebke RW, Luster MI (2009) Immunotoxicity of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate and the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Critical Rev Toxicol 39:76–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440802209804
Dorts J, Kestemont P, Marchand PA, D’Hollander W, Thezenas ML, Raes M, Silvestre F (2011) Ecotoxicoproteomics in gills of the sentinel fish species, Cottus gobio, exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Aquat Toxicol 103:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.01.015
Fang C, Huang Q, Ye T, Chen Y, Liu L, Kang M, Lin Y, Shen H, Dong S (2013) Embryonic exposure to PFOS induces immunosuppression in the fish larvae of marine medaka. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.03.005
Feng M, He Q, Meng L, Zhang X, Sun P, Wang Z (2015) Evaluation of single and joint toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate, perfluorooctanoic acid, and copper to Carassius auratus using oxidative stress biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 161:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.025
Franco-Martinez L, Romero D, García Navarro JA, Teles M, Tvarijonaviciute A (2016) Esterase activity (EA), total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) in gills of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to pollutants: analytical validation and effects evaluation by single and mixed heavy metal exposure. Mar Pollut Bull 102:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.12.010
Fromme H, Tittlemier SA, Völkel W, Wilhelm M, Twardella D (2009) Perfluorinated compounds – Exposure assessment for the general population in western countries. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:239–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.04.007
GHS, 2011. Globally Harmonized System for the classification and labelling of chemicals. (accessed 22.05.2021). https://unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_rev04/English/ST-SG-AC10-30-Rev4e.pdf
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2001) Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 35(7):339–1342. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001834k
Gunal AC, Tunca SK, Arslan P, Gül G, Sepici Dinçel A (2021) How does sublethal permethrin effect non-target aquatic organisms? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:52405–52417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14475-4
Gunduz G, Parlak H, Arslan OÇ, Boyacioglu M, Karaaslan MA (2013) Embryotoxic effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate compounds in Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Fresenius Environ Bull 22:171–177
Hagenaars A, Knapen D, Meyer IJ, van der Ven K, Hoff P, De Coen W (2008) Toxicity evaluation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in the liver of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat Toxicol 88(3):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.04.002
Halliwell B (1999) Antioxidant defence mechanisms: from the beginning to the end (of the beginning). Free Radic Res 31:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715769900300841
Hayman NT, Rosen G, Colvin MA, Conder J, Arblaster JA (2021) Aquatic toxicity evaluations of PFOS and PFOA for five standard marine endpoints. Chemosphere 273:129699
Hoff PT, Dongen WV, Esmans EL, Blust R, De Coen WM (2003) Evaluation of the toxicological effects of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat. Toxicol. 62:349–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00145-5
Hossain MM, Huang H, Yuan Y, Wan T, Jiang C, Dai Z, Xiong S, Cao M, Tu S (2021) Silicone stressed response of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in antioxidant enzyme activity and related gene expression. Environ Pollut 274:115836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115836
Houde M, Martin JW, Letcher RJ, Solomon KR, Muir DCG (2006) Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalky substances: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40(11):3463–3473. https://doi.org/10.1021/es052580b
Huang H, Huang C, Wang L, Ye X, Bai C, Simonich MT, Tanguay RL, Dong Q (2010) Toxicity, uptake kinetics and behavior assessment in zebrafish embryos following exposure to perfluorooctanesulphonicacid (PFOS). Aquat Toxicol 98:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.02.003
Huang J, Sun L, Mennigen JA, Liu Y, Liu S, Zhang M, Wang Q, Tu W (2020) Developmental toxicity of the novel PFOS alternative OBS in developing zebrafish: an emphasis on cilia disruption. J Hazardous Mater 409:124491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124491
Huset CA, Barlaz MA, Barofsky DF, Field JA (2011) Quantitative determination of fluorochemicals in municipal landfill leachates. Chemosphere 82:1380–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.072
Issartel J, Boulo V, Wallon S, Geffard O, Charmantier G (2010) Cellular and molecular osmoregulatory responses to cadmium exposure in Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Chemosphere 81:701–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.07.063
Jantzen CE, Annunziato KM, Cooper KR (2016) Behavioral, morphometric, and gene expression effects in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryonically exposed to PFOA, PFOS, and PFNA. Aquat Toxicol 180:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.09.011
Jeong TY, Yuk MS, Jeon J, Kim SD (2016) Multigenerational effect of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on the individual fitness and population growth of Daphnia magna. Sci Total Environ 569–570:1553–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.249
Jeong TY, Simpson MJ (2019) Reproduction stage differentiates the time-course regulation of metabolites in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 53:12764–12773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2020.100701
Ji K, Kim Y, Oh S, Ahn B, Jo H, Choi K (2008) Toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and perfluorooctanoic acid on freshwater macroinvertebrates (Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa) and fish (Oryzias latipes). Environ Toxicol Chem 27:2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-523.1
Jones PD, Hu W, De Coen W, Newsted JL, Giesy JP (2003) Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum proteins. Environ Toxicol and Chem. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-553
Jussila J, Jago J, Tsvetnenko E, Dunstan B, Evans LH (1997) Total and differential hemocyte counts in western rock lobsters (Panulirus cygnus George) under postharvest stress. Mar Freshwater Res 48:863–868. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF97216
Kaloyianni M, Dailianis S, Chrisikopoulou E, Zannou A, Koutsogiannaki S, Alamdari DH, Koliakos G, Dimitriadis VK (2009) Oxidative effects of inorganic and organic contaminants on haemolymph of mussels. Comparative Biochem Physiol C Toxico Pharma 149:631–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2009.01.006
Kannan K, Hansen KJ, Wade TL, Giesy JP (2002) Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Oysters, Crassostrea virginica, from the Gulf of Mexico and the Chesapeake Bay, USA. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-001-0003-8
Kannan K, Tao L, Sinclair E, Pastva SD, Jude DJ, Giesy JP (2005) Perfluorinated Compounds in Aquatic Organisms at Various Trophic Levels in a Great Lakes Food Chain. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0133-x
Kim H, Kim JS, Kim PJ, Won EJ, Lee YM (2018) Response of antioxidant enzymes to Cd and Pb exposure in water flea Daphnia magna: differential metal and age-specific patterns. Comp Biochem Physiology C Toxico Pharma 209:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2018.03.010
Kim WK, Lee SK, Jung J (2010) Integrated assessment of biomarker responses in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to perfluorinated organic compounds. J Hazard Mater 180:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.044
Kissa E (2001) Fluorinated Surfactants and Repellants, 2nd ed. Marcel Decker, New York, p 1–21
Khoei AJ (2022) Seasonal heavy metal accumulations in the bivalve Barbatia decussate and their relationships with water quality and the metal-induced biochemical biomarkers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:16103–16112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16893-w
Köksal G (1988) Astacus leptodactylus in Europe. In: Holdich DM, Lowery R eds Freshwater crayfish biology, management and exploitation. Croom Helm, London, UK, p 365–400
Kunacheva C, Fujii S, Tanaka S, Seneviratne STMLD, Lien NPH, Nozoe M, Kimura K, Shivakoti BR, Harada H (2012) Worldwide surveys of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in water environment in recent years. Water Sci Technol 66:2764–2771
Le Moullac G, Haffner P (2000) Environmental factors affecting immune responses in Crustacea. Aquaculture 191:121–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00422-1
Lindim C, Van Gils J, Cousins IT (2016) Europe-wide estuarine export and surface water concentrations of PFOS and PFOA. Water Res 103:124–132
Li MH (2009) Toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid to plants and aquatic invertebrates. Environ Toxicol 24:95–101
Liu C, Yu K, Shi X, Wang J, Lam PKS, Wu RSS, Zhou B (2007) Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by PFOS and PFOA in primary cultured hepatocytes of freshwater tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat Toxicol 82:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.02.006
Liu X, Xu Z, Chang X, Fang JKH, Song J, He J, Tai Z, Zhu Q, Hu M (2021) Enhanced immunity and hemocytes proliferation by three immunostimulants in tri-spine horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 115:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2021.06.001
Liu Z, Lu Y, Wang P, Wang T, Liu S, Johnson AC, Sweetman AJ, Baninla Y (2017) Pollution pathways and release estimation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in central and eastern China. Sci Total Environ 580:1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.085
Livingstone DR (2003) Oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to pollution and aquaculture. Rev. Méd. Vét. Toulouse. 154:427–430
Logeshwaran P, Sivaram AK, Surapaneni A, Kannan K, Naidu R, Megharaj M (2021) Exposure to perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) but not perflurorooctanoic acid (PFOA) at ppb concentration induces chronic toxicity in Daphnia carinata. Sci Total Environ 769:144577
Lu GH, Liu JC, Sun LS, Yuan LJ (2015) Toxicity of perfluorononanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate to Daphnia magna. Water Sci Eng 8:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2015.01.001
Luna LG (1968) Manual of histological staining methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Third Edition. McGraw Hill, New York
Martin JW, Whittle DM, Muir DC, Mabury SA (2004) Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in a food web from Lake Ontario. Environ Sci Technol 38(20):5379–5385. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049331s
Mello GL, Júnior HA, Garcia S, Vinatea L (2011) Acute toxicity of pyrazosulfuron‐ethyl and permethrin to juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei Acta Scientiarum. Biol Sci Maringá 338:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v33i1.6974
Miller NJ, Rice-Evans C, Davies MJ, Gopinathan V, Milner A (1993) A novel method for measuring antioxidant capacity and its application to monitoring the antioxidant status in premature neonates. Clin Sci 84(4):407–412
Moody CA, Hebert GN, Strauss SH, Field JA (2003) Occurrence and persistence of perfluorooctanesulfonate and other perfluorinated surfactants in groundwater at a fire-training area at Wurtsmith Air Force Base, Michigan, USA. J Environ Monit 5:341–345. https://doi.org/10.1039/B212497A
Oakes KD, Sibley PK, Martin JW, MacLean DD, Solomon KR, Mabury SA, Van Der Kraak GJ (2005) Short-term exposures of fish to perfluorooctane sulfonate: acute effects on fatty acyl-CoA oxidase activity, oxidative stress and circulating sex steroids. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1172–1181. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-419.1
Oliaei F, Kriens D, Weber R, Watson A (2013) PFOS and PFC releases and associated pollution from a PFC production plant in Minnesota (USA). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1977–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1275-4
Olsen GW, Burris JM, Ehresman DJ, Froehlich JW, Seacat AM, Butenhoff JL, Zobel LR (2007) Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ Health Perspect 115:9. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10009
Pala A (2019) The effect of a glyphosate-based herbicide on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant status in freshwater amphipod: Gammarus pulex (Crustacean). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:36869–6877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06804-5
Pan L, Zhang H (2006) Metallothionein, antioxidant enzymes and DNA strand breaks as biomarkers of Cd exposure in a marine crab, Charybdis japonica. Comp Biochem Physiol C 144:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.06.001
Patetsini E, Dimitriadis VK, Kaloyianni M (2013) Biomarkers in marine mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to environmentally relevant levels of the pesticides, chlorpyrifos and penoxsulam. Aquat Toxicol 126:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.09.009
Paul AG, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2009) First global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Sci Technol 43(2):386–392. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802216n
Perazzolo LM, Gargioni R, Ogliari P, Barracco MAA (2002) Evaluation of some hemato‐immunological parameters in the shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis submitted to environmental and physiological stress. Aquaculture 214:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00137-0
Qiu J, Wang W-N, Wang L-J, Liu Y-F, Wang A-L (2011) Oxidative stress, DNA damage and osmolality in the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei exposed to acute low temperature stress. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 154:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.02.007
Qin Q, Qin S, Wang L, Lei W (2012) Immune responses and ultrastructural changes of haemocytes in freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense exposed to elevated cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 106–107:140–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.08.013
Saikat S, Kreis I, Davies B, Bridgman S, Kamanyire R (2013) The impact of PFOS on health in the general population: a review. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EM30698K
Schultz MM, Barofsky DF, Field JA (2004) Quantitative determination of fluorotelomer sulfonates in groundwater by LC MS/MS. Environ Sci Technol 38:1828–1835. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035031j
Selvi M, Cavaş T, Karasu Benli AC, Koçak Memmi B, Cinkılıç N, Sepici Dinçel A, Vatan O, Yılmaz D, Sarıkaya R, Zorlu T, Erkoç F (2011) Sublethal toxicity of esbiothrin relationship with total antioxidant status and in vivo genotoxicity assessment in fish (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) using the micronucleus test and comet assay. Environ Toxicol 28:644–651. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20760
Sepici Dinçel A, Alparslan N, Karasu Benli AC, Selvi M, Sarıkaya R, Özkul İA, Erkoc F (2013) Haemolymph biochemical parameters reference intervals and total haemocyte counts of narrow clawed crayfish Astacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823). Ecol Indicat 24:305–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.07.002
Sepici Dincel A, Karasu Benli AC, Selvi M, Sarikaya R, Sahin D, Ozkul IA, Erkoc F (2009) Sublethal cyfluthrin toxicity to carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) fingerlings: Biochemical, hematological, histopathological alterations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1433–1439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.01.008
Seyoum A, Pradhan A, Jass J, Olsson PE (2020) Perfluorinated alkyl substances impede growth, reproduction, lipid metabolism and lifespan in Daphnia magna. Sci Total Environ 737:139682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139682
Sharma BM, Bharat GB, Tayal S, Nizzetto L, Čupr P, Larssen T (2014) Environment and human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in India: a systematic review of recent and historical data. Environ Int 66:48–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.01.022
Shi X, Liu C, Wu G, Zhou B (2009) Waterborne exposure to PFOS causes disruption of the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 77:1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.074
Shi X, Du Y, Lam PK, Wu RS, Zhou B (2008) Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:23–32
Shi X, Zhou B (2010) The role of Nrf2 and MAPK pathways in PFOS-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos. Toxic Sci 115:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq066
Smith VJ, Johnston PA (1992) Differential haemotoxic effect of PCB congeners in the common shrimp, Crangon crangon. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Com Pharm 101:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-8413(92)90099-S
Sprague JB (1971) Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish–III: Sublethal effects and “safe” concentrations. Water Res 5:245–266
Stahl T, Mattern D, Brunn H (2011) Toxicology of perfluorinated compounds. Environ Sci Eur 23:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/2190-4715-23-38
Stara A, Machova J, Velisek J (2012) Effect of chronic exposure to simazine on oxidative stress and antioxidant response in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Environ Toxicol Pharm 33:334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2011.12.019
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A Simple Method for Clinical Assay of Superoxide Dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/34.3.497
Touaylia S, Khazri A, Mezni A, Bejaoui M (2019) Effects of emerging persistent organic pollutant perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on the Crustacean Gammarus insensibilis. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1489717
Tse WKF, Li JW, Tse ACK, Chan TF, Ho JCH, Wu RSS, Wong CKC, Lai KP (2016) Fatty liver disease induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate: novel insight from transcriptome analysis. Chemosphere 159:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.060
UNEP (2006) In: Draft Risk Profile: Perflorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS), Programme U.N.E., Geneva
UNEP (2009) The conference of the parties 4 of the Stockholm Convention (COP-4) in Geneva placed perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride (PFOS and PFOSF) in Annex B. http://chm.pops.int/Convention/Pressrelease/COP4Geneva9May2009/tabid/542/language/en-US/Default.aspx
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotox Environ Saf 64(2):178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Verde V, Fogliano V, Ritieni A, Maiani G, Morisco F, Caporaso N (2002) Use of N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine to evaluate the oxidative status of human plasma. Free Radic Res 36:869–873. https://doi.org/10.1080/1071576021000005302
Wan HT, Zhao YG, Wei X, Hui KY, Giesy JP, Wong CKC (2012) PFOS-induced hepatic steatosis, the mechanistic actions on β-oxidation and lipid transport. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1820(7):1092–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.010
Xu D, Li C, Wen Y, Liu W (2013a) Antioxidant defense system responses and DNA damage of earthworms exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ Pollut 174:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.030
Xu Z, Wang Z, Li J-J, Chen C, Zhang PC, Dong L, Chen JH, Chen Q, Zhang X-T, Wang ZL (2013b) Protective effects of selenium on oxidative damage and oxidative stress related gene expression in rat liver under chronic poisoning of arsenic. Food Chem Toxicol 58:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.03.048
Yağan A, Kesim S, Liman N (2014) Effect of low‐dose doxycycline on serum oxidative status, gingival antioxidant levels, and alveolar bone loss in experimental periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol 85:478–489. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2013.130138
Yavuzcan HY, Benli AÇK (2004) Nitrite toxicity to crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus, the effects of sublethal nitrite exposure on hemolymph nitrite, total hemocyte counts, and hemolymph glucose. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:370–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.07.007
Young IS (2001) Measurement of total antioxidant capacity. J Clin Pathol 54:339. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.54.5.339
Yu JX, Xu EG, Li W, Jin S, Yuan T, Liu J, Li Z, Zhang T (2018) Acute toxicity of an emerging insecticide pymetrozine to Procambarus clarkii associated with rice-crayfish culture (RCIS). Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050984
Yucel Isıldar G, Gunal AC, Şahin D, Kocak Memmi B, Sepici Dinçel A (2020) How potential endocrine disruptor deltamethrin effects antioxidant enzyme levels and total antioxidant status on model organisms. Turk J Biochem 45:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1515/tjb-2019-0382
Zhang F, Wei J, Li Q, Jiang R, Yu N, Qin J, Chen L (2015) Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on the immune responses and expression of immune-related genes in Chinese mitten-handed crab Eriocheir sinensis. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 172–173:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.04.002
Zhang Y, Li Z, Kholodkevich S, Sharov A, Feng Y, Ren N, Sun K (2019) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress, histopathology, and transcriptome changes in the hepatopancreas of freshwater crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Sci Total Environ 666:944–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.159
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Gazi University Scientific Research Projects Unit, grant number 18/2018-01. The authors would like to thank Betul Dağoğlu Hark (PhD; Fırat University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics) for biostatistical analyses, support, advice and Gazi University Academic Writing Application and Research Center for proof reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Gazi University Scientific Research Projects Unit with grant number 18/2018-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NB: methodology, investigation, and writing; BE: methodology, investigation; ASD: methodology; AÇG: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Belek, N., Erkmen, B., Dinçel, A.S. et al. Does persistent organic pollutant PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) negative impacts on the aquatic invertebrate organism, Astacus leptodactylus [Eschscholtz, 1823]. Ecotoxicology 31, 1217–1230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02579-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02579-7