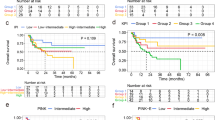
Abstract
Natural killer/T‐cell lymphoma (NKTCL) is an aggressive and malignant condition with a high mortality rate. Prognostic factors may assist to evaluate the outcome of the disease and may also be useful in selecting appropriate therapeutic strategies for patients. The study aims to describe NKTCL in terms of its clinical features, laboratory examinations, and immunophenotypes and to analyze relevance affecting patient survival outcomes. The patients diagnosed as NKTCL in Jinling Hospital from Jan. 2012 to Dec. 2022 were reviewed retrospectively in this study basing on histopathology. The analysis was performed to evaluate overall survival (OS). A total of 125 NKTCL patients were included, which mainly affected male more than female with the onset median age of 51.00 years old (range, 14 ~ 85 y). NKTCL commonly affects the nasopharynx and upper aerodigestive tract, intestines, and skin. The median overall survival was 13.00 months (range, 2–156 m), and the 5-year survival rate was 9.8%. Under univariable analysis revealed the following factors at diagnosis age: serum total IgEAb ≥ 54.6 IU/mL, IL-6 ≥ 32.445 ng/L, elevated PINK score, smoking, and extranasopharyngeal site were statistically significant predictors for OS. Compared to the patients who received radiotherapy alone or chemotherapy alone, the patients who received combined chemoradiotherapy had longer OS. We found that IL-6 and total IgEAb were significant prognostic factors in NKTCL patients. Also, extranasopharyngeal site was correlated with advanced disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding authors.
References
Alaggio R et al (2022) The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: lymphoid neoplasms. Leukemia 36(7):1720–1748
Kang S et al (2023) A new prognostic index for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: incorporation of serum beta-2 microglobulin to PINK. Cancer Res Treat 55(1):314–324
Shen Z et al (2023) Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index on extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma patients: a multicenter propensity score matched analysis of 1022 cases in Huaihai Lymphoma Working Group. Hematol Oncol 41(3):380–388
Kang S et al (2023) A new prognostic index for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: incorporation of serum β-2 microglobulin to PINK. Cancer Res Treat 55(1):314–324
Vásquez J et al (2016) Predictors of survival of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in a non-Asian population: a single cancer centre experience. Ecancermedicalscience 10:688
Tan KM et al (2019) A clinicohaematological prognostic model for nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a multicenter study. Sci Rep 9(1):14961
Zhou X et al (2019) Prognostic significance of peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte count and derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with newly diagnosed extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Manag Res 11:4243–4254
Chunli Y et al (2022) Real-world clinical features and survival outcomes associated with primary gastrointestinal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from 1999 to 2020. Cancer Med 12(3):2614–2623
Feng Y et al (2022) The expression and clinical significance of programmed cell death receptor 1 and its ligand in tumor tissues of patients with extranodal nasal NK/T cell lymphoma. Sci Rep 12(1):36
Chen Z et al (2020) A proposal for a prognostic index for non-nasal type natural killer/T cell lymphoma after asparaginase-based treatment. Ann Hematol 99(12):2811–2819
Liu X et al (2023) A novel prognostic model based on ferritin and nomogram-revised risk index could better stratify patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Med 12(9):10660–10671
Rong Q et al (2021) High IL-6 expression in the tumor microenvironment is associated with poor prognosis of patients with extranodal natural / killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL). Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 21(1):121–127
Bao C et al (2020) Increased serum level of interleukin-6 correlates with negative prognostic factors in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Transl Cancer Res 9(4):2378–2389
Wen H et al (2018) Recurrent ECSIT mutation encoding V140A triggers hyperinflammation and promotes hemophagocytic syndrome in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Nat Med 24(2):154–164
Vonderheid EC, Hamilton RG, Kadin ME (2021) Mycosis fungoides and its relationship to atopy, serum total IgE, and eosinophil counts. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 21(4):279-288.e7
Bahalı AG et al (2020) Prognostic factors of patients with mycosis fungoides. Adv Dermatol Allergol 37(5):796–799
Ferastraoaru D et al (2022) Relationship between low serum immunoglobulin E levels and malignancies in 9/11 World Trade Center responders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 129(6):769–775
Ferastraoaru D (2021) Increased malignancy rate in children with IgE deficiency: a single-center experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 43(4):e472–e477
Funding
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Dermatology Innovation Team Foundation (grant number CXTDA2017038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. FL, HL, and YD designed the study. YH and YG collected and analyzed the data. FL, YH, and YG prepared the manuscript. HS revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript, took responsibility for the content, and agreed to submit it for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jinling Hospital of Nanjing University (approval number 2023DZGZR-055) and was conducted according to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent to participate
Individual consent was not necessary because the study used existing clinical data and the identity of the patients was not disclosed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, Y., Gao, Y., Li, J. et al. Elevated serum IL-6 and total IgEAb are associated with poor survival in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 103, 1285–1292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05579-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05579-7