Abstract
Backgrounds
Neuronal guidance proteins (NGPs) have been demonstrated to guide the elongation of neuronal axonal growth cones in the developing central nervous system. Non-neuronal functions of NGPs have also been described, especially in relation to atherosclerosis.
Findings
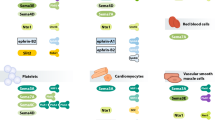
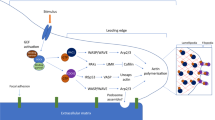
Netrin-1 and repulsive guidance molecule a (RGMa) are NGPs that have been shown to regulate endothelial cell adhesion and angiogenesis, macrophage migration and apoptosis, smooth muscle cells (SMCs) phenotypic dedifferentiation and mobility, chemokine activities, and inflammatory responses during atherosclerosis initiation and progression.
Purposes
However, mechanistic studies have generated controversy about the specific role of Netrin-1 in atherosclerosis due to the diversity of its structure, receptors and cell sources, and the actions of RGMa in atherosclerosis have not been reported in previous reviews. Therefore, the current work reviews the evidence for roles of Netrin-1 and RGMa in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis and discusses potential therapeutic targets in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852–66.
Wolf D, Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circulat Res. 2019;124(2):315–27.
Shapiro MD, Fazio S. From lipids to inflammation: new approaches to reducing atherosclerotic risk. Circulat Res. 2016;118(4):732–49.
Hussain A, Ballantyne CM. New approaches for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease: focus on lipoproteins and inflammation. Annual Rev Med. 2021;72:431–46.
Wentzel JJ, Chatzizisis YS, Gijsen FJ, et al. Endothelial shear stress in the evolution of coronary atherosclerotic plaque and vascular remodelling: current understanding and remaining questions. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;96(2):234–43.
Sansbury BE, Spite M. Resolution of acute inflammation and the role of resolvins in immunity, thrombosis, and vascular biology. Circulat Res. 2016;119(1):113–30.
Germolec DR, Shipkowski KA, Frawley RP, et al. Markers of inflammation. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1803:57–79.
Xia X, Hu Z, Wang S, et al. Netrin-1: an emerging player in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022;64:46–56.
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982–3021.
Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592(7855):524–33.
Goodman CS. Mechanisms and molecules that control growth cone guidance. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:341–77.
Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS. The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science. 1996;274(5290):1123–33.
Mirakaj V, Rosenberger P. Immunomodulatory functions of neuronal guidance proteins. Trends Immunol. 2017;38(6):444–56.
van Gils JM, Ramkhelawon B, Fernandes L, et al. Endothelial expression of guidance cues in vessel wall homeostasis dysregulation under proatherosclerotic conditions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(5):911–9.
Randolph GJ, Gautier EL. Emerging roles of neural guidance molecules in atherosclerosis: sorting out the complexity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(5):882–3.
Moore KJ, Fisher EA. Macrophages, atherosclerosis and the potential of Netrin-1 atherosclerosis a novel target for future therapeutic intervention. Future Cardiol. 2012;8(3):349–52.
Claro V, Ferro A. Netrin-1: focus on its role in cardiovascular physiology and atherosclerosis. JRSM Cardiovasc Disease. 2020;9:2048004020959574.
Bruikman CS, van Gils JM. Netrin-1 in coronary artery disease (CAD): mechanism of action and potential atherosclerosis a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Therapeutic Targets. 2019;23(9):729–31.
Bongo JB, Peng DQ. The neuroimmune guidance cue Netrin-1: a new therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. J Cardiol. 2014;63(2):95–8.
Layne K, Ferro A, Passacquale G. Netrin-1 as a novel therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease: to activate or inhibit? Cardiovasc Res. 2015;107(4):410–9.
Layne K, Goodman T, Ferro A, et al. The effect of aspirin on circulating Netrin-1 levels in humans is dependent on the inflammatory status of the vascular endothelium. Oncotarget. 2017;8(49):86548–55.
Passacquale G, Phinikaridou A, Warboys C, et al. Aspirin-induced histone acetylation in endothelial cells enhances synthesis of the secreted isoform of netrin-1 thus inhibiting monocyte vascular infiltration. Br J Pharmacol. 2015;172(14):3548–64.
Lin Z, Jin J, Bai W, et al. Netrin-1 prevents the attachment of monocytes to endothelial cells via an anti-inflammatory effect. Mol Immunol. 2018;103:166–72.
van Gils JM, Derby MC, Fernandes LR, et al. The neuroimmune guidance cue Netrin-1 promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting the emigration of macrophages from plaques. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(2):136–43.
Ramkhelawon B, Yang Y, van Gils JM, et al. Hypoxia induces Netrin-1 and Unc5b in atherosclerotic plaques: mechanism for macrophage retention and survival. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(6):1180–8.
Yang X, Zhang J, Chen L, et al. The role of UNC5b in ox-LDL inhibiting migration of RAW264.7 macrophages and the involvement of CCR7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505(3):637–43.
Khan JA, Cao M, Kang BY, et al. Systemic human Netrin-1 gene delivery by adeno-associated virus type 8 alters leukocyte accumulation and atherogenesis in vivo. Gene Ther. 2011;18(5):437–44.
Yuan X, Xiao H, Hu Q, et al. RGMa promotes dedifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells into a macrophage-like phenotype in vivo and in vitro. J Lipid Res. 2022;63(10):100276.
Sun Y, Manceau A, Frydman L, et al. Δ40p53 isoform up-regulates Netrin-1/UNC5B expression and potentiates Netrin-1 pro-oncogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(36):e2103319118.
Robinson RA, Griffiths SC, van de Haar LL, et al. Simultaneous binding of guidance cues NET1 and RGM blocks extracellular NEO1 signaling. Cell. 2021;184(8):2103–2120.e31.
Rajasekharan S, Kennedy TE. The netrin protein family. Genome Biol. 2009;10(9):239.
Kennedy TE, Serafini T, de la Torre JR, et al. Netrins are diffusible chemotropic factors for commissural axons in the embryonic spinal cord. Cell. 1994;78(3):425–35.
Cirulli V, Yebra M. Netrins: beyond the brain. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(4):296–306.
Delloye-Bourgeois C, Goldschneider D, Paradisi A, et al. Nucleolar localization of a Netrin-1 isoform enhances tumor cell proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5(236):ra57.
Harter PN, Zinke J, Scholz A, et al. Netrin-1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for poor patient survival in brain metastases. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92311.
Ko SY, Blatch GL, Dass CR. Netrin-1 as a potential target for metastatic cancer: focus on colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33(1):101–13.
Miloudi K, Binet F, Wilson A, et al. Truncated Netrin-1 contributes to pathological vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(8):3006–22.
Oksala N, Pärssinen J, Seppälä I, et al. Association of neuroimmune guidance cue Netrin-1 and its chemorepulsive receptor UNC5B with atherosclerotic plaque expression signatures and stability in human(s): Tampere Vascular Study (TVS). Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2013;6(6):579–87.
Puig O, Yuan J, Stepaniants S, et al. A gene expression signature that classifies human atherosclerotic plaque by relative inflammation status. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2011;4(6):595–604.
Rosenberger P, Schwab JM, Mirakaj V, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent induction of netrin-1 dampens inflammation caused by hypoxia [published correction appears in Nat Immunol. 2015 May;16(5):544]. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(2):195–202.
Ly NP, Komatsuzaki K, Fraser IP, et al. Netrin-1 inhibits leukocyte migration in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(41):14729–34.
Aherne CM, Collins CB, Masterson JC, et al. Neuronal guidance molecule netrin-1 attenuates inflammatory cell trafficking during acute experimental colitis. Gut. 2012;61(5):695–705.
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Libby P. The ins and outs of inflammatory cells in atheromata. Cell Metab. 2012;15(2):135–6.
Cynn E, Li DY, O'Reilly ME, et al. Human macrophage long intergenic noncoding RNA, SIMALR, suppresses inflammatory macrophage apoptosis via NTN1 (Netrin-1). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43(2):286–99.
Roufaiel M, Gracey E, Siu A, et al. CCL19-CCR7-dependent reverse transendothelial migration of myeloid cells clears Chlamydia muridarum from the arterial intima. Nat Immunol. 2016;17(11):1263–127 2.
Yang X, Zhang J, Chen L, et al. The role of UNC5b in ox-LDL inhibiting migration of RAW264.7 macrophages and the involvement of CCR7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505(3):637–43.
Hadi T, Boytard L, Silvestro M, et al. Macrophage-derived Netrin-1 promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by activating MMP3 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5022.
Silvestro M, Rivera CF, Alebrahim D, et al. The nonproteolytic intracellular domain of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase coordinately modulates abdominal aortic aneurysm and atherosclerosis in mice-brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022;42(10):1244–53.
Ramkhelawon B, Hennessy EJ, Ménager M, et al. Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat Med. 2014;20(4):377–84.
Sharma M, Schlegel M, Brown EJ, et al. Netrin-1 Alters Adipose Tissue Macrophage Fate and Function in Obesity. Immunometabolism. 2019;1(2):e190010.
Liu NM, Siu KL, Youn JY, et al. Attenuation of neointimal formation with Netrin-1 and Netrin-1 preconditioned endothelial progenitor cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95(3):335–48.
Zeng J, Lu C, Huang H, et al. Effect of recombinant netrin-1 protein combined with peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cells on angiogenesis in rats with arteriosclerosis obliterans. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:3361605.
Camaré C, Pucelle M, Nègre-Salvayre A, et al. Angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. Redox Biol. 2017;12:18–34.
Pelisek J, Well G, Reeps C, et al. Neovascularization and angiogenic factors in advanced human carotid artery stenosis. Circ J. 2012;76(5):1274–82.
Khan JA, Cao M, Kang BY, et al. Systemic human Netrin-1 gene delivery by adeno-associated virus type 8 alters leukocyte accumulation and as in vivo. Gene Ther. 2011;18(5):437–44.
Bruikman CS, Vreeken D, Hoogeveen RM, et al. Netrin-1 and the grade of atherosclerosis are inversely correlated in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40(2):462–72.
Livesey FJ. Netrins and netrin receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999;56(1-2):62–8.
Nikolopoulos SN, Giancotti FG. Netrin-integrin signaling in epithelial morphogenesis, axon guidance and vascular patterning. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(3):e131–5.
Hong K, Hinck L, Nishiyama M, et al. A ligand-gated association between cytoplasmic domains of UNC5 and DCC family receptors converts netrin-induced growth cone attraction to repulsion. Cell. 1999;97(7):927–41.
Bruikman CS, Vreeken D, Zhang H, et al. The identification and function of a Netrin-1 mutation in a pedigree with premature atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2020;301:84–92.
Schlegel M, Moore KJ. A heritable netrin-1 mutation increases atherogenic immune responses. Atherosclerosis. 2020;301:82–3.
Gautier EL, Huby T, Witztum JL, et al. Macrophage apoptosis exerts divergent effects on atherogenesis atherosclerosis a function of lesion stage. Circulation. 2009;119(13):1795–804.
Tabas I, Bornfeldt KE. Macrophage phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):653–67.
Muñoz JC, Martín R, Alonso C, et al. Relation between serum levels of chemotaxis-related factors and the presence of coronary artery calcification atherosclerosis expression of subclinical atherosclerosis. Clin Biochem. 2017;50(18):1048–55.
Schlegel M, Sharma M, Brown EJ, et al. Silencing myeloid netrin-1 induces inflammation resolution and plaque regression. Circ Res. 2021;129(5):530–46.
Hu Q, Chen Z, Yuan X, et al. Common polymorphisms in the RGMa promoter are associated with cerebrovascular atherosclerosis burden in chinese han patients with acute ischemic cerebrovascular accident. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:743868.
Guo D, Zhu Z, Zhong C, et al. Increased serum Netrin-1 is associated with improved prognosis of ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2019;50(4):845–52.
Leocádio P, Menta P, Dias M, et al. High serum Netrin-1 and IL-1β in elderly females with ACS: worse prognosis in 2-years follow-up. Níveis Elevados de Netrina-1 e IL-1β em Mulheres Idosas com SCA: Pior Prognóstico no Acompanhamento de Dois Anos. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020;114(3):507–14.
Kızmaz M, Marakoğlu K, Kıyıcı A, et al. Plasma Netrin-1 levels significantly increase in smokers. Clin Biochem. 2016;49(10-11):832–4.
Mutlu H, Akilli N, Cander B, et al. Effect of serum netrin-1 levels on diagnosis and prognosis in patients admitted to the emergency service for acute coronary syndrome. Cureus. 2020;12(4):e7741.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071338).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept: Xiaofan Yuan, Guanru Shen, and Xinyue Qin. Designed figures: Hongmei Xiao and Zijie Wang. Drafted the manuscript: Xiaofan Yuan, Yue Ma, and Xinyue Qin.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, X., Shen, G., Xiao, H. et al. Netrin-1 and RGMa: Novel Regulators of Atherosclerosis-Related Diseases. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-023-07478-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-023-07478-5