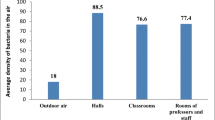
Abstract
Exposure to bioaerosols causes infection, over-sensitivity, respiratory, and lung diseases. This study was conducted at Sanandaj wastewater treatment plant in three seasons of winter, spring and summer to investigate the type and density of bio-aerosols. Sampling was performed using a sampling pump with a discharge rate of 28.3 L/min at a height of 1.5 m above the ground; the samples were taken from five stations: treatment plant entrance, aeration tank, grit chamber, drying sludge bed and laboratory. At each sampling point, time, temperature, relative humidity (Soleimani et al.), wind speed and particulate matter were recorded. In order to identify the bacteria, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and culture-based methods were applied. It was also found that there was not a significant relationship between bacterial count and RH, wind direction, wind speed and temperature. Regarding fungi, the results showed that RH and wind direction and wind has a significant relationship with the concentration of fungi. The most predominant bacteria and fungi were as follows: Staphylococcus, Enterobacteriaceae, Bacillus, Acinetobacter, Micrococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria, Listeria, and Pseudomonas and Penicillium, Aspergillus flavus. The concentration of bacteria in the air was significantly correlated with < 4, < 5, < 7 and < 10 μm suspended particles. However, there was a correlation between particle number of 10 μm and fungi concentration in the air.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Andualem, Z., Gizaw, Z., Bogale, L., & Dagne, H. (2019). Indoor bacterial load and its correlation to physical indoor air quality parameters in public primary schools. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine, 14, 2.
Aslanzadeh, J. (2006). Biochemical profile-based microbial identification systems. Advanced techniques in diagnostic microbiology, 84–116.
Awad, A. H., Saeed, Y., Hassan, Y., Fawzy, Y., & Osman, M. (2018). Air microbial quality in certain public buildings, Egypt: A comparative study. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 9, 617–626.
Baird, R. (1998). Pharmaceutical microbiology.
Behdarvand, N., Godini, E., Godini, H., & ShamsKhoramabadi, G. (2017). Study of effective factors on E. coli removal from water using solar radiation disinfection. Journal of Environmental Health Enginering, 5, 73–82.
Brągoszewska, E., Mainka, A., & Pastuszka, J. (2017). Concentration and size distribution of culturable bacteria in ambient air during spring and winter in Gliwice: A typical urban area. Atmosphere, 8, 239.
Brągoszewska, E., & Pastuszka, J. S. (2018). Influence of meteorological factors on the level and characteristics of culturable bacteria in the air in Gliwice, Upper Silesia (Poland). Aerobiologia, 34, 241–255.
Breza-Boruta, B, Paluszak, Z. (2007). Influence of water treatment plant on microbiological composition of air bioaerosol. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 16.
Brisebois, E., Veillette, M., Dion-Dupont, V., Lavoie, J., Corbeil, J., Culley, A., & Duchaine, C. (2018). Human viral pathogens are pervasive in wastewater treatment center aerosols. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 67, 45–53.
Choobineh, A., Rostami, R., & Tabatabaei, S. H. (2009). Assessment of bioaerosols types and concentration in ambient air of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences educational hospitals, 2008. Iran Occupational Health, 6, 69–76.
Ding, W., Li, L., Han, Y., Liu, J., & Liu, J. (2016). Site-related and seasonal variation of bioaerosol emission in an indoor wastewater treatment station: Level, characteristics of particle size, and microbial structure. Aerobiologia, 32, 211–224.
Dutkiewicz, J., Cholewa, G., Sitkowska, J., Krysinska-Traczyk, E., Skorska, C., & Prazmo, Z. (2003). Exposure to bioaerosols in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 10, e8.
Falahati, M., Ebrahimi, M., Salek, M. A. R., Roudbary, M., Ghanbari, S., Mokhtarian, K., Khoshmirsafa, M., & Falak, R. (2017). Comparison of ige-reactivity of aspergillus fumigatus, aspergillus flavous and aspergillus niger with type 1 hypersensitive patients’sera. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences, 23, 10–20.
Fan, C., Li, Y., Liu, P., Mu, F., Xie, Z., Lu, R., Qi, Y., Wang, B., & Jin, C. (2019). Characteristics of airborne opportunistic pathogenic bacteria during autumn and winter in Xi’an, China. Science of the Total Environment, 672, 834–845.
Fathi, S., Hajizadeh, Y., Nikaeen, M., & Gorbani, M. (2017). Assessment of microbial aerosol emissions in an urban wastewater treatment plant operated with activated sludge process. Aerobiologia, 33, 507–515.
Fernandez, M. O., Thomas, R. J., Garton, N. J., Hudson, A., Haddrell, A., & Reid, J. P. (2019). Assessing the airborne survival of bacteria in populations of aerosol droplets with a novel technology. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 16, 20180779–20180779.
Filipkowska, Z., Janczukowicz, W., Krzemieniewski, M., Pesta, J. (2002). Municipal wastewater treatment plant with activated sludge tanks aerated by CELPOX Devices as a source of microbiological pollution of the atmosphere. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 11.
Fracchia, L., Pietronave, S., Rinaldi, M., & Martinotti, M. G. (2006). Site-related airborne biological hazard and seasonal variations in two wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 40, 1985–1994.
Gotkowska-Płachta, A., Filipkowska, Z., Korzeniewska, E., Janczukowicz, W., Dixon, B., Gołaś, I., & Szwalgin, D. (2013). Airborne microorganisms emitted from wastewater treatment plant treating domestic wastewater and meat processing industry wastes. CLEAN–Soil. Air, Water, 41, 429–436.
Heinonen-Tanski, H., Reponen, T., & Koivunen, J. (2009). Airborne enteric coliphages and bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Research, 43, 2558–2566.
Hua, N.-P., Kobayashi, F., Iwasaka, Y., Shi, G.-Y., & Naganuma, T. (2007). Detailed identification of desert-originated bacteria carried by Asian dust storms to Japan. Aerobiologia, 23, 291–298.
Jamriska, M., DuBois, T. C., & Skvortsov, A. (2012). Statistical characterisation of bio-aerosol background in an urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 54, 439–448.
Karra, S., & Katsivela, E. (2007). Microorganisms in bioaerosol emissions from wastewater treatment plants during summer at a Mediterranean site. Water Research, 41, 1355–1365.
Katsivela, E., Latos, E., Raisi, L., Aleksandropoulou, V., & Lazaridis, M. (2017). Particle size distribution of cultivable airborne microbes and inhalable particulate matter in a wastewater treatment plant facility. Aerobiologia, 33, 297–314.
Kermani, M., Dehghani, A., Farzadkia, M., Nadafi, K., Bahrami Asl, F., & Zeinalzadeh, D. (2015). Investigation of airborne bactria and fungi in Tehran’s Shahrake Ghods WWTP and its association with environmental parameters. Journal of Health, 6, 57–68.
Khodarahmi, F. (2015). Study of type and density of bacteria from Ahvaz air in normal and dusty conditions during different seasons. Scientific Journal of Ilam University of Medical Sciences, 23, 143–152.
Khodarahmi, F., Godarzi, G., & Hashemishahraki, A. (2015). Study of relationbetween actinomycetes growth potential with the concentration of suspended particles and environmental conditions in normal and dusty conditions and in Ahvaz during different seasons in 2011–2012 years. Scientific Journal of Ilam University of Medical Sciences, 23, 69–80.
Korzeniewska, E. J. F. B. (2011). Emission of bacteria and fungi in the air from wastewater treatment plants-a review. Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, 393–407.
Krumins, V., Mainelis, G., Kerkhof, L. J., Fennell, D. E. J. E. S., & Letters, T. (2014). Substrate-dependent rRNA production in an airborne bacterium. ACS Publications, 1, 376–381.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., Tamura, K., & Battistuzzi, U. F. (2018). MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35(6), 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096.
Li, J., Zhou, L., Zhang, X., Xu, C., Dong, L., & Yao, M. (2016). Bioaerosol emissions and detection of airborne antibiotic resistance genes from a wastewater treatment plant. Atmospheric Environment, 124, 404–412.
Li, L., Gao, M., & Liu, J. (2011). Distribution characterization of microbial aerosols emitted from a wastewater treatment plant using the Orbal oxidation ditch process. Process Biochemistry, 46, 910–915.
Li, S., Feng, K., & Li, M. (2017). Identifying the main contributors of air pollution in Beijing. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, S359–S365.
Lin, W.-H., & Li, C.-S. (2000). Associations of fungal aerosols, air pollutants, and meteorological factors. Aerosol Science & Technology, 32, 359–368.
Małecka-Adamowicz, M., Donderski, W., Dokładna, W. (2011). Microflora of air in the sewage treatment plant of kapuściska in Bydgoszcz. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 20.
Masclaux, F. G., Hotz, P., Gashi, D., Savova-Bianchi, D., & Oppliger, A. J. E. R. (2014). Assessment of airborne virus contamination in wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Research, 133, 260–265.
Oppliger, A., Hilfiker, S., & Vu Duc, T. (2005). Influence of seasons and sampling strategy on assessment of bioaerosols in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 49, 393–400.
Orsini, M., Laurenti, P., Boninti, F., Arzani, D., Ianni, A., & Romano-Spica, V. J. W. R. (2002). A molecular typing approach for evaluating bioaerosol exposure in wastewater treatment plant workers. Water Research, 36, 1375–1378.
Park, D., Kim, Y.-H., Park, C. W., Hwang, J., & Kim, Y.-J. (2009). New bio-aerosol collector using a micromachined virtual impactor. Journal of Aerosol Science, 40, 415–422.
Pascual, L., Pérez-Luz, S., Yáñez, M. A., Santamaría, A., Gibert, K., Salgot, M., Apraiz, D., & Catalán, V. (2003). Bioaerosol emission from wastewater treatment plants. Aerobiologia, 19, 261–270.
Sánchez-Monedero, M., Aguilar, M., Fenoll, R., & Roig, A. (2008). Effect of the aeration system on the levels of airborne microorganisms generated at wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 42, 3739–3744.
Soleimani, Z., Parhizgari, N., Rad, H. D., Akhoond, M. R., Kermani, M., Marzouni, M. B., Goudarzi, H., & Goudarzi, G. (2015). Normal and dusty days comparison of culturable indoor airborne bacteria in Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia, 31, 127–141.
Surfer. (1999). Surfer 7.0. Contouring and 3D surface mapping for scientist's engineers: User's Guide. Golden software New York.
Szyłak-Szydłowski, M., Kulig, A., & Miaśkiewicz-Pęska, E. (2016). Seasonal changes in the concentrations of airborne bacteria emitted from a large wastewater treatment plant. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 115, 11–16.
Tang, J. W. (2009). The effect of environmental parameters on the survival of airborne infectious agents. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 6, S737–S746.
Turner, S., Pryer, K. M., Miao, V. P., & Palmer, J. D. (1999). Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 1(46), 327–338.
Xia, Y. (2020). Correlation and association analyses in microbiome study integrating multiomics in health and disease. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 171, 309–491.
Xu, Y., Zheng, C., Liu, Z., & Yan, K. (2013). Electrostatic precipitation of airborne bio-aerosols. Journal of Electrostatics, 71, 204–207.
Yang, K., Li, L., Wang, Y., Xue, S., Han, Y., & Liu, J. (2019). Airborne bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant: Emission characterization, source analysis and health risk assessment. Water Research, 149, 596–606.
Acknowledgements
This article was extracted from the MSc dissertation of the first author. The authors would like to thank Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences for its financial support provided for this research work (IR.MUK.REC.1397/164).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jari, H., Maleki, A., Dehestani Athar, S. et al. Airborne bacteria and fungi in a wastewater treatment plant: type and characterization of bio-aerosols, emission characterization and mapping. Aerobiologia 38, 163–176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-022-09740-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-022-09740-z