Abstract
Introduction
/objectives
Several biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) have been widely used for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These drugs target different molecules important for the pathophysiology of RA; however, only a few studies have compared the effects of these biological drugs on cytokines and bone metabolic markers. The main aim of this study is to clarify the effects of bDMARDs with different modes of action on the cytokine and bone metabolic marker levels in patients with RA.
Methods
Patients with RA who were initiated on infliximab, tocilizumab, or abatacept as the first bDMARD were prospectively enrolled in this study. Serum cytokine and bone metabolic marker levels were measured longitudinally, and changes in their levels were compared.
Results
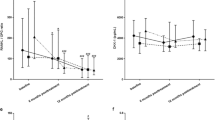
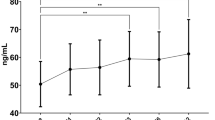
A total of 174 patients were enrolled in this study, with 55, 70, and 49 patients in the infliximab, tocilizumab, and abatacept groups, respectively. At six months, despite the similar clinical effectiveness of the three drugs, changes in the cytokine and bone metabolic marker levels were distinct; interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were significantly increased with infliximab, interleukin-6 levels were increased with tocilizumab, and interleukin-1β and interleukin-8 levels were increased with abatacept treatment. Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin levels increased more significantly with tocilizumab than with infliximab, while osteopontin and osteonectin levels decreased with infliximab treatment.
Conclusions
bDMARDs with different modes of action exert different effects on the cytokine and bone metabolic marker levels in patients with RA.
Key Points • While clinical effectiveness is comparable with infliximab, tocilizumab, and abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, changes in cytokine and bone metabolic marker levels are distinct among bDMARDs. • Especially, changes in interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α levels with infliximab, interleukin-6, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin levels with tocilizumab, and interleukin-1β, interleukin-8 levels with abatacept are significant. |




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that underlie this article will be shared if a reasonable request is made to the corresponding author.
References
Ødegård S, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Kvien TK, Mowinckel P, Uhlig T (2006) Association of early radiographic damage with impaired physical function in rheumatoid arthritis: a ten-year, longitudinal observational study in 238 patients. Arthritis Rheum 54(1):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21548
Schett G, Elewaut D, McInnes IB, Dayer JM, Neurath MF (2013) How cytokine networks fuel inflammation: toward a cytokine-based disease taxonomy. Nat Med 19(7):822–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3260
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Maini RN (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med 343(22):1594–1602. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200011303432202
Nishimoto N, Hashimoto J, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Kishimoto T (2007) Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an x ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis 66(9):1162–1167. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2006.068064
Kremer JM, Genant HK, Moreland LW, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, Westhovens R (2006) Effects of abatacept in patients with methotrexate-resistant active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 144(12):865–876. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-144-12-200606200-00003
Walsh NC, Reinwald S, Manning CA, Condon KW, Iwata K, Burr DB, Gravallese EM (2009) Osteoblast function is compromised at sites of focal bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. J Bone Miner Res 24(9):1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.090320
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2000) TNF-alpha induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand. J Clin Invest 106(12):1481–1488. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci11176
Palmqvist P, Persson E, Conaway HH, Lerner UH (2002) IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M stimulate bone resorption and regulate the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and receptor activator of NF-kappa B in mouse calvariae. J Immunol 169(6):3353–3362. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.3353
Axmann R, Herman S, Zaiss M, Franz S, Polzer K, Zwerina J, Schett G (2008) CTLA-4 directly inhibits osteoclast formation. Ann Rheum Dis 67(11):1603–1609. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.080713
Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, Zwerina J, Ominsky MS, Dwyer D, Schett G (2007) Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med 13(2):156–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1538
Kaneshiro S, Ebina K, Shi K, Higuchi C, Hirao M, Okamoto M, Hashimoto J (2014) IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab 32(4):378–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0514-1
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310302
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Hawker G (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
van der Heijde D (1999) How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol 26(3):743–745
Takeshita M, Suzuki K, Kikuchi J, Izumi K, Kurasawa T, Yoshimoto K, Takeuchi T (2015) Infliximab and etanercept have distinct actions but similar effects on cytokine profiles in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 75(2):222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.04.011
Austrup F, Vestweber D, Borges E, Löhning M, Bräuer R, Herz U, Hamann A (1997) P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T-helper-1 but not T-helper-2 cells into inflammed tissues. Nature 385(6611):81–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/385081a0
Tak PP, Taylor PC, Breedveld FC, Smeets TJ, Daha MR, Kluin PM, Maini RN (1996) Decrease in cellularity and expression of adhesion molecules by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39(7):1077–1081. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780390702
Aeberli D, Seitz M, Jüni P, Villiger PM (2005) Increase of peripheral CXCR3 positive T lymphocytes upon treatment of RA patients with TNF-alpha inhibitors. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44(2):172–175. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh437
Charles P, Elliott MJ, Davis D, Potter A, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Maini RN (1999) Regulation of cytokines, cytokine inhibitors, and acute-phase proteins following anti-TNF-alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 163(3):1521–1528
Brennan FM, McInnes IB (2008) Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 118(11):3537–3545. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci36389
Haworth C, Brennan FM, Chantry D, Turner M, Maini RN, Feldmann M (1991) Expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol 21(10):2575–2579. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830211039
Butler DM, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Brennan FM (1995) Modulation of proinflammatory cytokine release in rheumatoid synovial membrane cell cultures. Comparison of monoclonal anti TNF-alpha antibody with the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Eur Cytokine Netw 6(4):225–230
Brennan FM, Chantry D, Jackson A, Maini R, Feldmann M (1989) Inhibitory effect of TNF alpha antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2(8657):244–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90430-3
Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T, Nakahara H, Takagi N, Kakehi T (2008) Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood 112(10):3959–3964. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846
Wenink MH, Santegoets KC, Platt AM, van den Berg WB, van Riel PL, Garside P, McInnes IB (2012) Abatacept modulates proinflammatory macrophage responses upon cytokine-activated T cell and Toll-like receptor ligand stimulation. Ann Rheum Dis 71(1):80–83. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200348
Bonelli M, Ferner E, Göschl L, Blüml S, Hladik A, Karonitsch T, Scheinecker C (2013) Abatacept (CTLA-4IG) treatment reduces the migratory capacity of monocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65(3):599–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37787
Chang IC, Chiang TI, Yeh KT, Lee H, Cheng YW (2010) Increased serum osteopontin is a risk factor for osteoporosis in menopausal women. Osteoporos Int 21(8):1401–1409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-009-1107-7
Chellaiah MA, Kizer N, Biswas R, Alvarez U, Strauss-Schoenberger J, Rifas L, Hruska KA (2003) Osteopontin deficiency produces osteoclast dysfunction due to reduced CD44 surface expression. Mol Biol Cell 14(1):173–189. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e02-06-0354
Chopin F, Garnero P, le Henanff A, Debiais F, Daragon A, Roux C, Thomas T (2008) Long-term effects of infliximab on bone and cartilage turnover markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(3):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.076604
Okano T, Koike T, Tada M, Sugioka Y, Mamoto K, Wakitani S, Nakamura H (2014) The limited effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor blockade on bone health in patients with rheumatoid arthritis under the use of glucocorticoid. J Bone Miner Metab 32(5):593–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0535-9
Vis M, Havaardsholm EA, Haugeberg G, Uhlig T, Voskuyl AE, van de Stadt RJ, Lems WF (2006) Evaluation of bone mineral density, bone metabolism, osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of the NFkappaB ligand serum levels during treatment with infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65(11):1495–1499. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.044198
Lange U, Teichmann J, Müller-Ladner U, Strunk J (2005) Increase in bone mineral density of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-alpha antibody: a prospective open-label pilot study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44(12):1546–1548. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei082
Marotte H, Pallot-Prades B, Grange L, Gaudin P, Alexandre C, Miossec P (2007) A 1-year case-control study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis indicates prevention of loss of bone mineral density in both responders and nonresponders to infliximab. Arthritis Res Ther 9(3):R61. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2219
Bay-Jensen AC, Platt A, Byrjalsen I, Vergnoud P, Christiansen C, Karsdal MA (2014) Effect of tocilizumab combined with methotrexate on circulating biomarkers of synovium, cartilage, and bone in the LITHE study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43(4):470–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.07.008
Karsdal MA, Schett G, Emery P, Harari O, Byrjalsen I, Kenwright A, Platt A (2012) IL-6 receptor inhibition positively modulates bone balance in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: biochemical marker analysis of bone metabolism in the tocilizumab RADIATE study (NCT00106522). Semin Arthritis Rheum 42(2):131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2012.01.004
Garnero P, Thompson E, Woodworth T, Smolen JS (2010) Rapid and sustained improvement in bone and cartilage turnover markers with the anti-interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab plus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate: results from a substudy of the multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of tocilizumab in inadequate responders to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum 62(1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.25053
Briot K, Rouanet S, Schaeverbeke T, Etchepare F, Gaudin P, Perdriger A, Roux C (2015) The effect of tocilizumab on bone mineral density, serum levels of Dickkopf-1 and bone remodeling markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 82(2):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.10.015
Hasegawa T, Kikuta J, Sudo T, Matsuura Y, Matsui T, Simmons S, Ishii M (2019) Identification of a novel arthritis-associated osteoclast precursor macrophage regulated by FoxM1. Nat Immunol 20(12):1631–1643. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0526-7
Komine M, Kukita A, Kukita T, Ogata Y, Hotokebuchi T, Kohashi O (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha cooperates with receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand in generation of osteoclasts in stromal cell-depleted rat bone marrow cell culture. Bone 28(5):474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00420-3
Yao Z, Getting SJ, and Locke IC (2021) Regulation of TNF-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Cells 11(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010132
Yokota K, Sato K, Miyazaki T, Kitaura H, Kayama H, Miyoshi F, Mimura T (2014) Combination of tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-6 induces mouse osteoclast-like cells with bone resorption activity both in vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(1):121–129. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38218
Hashizume M, Hayakawa N, Mihara M (2008) IL-6 trans-signalling directly induces RANKL on fibroblast-like synovial cells and is involved in RANKL induction by TNF-alpha and IL-17. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(11):1635–1640. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken363
O’Brien CA, Gubrij I, Lin SC, Saylors RL, Manolagas SC (1999) STAT3 activation in stromal/osteoblastic cells is required for induction of the receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand and stimulation of osteoclastogenesis by gp130-utilizing cytokines or interleukin-1 but not 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem 274(27):19301–19308. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.27.19301
Adam S, Simon N, Steffen U, Andes FT, Scholtysek C, Müller DI H, Hueber AJ (2020) JAK inhibition increases bone mass in steady-state conditions and ameliorates pathological bone loss by stimulating osteoblast function. Sci Transl Med 12(530):eaay4447. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aay4447
Finzel S, Kraus S, Figueiredo CP, Regensburger A, Kocijan R, Rech J, Schett G (2019) Comparison of the effects of tocilizumab monotherapy and adalimumab in combination with methotrexate on bone erosion repair in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 78(9):1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214894
Finzel S, Rech J, Schmidt S, Engelke K, Englbrecht M, Schett G (2013) Interleukin-6 receptor blockade induces limited repair of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis: a micro CT study. Ann Rheum Dis 72(3):396–400. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201075
MøllerDøhn U, Boonen A, Hetland ML, Hansen MS, Knudsen LS, Hansen A, Østergaard M (2009) Erosive progression is minimal, but erosion healing rare, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. A 1 year investigator-initiated follow-up study using high-resolution computed tomography as the primary outcome measure. Ann Rheum Dis 68(10):1585–1590. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.097048
Pederson L, Ruan M, Westendorf JJ, Khosla S, Oursler MJ (2008) Regulation of bone formation by osteoclasts involves Wnt/BMP signaling and the chemokine sphingosine-1-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(52):20764–20769. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805133106
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. H Kondo for her help with patients’ recruitment, and Ms. Y Ikeda for her technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hiroya Tamai contributed to the acquisition of and maintaining the data, analysis of the data, interpretation of the results, and writing the manuscript. Naoshi Nishina, Jun Kikuchi, Keisuke Izumi, Keiko Yoshimoto, and Kunihiro Yamaoka contributed to the acquisition of and maintaining the data, interpretation of the results, and critically reviewed the manuscript. Kotaro Otomo contributed to the interpretation of the results and critically reviewed the manuscript. Tsutomu Takeuchi contributed to the design of the study and interpretation of the results and critically reviewed the manuscript. Yuko Kaneko contributed to the design of the study, interpretation of the result, writing the manuscript and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors finally approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Tamai received honoraria from AbbVie and Eisai. Dr. Kikuchi received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai and Mitsubishi-Tanabe. Dr. Izumi received honoraria from AbbVie, Asahi-Kasei, Ayumi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eisai and Eli Lilly. Dr. Otomo received honoraria from AbbVie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Glaxo SmithKline, Jansen, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and UCB. Dr. Yamaoka received honoraria from Pfizer, Chugai Pharma, Takeda Industrial Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma, GlaxoSmithkline, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharma, Eisai Pharma, Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan, Asahikasei Pharma Corp, Ono Pharma, Otsuka Pharma, Nippon Shinyaku, Gilead G.K, Daiichi Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, Japan Tobacco Inc., Hisamitsu Pharma Co, MSD, Sanofi, AYUMI Pharma Co, and Nippon Kayaku. Dr. Takeuchi received honoraria from Astellas, AbbVie, Ayumi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Glaxo Smith Kline, Janssen, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Nippon-kayaku, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB and research support from Asahi Kasei, AbbVie, Ayumi, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Sanofi, and UCB. Dr. Kaneko received honoraria from Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Ayumi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eisai, Elli Lilly, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Novartis, UCB, and research support from AbbVie, Chugai, Eisai, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, and UCB. The other authors declare no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamai, H., Nishina, N., Kikuchi, J. et al. Serum cytokines and bone metabolic markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Clin Rheumatol 42, 721–730 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-022-06390-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-022-06390-x