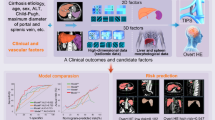
Abstract
Purpose
To develop and assess machine learning (ML) models' ability to predict post-procedural hepatic encephalopathy (HE) following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement.
Materials and Methods
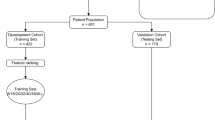
In this retrospective study, 327 patients who underwent TIPS for hepatic cirrhosis between 2005 and 2019 were analyzed. Thirty features (8 clinical, 10 laboratory, 12 procedural) were collected, and HE development regardless of severity was recorded one month follow-up. Univariate statistical analysis was performed with numeric and categoric data, as appropriate. Feature selection is used with a sequential feature selection model with fivefold cross-validation (CV). Three ML models were developed using support vector machine (SVM), logistic regression (LR) and CatBoost, algorithms. Performances were evaluated with nested fivefold-CV technique.
Results
Post-procedural HE was observed in 105 (32%) patients. Patients with variceal bleeding (p = 0.008) and high post-porto-systemic pressure gradient (p = 0.004) had a significantly increased likelihood of developing HE. Also, patients having only one indication of bleeding or ascites were significantly unlikely to develop HE as well as Budd-Chiari disease (p = 0.03). The feature selection algorithm selected 7 features. Accuracy ratios for the SVM, LR and CatBoost, models were 74%, 75%, and 73%, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.82, 0.83, and 0.83, respectively.
Conclusion
ML models can aid identifying patients at risk of developing HE after TIPS placement, providing an additional tool for patient selection and management.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The computer code will be shared at the corresponding author’s github page after peer-review process.
References
Sun SH, Eche T, Dorczynski C, Otal P, Revel-Mouroz P, Zadro C, et al. Predicting death or recurrence of portal hypertension symptoms after TIPS procedures. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2022;32(5):3346–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08437-0.
García-Pagán JC, Caca K, Bureau C, Laleman W, Appenrodt B, Luca A, et al. Early use of TIPS in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2370–9.
Bureau C, Thabut D, Oberti F, Dharancy S, Carbonell N, Bouvier A, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts with covered stents increase transplant-free survival of patients with cirrhosis and recurrent ascites. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):157–63.
Shawcross DL, Shabbir SS, Taylor NJ, Hughes RD. Ammonia and the neutrophil in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology [Internet]. 2010;51(3):1062–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23367.
Li X, Partovi S, Coronado WM, Gadani S, Martin C, Thompson D, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy after tips placement: predictive factors, prevention strategies, and management. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol [Internet]. 2022;45(5):570–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-03045-3.
Zhong B-Y, Wang W-S, Shen J, Du H, Zhang S, Li W-C, et al. Single-centre retrospective training cohort using artificial intelligence for prognostic prediction of encephalopathy, mortality, and liver dysfunction after early TIPS creation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol [Internet]. 2021;44(10):1597–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-02907-0.
Bai M, Qi X, Yang Z, Yin Z, Nie Y, Yuan S, et al. Predictors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(6):943–51.
Flud CR, Duarte-Rojo A. Prognostic implications of minimal/covert hepatic encephalopathy: large-scale validation cohort studies. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019;9(1):112–6.
Nardelli S, Gioia S, Pasquale C, Pentassuglio I, Farcomeni A, Merli M, et al. Cognitive impairment predicts the occurrence of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG [Internet]. 2016;111(4):523.
Riggio O, Masini A, Efrati C, Nicolao F, Angeloni S, Salvatori FM, et al. Pharmacological prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a randomized controlled study. J Hepatol [Internet]. 2005;42(5):674–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2004.12.028.
Yin X, Zhang F, Guo H, Peng C, Zhang W, Xiao J, et al. A nomogram to predict the risk of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in Cirrhotic Patients. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2020;10(1):9381. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65227-2.
Coronado WM, Ju C, Bullen J, Kapoor B. Predictors of occurrence and risk of hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS creation: a 15-year experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol [Internet]. 2020;43(8):1156–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02512-7.
Casadaban LC, Parvinian A, Minocha J, Lakhoo J, Grant CW, Ray CE, et al. Clearing the confusion over hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS creation: incidence, prognostic factors, and clinical outcomes. Dig Dis Sci [Internet]. 2015;60(4):1059–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3391-0.
Young S, Bermudez J, Zhang L, Rostambeigi N, Golzarian J. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement: a comparison of outcomes between patients with hepatic hydrothorax and patients with refractory ascites. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019;100(5):303–8.
Cam I, Gencturk M, Shrestha P, Golzarian J, Flanagan S, Lim N, et al. Ultrasound-guided portal vein access and percutaneous wire placement in the portal vein are associated with shorter procedure times and lower radiation doses during TIPS placement. Am J Roentgenol [Internet]. 2021;216(5):1291–9. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23846.
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Int Res. 2002;16(1):321–57.
Kocak B, Durmaz ES, Ates E, Kilickesmez O. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: a practical guide for beginners. Diagn Interv Radiol [Internet]. 2019;25(6):485–95.
Bemister-Buffington J, Wolf AJ, Raschka S, Kuhn LA. Machine learning to identify flexibility signatures of class a GPCR inhibition. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):454.
Ball TM, Squeglia LM, Tapert SF, Paulus MP. Double dipping in machine learning: problems and solutions. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging [Internet]. 2020;5(3):261–3.
Varma S, Simon R. Bias in error estimation when using cross-validation for model selection. BMC Bioinform [Internet]. 2006;7:91.
Lewis DS, Lee T-H, Konanur M, Ziegler C, Hall MD, Pabon-Ramos WM, et al. Proton pump inhibitor use is associated with an increased frequency of new or worsening hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation. J Vasc Interv Radiol [Internet]. 2019;30(2):163–9.
Yang C, Zhu X, Liu J, Shi Q, Du H, Chen Y, et al. Development and validation of prognostic models to estimate the risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS creation: a multicenter study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2022;13(3):e00461.
Cai W, Lin H, Qi R, Lin X, Zhao Y, Chen W, et al. Psoas Muscle Density Predicts Occurrences of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients Receiving Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts within 1 year. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol [Internet]. 2022;45(1):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-02961-8.
Li Y, He X, Pang H. A model to predict early hepatic encephalopathy in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Turk J Gastroenterol Off J Turk Soc Gastroenterol. 2019;30(8):702–7.
Young S, Rostambeigi N, Golzarian J, Lim N. MELD or sodium MELD: a comparison of the ability of two scoring systems to predict outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement. Am J Roentgenol [Internet]. 2020;215(1):215–22. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.19.21726.
Chen L, Xiao T, Chen W, Long Q, Li R, Fang D, et al. Outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt through the left branch vs. the right branch of the portal vein in advanced cirrhosis: a randomized trial. Liver Int [Internet]. 2009;29(7):1101–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02016.x.
Cheng S, Yu X, Chen X, Jin Z, Xue H, Wang Z, et al. CT-based radiomics model for preoperative prediction of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Br J Radiol [Internet]. 2022;95(1132):20210792. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20210792.
Haibo H, Garcia EA. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng [Internet]. 2009;21(9):1263–84.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
İnce, O., Önder, H., Gençtürk, M. et al. Machine Learning Insights: Predicting Hepatic Encephalopathy After TIPS Placement. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 46, 1715–1725 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-023-03593-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-023-03593-w