Abstract
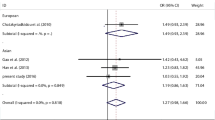
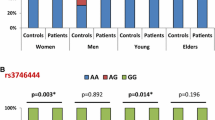
Single nucleotide polymorphism is known to alter the expression and processing of miRNAs leading to a variety of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, disagreement is present up to date regarding the association of miRNA-146a and miRNA-499 polymorphisms with RA. The goal of this study was to assess the association of polymorphisms at miRNA-146a and miRNA-499 with the pathogenesis of RA in patients originating from Pakistan. Initially, eleven hundred subjects (1100) comprises of 550 RA patients and 550 healthy controls were investigated in the case–control analysis. Spectrophotometric measurement of lipids and C-reactive protein was used, whereas interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-1 and TNF-receptor associated factor-6 values were quantified by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Secondly, heritability of susceptible alleles was tested from 70 trio-families. The miRNA-146a rs2910164 and miRNA-499 rs3746444 polymorphisms were genotyped using the polymerase chain reaction followed by restriction digestion. A Significant association of miRNA-146a and miRNA-499 genotypes was observed with RA patients (P < 0.05, respectively). The miRNA-146a rs2910164 G (OR = 1.4, P < 0.05) and miRNA-499 rs3746444 C (OR = 1.6, P < 0.0001) allele was significantly associated with RA in comparison with controls, respectively. Besides, the transmission analysis revealed a significant (P < 0.05) inheritance of rs2910164 G and rs3746444 C allele from parents to affected offspring. The current research concludes that miRNA-146a (rs2910164; C > G) and miRNA-499 (rs3746444; T > C) polymorphisms are linked to RA in the population studied. Furthermore, it was demonstrated for the first time in our high-risk cohort that the rs2910164 G and rs3746444 C allele was strongly related to familial RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the current results are included in this article. For more information please contact at sabirhussain@comsats.du.pk.
References
Guo Q, Wang Y, Dan Xu, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Jiake Xu. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018;6:15.
Zhou M, Jiang B, Xiong M, Zhu X. An updated meta-analysis of the associations between MicroRNA polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1604.
Silman AJ, Pearson JE. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002;4(Suppl 3):S265-272.
Almutairi K, Nossent J, Preen D, Keen H, Inderjeeth C. The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis based on a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(5):863–77.
Rudan I, Sidhu S, Papana A, Meng SJ, Xin-Wei Y, Wang W, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and analysis. J glob health. 2015;5(1):010409.
Solimando AG, Ribatti D, Vacca A, Einsele H. Targeting B-cell non Hodgkin lymphoma: new and old tricks. Leuk Res. 2016;42:93–104.
Macgregor AJ, Snieder H, Rigby AS, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Aho K, Silman AJ. Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheu. 2000;43:30–7.
Speed D, Balding DJ. MultiBLUP: improved SNP-based prediction for complex traits. Genome Res. 2014;24:1550–7.
Apparailly F. Looking for microRNA polymorphisms as new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci? Joint Bone Spine. 2010;77(5):377–9.
El-Shal AS, Aly NM, Galil SM, Moustafa MA, Kandel WA. Association of microRNAs genes polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian female patients. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(6):626–31.
Moran-Moguel MC, Petarra-Del Rio S, Mayorquin-Galvan EE, Zavala-Cerna MG. Rheumatoid arthritis and miRNAs: a critical review through a functional view. J immunol res. 2018;2018:2474529.
Ayeldeen G, Nassar Y, Ahmed H, Shaker O, Gheita T. Possible use of miRNAs-146a and -499 expression and their polymorphisms as diagnostic markers for rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;449(1–2):145–56.
Ying B, Shi Y, Pan X, Song X, Huang Z, Niu Q, Cai B, Wang L. Association of polymorphisms in the human IL-10 and IL-18 genes with rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:379–85.
Huang CH, Cong L, Xie J, Qiao B, Lo SH, Zheng T. Rheumatoid arthritis associated gene–gene interaction network for rheumatoid arthritis candidate genes. BMC Proc. 2009;3(Suppl 7):S75.
Ullah S, John P, Bhatti A (2013). Evaluation of expression pattern of Mirna146a in Pakistani rheumatoid arthritis patients. In: frontiers in immunology Conference Abstract: 15th international congress of immunology (ICI). doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/conf.fimmu.2013.02.00037.
Hashemi M, Eskandari-Nasab E, Zakeri Z, Atabaki M, Bahari G, Jahantigh M, et al. Association of pre-miRNA-146a rs2910164 and pre-miRNA-499rs3746444 polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7:287–91.
Shaker OG, El Boghdady NA, El Sayed AE. Association of MiRNA-146a, MiRNA-499, IRAK1 and PADI4 polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian population. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46:2239–49.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovitis J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569–81.
Shah SFA, Iqbal T, Qamar R, Rafiq MA, Hussain S. ARG1 gene polymorphisms and their association in individuals with essential hypertension: a case-control study. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37(7):609–16.
Scott IC, Steer S, Lewis CM, Cope AP. Precipitating and perpetuating factors of rheumatoid arthritis immunopathology: linking the triad of genetic predisposition, environmental risk factors and autoimmunity to disease pathogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:447–68.
Okada Y, Wu D, Trynka G, et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature. 2014;506:376–81.
Holoshitz J. The rheumatoid arthritis HLA-DRB1 shared epitope. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22(3):293–8.
Huang RY, Wu JQ, Liu ZH, Sun SL. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: what is the latest with regards to diagnostics? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2019;19(5):363–6.
Wang D, Pan G. (2019) Association of rs2910164 Polymorphism in miRNA-146 and rs3746444 Polymorphism in miRNA-499 with Inflammatory Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int 2019; Article ID 7305750.
Fattah SA, Ghattas MH, Saleh SM, Abo-Elmatty DM. Pre-micro RNA-499 Gene Polymorphism rs3746444 T/C is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian population. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2018;33(1):96–101.
Li K, Tie H, Hu N, Chen H, Yin X, Peng C. Association of two polymorphisms rs2910164 in miRNA-146a and rs3746444 in miRNA-499 with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Hum Immunol. 2014;75(7):602–8.
Zhang LL, Wu XX, Wang XF, Di DS, Huang Q, Liu RS, Shuai ZW, Ye DQ, Leng RX. Genetic variant in microRNA-146a gene is associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Med. 2021;53(1):824–9.
Zhoua X, Zhub J, Zhangc H, Zhouc G, Huangc Y, Liu R. Is the microRNA-146a (rs2910164) polymorphism associated with rheumatoid arthritis? Association of microRNA-146a (rs2910164) polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis could depend on gender. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82:166–71.
Yang B, Zhang JL, Shi YY, et al. Association study of single nucleotide polymorphisms in premiRNA and rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:4913–9.
Ramkaran P, Khan S, Phulukdaree A, Moodley D, Chuturgoon AA. miR-146a polymorphism influences levels of miR-146a, IRAK-1, and TRAF-6 in young patients with coronary artery disease. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(2):259–66.
Shao Y, Li J, Cai Y, Xie Y, Ma G, Li Y, et al. The functional polymorphisms of miR-146a are associated with susceptibility to severe sepsis in the Chinese population. Mediat Inflamm. 2014;2014:1–10.
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR, de la Chapelle A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(20):7269–74.
El Gazzar M, Church A, Liu T, McCall CE. MicroRNA-146a regulates both transcription silencing and translation disruption of TNF-α during TLR4-induced gene reprogramming. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90:509–19.
Laird NM, Lange C. Family-based designs in the age of large-scale gene-association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(5):385–94.
Xu X, Qin L, Tian Y, Wang M, Li G, Du Y, Chen ZJ, Li W. Family-based analysis of GGT1 and HNF1A gene polymorphisms in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Biomed Online. 2018;36(1):115–9.
Hussain S, Iqbal T, Javed Q. TNF-alpha-308G>A polymorphism and the risk of familial CAD in a Pakistani population. Hum Immunol. 2015;76(1):13–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all the volunteers and participants of the study and COMSATS University Islamabad for providing the facilities. The current research was partially supported by COMSATS University Islamabad, Pakistan under general Laboratory funds for the Department of Biosciences.
Funding
The study was conducted in COMSATS University Islamabad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the design and concept of proposed study. Materials were provided by S H, S M N, and Z M. The samples diagnosis and collection were done by T K, and the processing was done by Z u I, and U B. Experiments were conducted by Z U I, U B. Statistical analysis and paper writing was done by S H, S M N, and Z M. All authors read and approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval.
This study was conducted via a collaboration between COMSATS University Islamabad and Federal Government Polyclinic hospital Islamabad, Pakistan. Approvals were obtained from the ethical review committees and institutional review boards of both the institutes according to the Declaration of Helsinki revised in 2013.
Informed consent
Signed written informed consent was obtained from all the participants of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ul Islam, Z., Baneen, U., Khaliq, T. et al. Association analysis of miRNA-146a and miRNA-499 polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis: a case–control and trio-family study. Clin Exp Med 23, 1667–1675 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00916-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00916-y