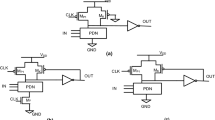
Abstract
A novel domino logic XOR /XNOR cell design is presented that is appropriate for low-power and low-voltage domain. The proposed domino XOR/XNOR cell is implemented using Predictive Technology Model (PTM) for CMOS technology using HSPICE simulator at 22-nm node. Important device performance parameters such as propagation delay (tp), power consumption (pwr), power delay product (PDP) and energy delay product (EDP) are investigated, and the results are analyzed with existing XOR/XNOR cells. The proposed design consumes less power as compared to other existing design and hence provides improved PDP and EDP. The same has been validated using simulation results. Consequently, this article carries robustness analysis to study the impact of voltage and temperature variations on power consumption of the proposed circuit. The proposed XOR/XNOR cell is also used to design a power-efficient 4-bit even parity generator (EPG) as an application. This research paper proposes a low-power domino logic XOR/XNOR cell architecture using 0.7 V supply with a total power consumption of 0.314 µW. The proposed power-efficient domino XOR/XNOR cell is strong candidate suitable for biomedical applications. Almost in every biomedical application, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) plays a key role for sensing the different input parameters like pressure and temperature, whereas adders are used as data path in digital signal processing unit. Therefore, the use of proposed XOR/XNOR cell design guarantees power-efficient high-performance portable biomedical applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing was not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
M. Aguirre-Hernandez, M. Linares-Aranda, CMOS full-adders for energy-efficient arithmetic applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 19(4), 718–721 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2009.2038166
M. Alioto, G. Palumbo, M. Pennisi, Understanding the effect of process variations on the delay of static and domino logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 18(5), 697–710 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2009.2015455
M. Amini-Valashani, M. Ayat, S. Mirzakuchaki, Design and analysis of a novel low-power and energy-efficient 18T hybrid full adder. Microelectron. J. 74, 49–59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2018.01.018
A. Anita Angeline, V.S. Kanchana Bhaaskaran, High speed wide fan-in designs using clock controlled dual keeper domino logic circuits. ETRI J. 41(3), 383–395 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4218/etrij.2018-0313
C. Cheng, S. Chang, J. Wang, W. Jone, Charge sharing fault detection for CMOS domino logic circuits. Proceedings 1999 IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI Systems (EFT'99) (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/dftvs.1999.802872
E.S. Chew, M.W. Phyu, W.L. Goh, in Ultra low-power full-adder for biomedical applications. 2009 IEEE International Conference of Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC) (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/edssc.2009.5394177
S. Garg, T.K. Gupta, Low power domino logic circuits in deep-submicron technology using CMOS. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 21(4), 625–638 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.06.013
S. Garg, T.K. Gupta, Low leakage domino logic circuit for wide fan-in gates using CNTFET. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 13(2), 163–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cds.2018.5135
S. Ghalamdoost Pirbazari, A. Souri, R. Faghih Mirzaee, S. Jabbehdari, Multi valued parity generator based on Sudoku tables: properties and detection probability. IET Commun. 14(14), 2377–2386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-com.2019.0247
S.R. Ghimiray, P. Meher, P.K. Dutta, An improved charge-sharing elimination pseudo-domino logic. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 48(8), 1346–1362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.2798
S. Goel, A. Kumar, M.A. Bayoumi, Design of robust, energy-efficient full adders for deep-submicrometer design using Hybrid-CMOS logic style. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 14(12), 1309–1321 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2006.887807
M. Hajiqasemi, H. Beitollahi, in A novel design of domino XOR gate. 2020 25th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/csicc49403.2020.9050076
M. Jhamb, T. Dhall, T. Verma, H. Pudi, Pipelined adders for ultralow-power wearables. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 27(1), 153–166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-1711-211
J. Kandpal, A. Tomar, M. Agarwal, K.K. Sharma, High-speed hybrid-logic full adder using high-performance 10-T XOR–XNOR cell. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 28(6), 1413–1422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2020.2983850
S. Kang, Y. Leblebici, Cmos Digital Integrated Circuits (Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2003)
L.M. Koshy, G.J. Chandran, Low leakage and high performance tag comparator implemented in 180 nm CMOS technology. Procedia Comput. Sci. 46, 1261–1267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.01.046
H. Mahmoodi-Meimand, K. Roy, Diode-footed domino: a leakage-tolerant high fan-in dynamic circuit design style. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 51(3), 495–503 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2004.823665
M. Mewada, M. Zaveri, in An input test pattern for characterization of a full-adder and N-bit ripple carry adder. 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI) (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/icacci.2016.7732055
F. Moradi, H. Mahmoodi, A. Peiravi, in A high speed and leakage-tolerant domino logic for high fan-in gates. Proceedings of the 15th ACM Great Lakes symposium on VLSI—GLSVSLI '05 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1057661.1057775
F. Moradi, A. Peiravi, H. Mahmoodi, in A new leakage-tolerant design for high fan-in domino circuits. Proceedings. The 16th International Conference on Microelectronics, 2004. ICM (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/icm.2004.1434707
F. Moradi, T. Vu Cao, E.I. Vatajelu, A. Peiravi, H. Mahmoodi, D.T. Wisland, Domino logic designs for high-performance and leakage-tolerant applications. Integration 46(3), 247–254 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2012.04.005
M. Moradinezhad Maryan, M. Amini-Valashani, S.J. Azhari, A new circuit-level technique for leakage and short-circuit power reduction of static logic gates in 22-nm CMOS technology. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40(7), 3536–3560 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01639-9
V. Nandan, R.G.S. Rao, Minimization of digital logic gates and ultra-low power AES encryption core in 180CMOS technology. Microprocess. Microsyst. 74, 103000 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103000
Nanoscale Integration and Modeling (NIMO) Group, Arizona State University (ASU). [Online]. https://ptm.asu.edu/
D. Radhakrishnan, Low-voltage low-power CMOS full adder. IEE Proc. Circuits Devices Syst. 148(1), 19 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-cds:20010170
M. Sadollahi, K. Hamashita, K. Sobue, G.C. Temes, An 11-Bit 250-nW 10-kS/S SAR ADC with doubled input range for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(1), 61–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2017.2712066
U. Sharma, M. Jhamb, in A 0.7 V 0.144 µW frequency divider design with CNTFET-based master slave D-flip flop. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, pp. 387–395 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3767-4_37
P. Srivastava, A. Islam, CNFET-based design of resilient MCML XOR/XNOR circuit at 16-NM technology node. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 22(3), 261–267 (2015)
P. Tyagi, R. Pandey, High-speed and area-efficient scalable N -bit digital comparator. IET Circuit Devices Syst. 14(4), 450–458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cds.2018.5562
S. Wang, C. Hung, A 0.3v 10b 3ms/S Sar adc with comparator calibration and kickback noise reduction for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuit Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tbcas.2020.2982912
H.Y. Yang, R. Sarpeshkar, A bio-inspired ultra-energy-Efficient analog-to-Digital converter for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 53(11), 2349–2356 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2006.884463
Acknowledgements
The author wants to take an opportunity to express heartfelt gratitude to reviewer and editor as they helped the author to build this research article a quality treatise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, U., Jhamb, M. A Novel Design of Voltage and Temperature Resilient 9-T Domino Logic XOR /XNOR Cell. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 6314–6332 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02085-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02085-5