Abstract
Purpose
Accumulating evidence suggests that Staphylococcus aureus plays a significant role as a disease modifier in upper and lower airway diseases. We aimed to assess the association between staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) with allergic diseases and the degree of allergen sensitisation in children, which remains unclear.
Methods
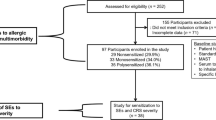
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 455 patients aged 3–18 years between March 2018 and March 2022. Clinical history and demographic data were obtained. The baseline study included paranasal sinus X-ray scan, multiple allergen simultaneous test, and ImmunoCAP® for measuring serum total and specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels to allergens and staphylococcal enterotoxin A and B (SEA and SEB).
Results
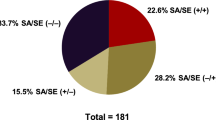
The mean age was 9.77 ± 4.3 years. 133 patients (29.2%) were sensitised to one inhalant allergen, and 188 patients (41.3%) showed polysensitisation. Patients sensitised to SEs showed higher total and specific IgE levels and total eosinophil counts compared to non-SE-sensitised patients. Sensitisation to SEs is closely associated with polysensitisation to inhalant allergens and allergic multimorbidity. When the SE-IgE value was 0.35 or higher, the odds ratio for allergen polysensitisation was significantly higher than when the SE-IgE value was lower than 0.35.
Conclusions
Association between polysensitisation and sensitisation to SEs in children shows the higher the specific IgE levels for SEs, the higher the likelihood of polysensitisation. Considering the relationship between polysensitisation, high IgE levels, and the severity of allergic morbidity, sensitisation to SEs is thought to be related to allergy severity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
van Belkum A, Verkaik NJ, de Vogel CP, Boelens HA, Verveer J, Nouwen JL, Verbrugh HA, Wertheim HF (2009) Reclassification of Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage types. J Infect Dis 199:1820–1826. https://doi.org/10.1086/599119
Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Verbrugh HA, Nouwen JL (2005) The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect Dis 5:751–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70295-4
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr (2015) Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:603–661. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00134-14
Teufelberger AR, Broker BM, Krysko DV, Bachert C, Krysko O (2019) Staphylococcus aureus orchestrates type 2 airway diseases. Trends Mol Med 25:696–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2019.05.003
Muluk NB, Altin F, Cingi C (2018) Role of superantigens in allergic inflammation: their relationship to allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinosinusitis, asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 32:502–517. https://doi.org/10.1177/1945892418801083
Zhang N, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Patou J, Dhaliwal B, Gould H, Bachert C (2011) Mucosal tissue polyclonal IgE is functional in response to allergen and SEB. Allergy 66:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02448.x
Bachert C, Zhang N (2012) Chronic rhinosinusitis and asthma: novel understanding of the role of IgE “above atopy.” J Intern Med 272:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2012.02559.x
Bachert C, Gevaert P, Howarth P, Holtappels G, van Cauwenberge P, Johansson SG (2003) IgE to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in serum is related to severity of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:1131–1132
Huvenne W, Hellings PW, Bachert C (2013) Role of staphylococcal superantigens in airway disease. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 161:304–314. https://doi.org/10.1159/000350329
Tomassen P, Jarvis D, Newson R, Van Ree R, Forsberg B, Howarth P, Janson C, Kowalski ML, Kramer U, Matricardi PM, Middelveld RJ, Todo-Bom A, Toskala E, Thilsing T, Brozek G, Van Drunen C, Burney P, Bachert C (2013) Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin-specific IgE is associated with asthma in the general population: a GA(2)LEN study. Allergy 68:1289–1297. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12230
Song WJ, Chang YS, Lim MK, Yun EH, Kim SH, Kang HR, Park HW, Tomassen P, Choi MH, Min KU, Cho SH, Bachert C (2014) Staphylococcal enterotoxin sensitization in a community-based population: a potential role in adult-onset asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 44:553–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12239
Semic-Jusufagic A, Bachert C, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Lowe L, Woodcock A, Simpson A, Custovic A (2007) Staphylococcus aureus sensitization and allergic disease in early childhood: population-based birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:930–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.12.639
Lee EJ, Kim CH, Yoon JH, Cho HJ, Hwang CS, Park DJ (2021) Can the sensitisation to staphylococcal enterotoxin predict the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278:2829–2836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06526-2
Berger WE (2003) Overview of allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 90:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1081-1206(10)61653-5
Bachert C, van Steen K, Zhang N, Holtappels G, Cattaert T, Maus B, Buhl R, Taube C, Korn S, Kowalski M, Bousquet J, Howarth P (2012) Specific IgE against Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: an independent risk factor for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.012
Bennett MR, Thomsen IP (2020) Epidemiological and clinical evidence for the role of toxins in S. aureus human disease. Toxins (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060408
Holtfreter S, Broker BM (2005) Staphylococcal superantigens: do they play a role in sepsis? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 53:13–27
Grumann D, Nubel U, Broker BM (2014) Staphylococcus aureus toxins–their functions and genetics. Infect Genet Evol 21:583–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2013.03.013
Oliveira D, Borges A, Simoes M (2018) Staphylococcus aureus toxins and their molecular activity in infectious diseases. Toxins (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060252
Bachert C, Gevaert P, van Cauwenberge P (2002) Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: a key in airway disease? Allergy 57:480–487. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1398-9995.2002.02156.x
Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Watelet JB, Claeys G, Holtappels G, Claeys C, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2004) Staphylococcus aureus colonization and IgE antibody formation to enterotoxins is increased in nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:981–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.07.013
Sollid JU, Furberg AS, Hanssen AM, Johannessen M (2014) Staphylococcus aureus: determinants of human carriage. Infect Genet Evol 21:531–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2013.03.020
Breuer K, Wittmann M, Bosche B, Kapp A, Werfel T (2000) Severe atopic dermatitis is associated with sensitization to staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Allergy 55:551–555. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1398-9995.2000.00432.x
Arkwright PD, Cookson BD, Haeney MR, Sanyal D, Potter MR, David TJ (2001) Children with atopic dermatitis who carry toxin-positive Staphylococcus aureus strains have an expansion of blood CD5-B lymphocytes without an increase in disease severity. Clin Exp Immunol 125:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01620.x
Breuer K, Hausser S, Kapp A, Werfel T (2002) Staphylococcus aureus: colonizing features and influence of an antibacterial treatment in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 147:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04872.x
Patel D, Jahnke MN (2015) Serious complications from staphylococcal aureus in atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol 32:792–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pde.12665
Jappe U, Heuck D, Witte W, Gollnick H (1998) Superantigen production by Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis: no more than a coincidence? J Invest Dermatol 110:844–846. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00177.x
Yagi S, Wakaki N, Ikeda N, Takagi Y, Uchida H, Kato Y, Minamino M (2004) Presence of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin A in sera of patients with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy 34:984–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.1687.x
Leung DY, Harbeck R, Bina P, Reiser RF, Yang E, Norris DA, Hanifin JM, Sampson HA (1993) Presence of IgE antibodies to staphylococcal exotoxins on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Evidence for a new group of allergens. J Clin Invest 92:1374–1380. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI116711
Tomczak H, Wrobel J, Jenerowicz D, Sadowska-Przytocka A, Wachal M, Adamski Z, Czarnecka-Operacz MM (2019) The role of Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis: microbiological and immunological implications. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 36:485–491. https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2018.77056
Song WJ, Sintobin I, Sohn KH, Kang MG, Park HK, Jo EJ, Lee SE, Yang MS, Kim SH, Park HK, Kwon YE, Kim TB, Kim SH, Park HW, Chang YS, Lee BJ, Jee YK, Choi BW, Bachert C, Cho SH (2016) Staphylococcal enterotoxin IgE sensitization in late-onset severe eosinophilic asthma in the elderly. Clin Exp Allergy 46:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12652
Sintobin I, Siroux V, Holtappels G, Pison C, Nadif R, Bousquet J, Bachert C (2019) Sensitisation to staphylococcal enterotoxins and asthma severity: a longitudinal study in the EGEA cohort. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00198-2019
Rossi RE, Monasterolo G (2004) Prevalence of serum IgE antibodies to the Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins (SAE, SEB, SEC, SED, TSST-1) in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 133:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1159/000076833
Gabet S, Just J, Couderc R, Bousquet J, Seta N, Momas I (2016) Early polysensitization is associated with allergic multimorbidity in PARIS birth cohort infants. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 27:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.12622
Sorensen M, Klingenberg C, Wickman M, Sollid JUE, Furberg AS, Bachert C, Bousquet J (2017) Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin sensitization is associated with allergic poly-sensitization and allergic multimorbidity in adolescents. Allergy 72:1548–1555. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.13175
Tsilochristou O, du Toit G, Sayre PH, Roberts G, Lawson K, Sever ML, Bahnson HT, Radulovic S, Basting M, Plaut M, Lack G, Immune Tolerance Network Learning Early About Peanut Allergy Study T (2019) Association of Staphylococcus aureus colonization with food allergy occurs independently of eczema severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 144:494–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.04.025
Savage J, Johns CB (2015) Food allergy: epidemiology and natural history. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 35:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2014.09.004
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Wickman M, Keil T, Valenta R, Haahtela T, Lodrup Carlsen K, van Hage M, Akdis C, Bachert C, Akdis M, Auffray C, Annesi-Maesano I, Bindslev-Jensen C, Cambon-Thomsen A, Carlsen KH, Chatzi L, Forastiere F, Garcia-Aymerich J, Gehrig U, Guerra S, Heinrich J, Koppelman GH, Kowalski ML, Lambrecht B, Lupinek C, Maier D, Melen E, Momas I, Palkonen S, Pinart M, Postma D, Siroux V, Smit HA, Sunyer J, Wright J, Zuberbier T, Arshad SH, Nadif R, Thijs C, Andersson N, Asarnoj A, Ballardini N, Ballereau S, Bedbrook A, Benet M, Bergstrom A, Brunekreef B, Burte E, Calderon M, De Carlo G, Demoly P, Eller E, Fantini MP, Hammad H, Hohman C, Just J, Kerkhof M, Kogevinas M, Kull I, Lau S, Lemonnier N, Mommers M, Nawijn M, Neubauer A, Oddie S, Pellet J, Pin I, Porta D, Saes Y, Skrindo I, Tischer CG, Torrent M, von Hertzen L (2015) Are allergic multimorbidities and IgE polysensitization associated with the persistence or re-occurrence of foetal type 2 signalling? The MeDALL hypothesis. Allergy 70:1062–1078. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12637
Bousquet J, Kjellman NI (1986) Predictive value of tests in childhood allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 78:1019–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(86)90296-4
Amaral AF, Minelli C, Guerra S, Wjst M, Probst-Hensch N, Pin I, Svanes C, Janson C, Heinrich J, Jarvis DL (2015) The locus C11orf30 increases susceptibility to poly-sensitization. Allergy 70:328–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12557
Tamari M, Tanaka S, Hirota T (2013) Genome-wide association studies of allergic diseases. Allergol Int 62:21–28. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.13-RAI-0539
Marsh DG, Chase GA, Freidhoff LR, Meyers DA, Bias WB (1979) Association of HLA antigens and total serum immunoglobulin E level with allergic response and failure to respond to ragweed allergen Ra3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:2903–2907. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.6.2903
D’Amato M, Picardi A, Menna T, Di Somma C, Ariano R, di Pietro A, Charron D, Maggi E, Matricardi P, Plebani A, Poto S, Testa G, Sacerdoti G, Ruffilli A (1999) HLA-DRB1* and allergy to Parietaria: linkage and association analyses. Hum Immunol 60:1250–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0198-8859(99)00112-3
Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Keil T, Kopp M, Zielen S, Schauer U, von Berg A, Wahn U, Hamelmann E (2008) Specific IgE serum concentration is associated with symptom severity in children with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy 63:1339–1344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01692.x
Ha EK, Baek JH, Lee SY, Park YM, Kim WK, Sheen YH, Lee SJ, Bae Y, Kim J, Lee KJ, Ahn K, Kwon HJ, Han MY (2016) Association of polysensitization, allergic multimorbidity, and allergy severity: a cross-sectional study of school children. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 171:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1159/000453034
Funding
This work was supported by a faculty research grant from Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine [grant no. 2022-52-0054 to E.J.L.] and by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Republic of Korea [grant no. NRF-2021R1A2C1010082 to E.J.L.].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.J.L. and C.H.K. designed the study, managed data extraction, and interpreted the data. H.S.L., M.H.K. and D.H.K. performed the statistical analyses. E.J.L., Y.-H.L. and M.H.K. prepared the manuscript. Y.-H.L. and M.H.K. formatted the manuscript. E.J.L., Y.-H.L., C.H.K., H.S.L., M.H.K., D.H.K. and J.H.L. interpreted data and reviewed the manuscript. E.J.L. initiated and supervised this study. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Wonju, Republic of Korea (IRB No. CR318104), in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YH., Kim, M., Ku, C.H. et al. Association between poly-sensitisation and sensitisation to staphylococcal enterotoxin A and B affecting allergic severity in children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 4121–4129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07968-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07968-0